Question: LaFontaine Accessories makes a variety of computer
LaFontaine Accessories makes a variety of computer bags, carrier bags, and so on. LaFontaine uses activity-based costing for its products. The production manager has identified the following cost drivers and rates for overhead. The manufacturing facility at LaFontaine never has any workin- process at the end of the month.
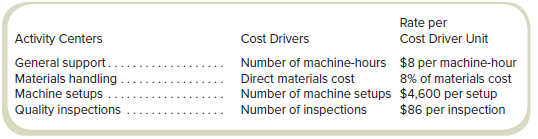
Direct materials costs were $850,000 and direct labor costs were $835,000 during January, when the manufacturing facility made 750 inspections, had 36 setups, and ran the machines for 18,000 hours.
Required
Use T-accounts to show the flow of materials, labor, and overhead costs from the four overhead activity centers through Work-in-Process Inventory and out to Finished Goods Inventory. Use the accounts Materials Inventory, Wages Payable, Work-in-Process Inventory, Finished Goods Inventory, and four overhead applied accounts.
> The external environment of the global automobile industry is quite complex. Regulations vary from country to country and in the United States even from one state to another. Firms must be prepared to anticipate and respond to these external forces. It a
> How much less salary would (did) you accept to find employment with a company that is aligned with your values?
> Identify your personal values. How do you expect these values to affect your work life or your career choice?
> Citing the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA), Airbnb is challenging the New York law and others in the United States, arguing that it merely operates a digital marketplace, and thus is not responsible for the content that users place on its site. D
> Do you agree with the assessment that Elon Musk and Tesla successfully fulfilled the first master plan published in 2006? Why or why not? To answer this question, apply the three-step process for crafting a good strategy explained in Section 1.1 (diagnos
> Western Services has three service departments: Information Systems (IS), Personnel, and Administration. There are two operating departments: Residential and Commercial. A summary of costs and other data for each department prior to allocation of service
> Edwin Parts, a job shop, recorded the following transactions in May: 1. Purchased $87,200 in materials on account. 2. Issued $3,650 in supplies from the materials inventory to the production department. 3. Issued $43,600 in direct materials to the produc
> Edwina Industrial Products (EIP) manufactures cleaning products. The Grant Street Plant produces a single product in three departments: Mixing, Refining, and Packaging. Additional materials are added in the Refining Process when units are 40 percent comp
> Rutland Business Services (RBS) provides miscellaneous consulting and services to local businesses. In August, RBS worked for three clients. It worked 270 hours for Selden Contracting, 170 hours for Moenhart Insurance, and 230 hours for Englewood Medical
> Refer to the data in Problem 8-61. The Refining Department uses the FIFO method of process costing. The Mixing Department at the Grant Street Plant uses the weighted-average method of process costing. If the Mixing Department at the Plant had used the FI
> Refer to the information and data in Problem 7-60. Required Graphically illustrate the effect of using monthly rates versus an annual rate for applying overhead. Problem 7-60:
> Refer to the information and data in Problem 7-58. Required Help the managers at Highway 1 Manufacturing by illustrating graphically the effect of using monthly rates versus an annual rate for applying overhead. Problem 7-58:
> Breckenridge Corporation manufactures a part in a single production process in Department B. The company reports the following information about conversion costs for June: Work-in-process ending inventory was 45 percent complete with respect to conversio
> Patton Dyes manufactures colorings, primarily for textiles. Information on the work in process follows: ∙ Beginning inventory, 115,000 partially complete liters. ∙ Ending inventory, 85,000 liters; units are 25 percent complete with respect to materials a
> Refer to the data in Exercise 8-20. Required Compute the equivalent units for materials and conversion costs for December using the FIFO method. Exercise 8-20: Trevor Mills produces agricultural feed at its only plant. Materials are added at the beginni
> Suppose a manager can reduce the processing time for loan applications by reducing the amount of time the application awaits action. How does the reduction add value to the organization?
> Trevor Mills produces agricultural feed at its only plant. Materials are added at the beginning of the process. Information on work-in-process in December follows: ∙ Beginning inventory, 16,000 partially complete units, 10 percent complete with respect t
> Refer to the information in Exercise 11-50 for Forest Products. Required Forest Products uses the estimated net realizable value method to allocate joint costs. What joint costs would be allocated to each of the three products in November? Exercise 11-5
> Forest Products, Inc. manufactures three products (FP-10, FP-20, and FP-40) from a single, joint input. None of the products can be sold without further processing. In November, joint product costs were $240,000. Additional information follows: Required
> Refer to the facts in Exercise 11-47. Required Barrett Chemicals uses the physical quantities method to allocate joint costs. What joint costs would be allocated to each product in May? Exercise 11-47:
> Barrett Chemicals manufactures four chemicals, Chem-1, Chem-2, Chem-3, and Chem-4, from a joint process. The total joint costs in May were $564,000. Additional information follows: Required Barrett Chemicals uses the net realizable value method to alloca
> St. John Mining operates several facilities. At one, a typical batch of an ore, Pryex, run through the processing plant yields three products: PX-10, PX-20, and PX-30. At the split-off point, the $110,000 after incurring additional processing costs of $2
> Refer to the data for Monroe Materials in Exercise 11-41. Required Assign costs to Alpha, Beta, and Gamma for February using the physical quantities method. Exercise 11-41:
> Monroe Materials processes a purchased material, PM-20, and produces three outputs, Alpha, Beta, and Gamma. In February, the costs to process PM-20 are $524,000 for materials and $196,000 for conversion costs. The results of the processing follow: Requir
> Memorial Services, Inc. (MSI) has three service departments (IT, Accounting, and HR) and two production departments (West and East). The usage data for each of the service departments for the previous period follow: The direct costs of the service depart
> Refer to the data for Mack Precision Tool and Die in Exercise 11-25. Required Use the step method to allocate the service costs, using the following: a. The order of allocation starts with Repair. b. The allocations are made in the reverse order (startin
> What are examples of two nonvalue-added activities that could be found in organizations that manufacture (a) lumber and (b) furniture?
> Woodstock Binding has two service departments, IT (Information Technology) and HR (Human Resources), and two operating departments, Publishing and Binding. Management has decided to allocate IT costs on the basis of IT Tickets (issued with each IT reques
> Refer to the data in Exercise 10-59. Required Construct a cost of quality report for year 1 and year 2. Exercise 10-59:
> One of Camely Chemicals’ facilities manufactures a hazardous chemical. The following represents the financial information from the plant for the most recent two years: Required a. Classify these items into prevention (P), appraisal (A),
> Refer to the data in Exercise 10-57. Required Construct a cost of quality report for May and June. Exercise 10-57:
> The following represents the financial information for Plaza Plastics for May and June: Required a. Classify these items into prevention (P), appraisal (A), internal failure (IF), or external failure (EF) costs. b. Calculate the ratio of the prevention,
> Refer to the data in Exercise 10-55. Required Construct a cost of quality report for Quarter 1 and Quarter 2. Exercise 10-55:
> Cass Company has recorded the following information for the last six months of operations from its cost of quality system: Required a. Classify these items into prevention (P), appraisal (A), internal failure (IF), or external failure (EF) costs. b. Calc
> Fraser Plastics produces plastic parts for use in various products. The following represents accounts in its cost of quality system. Required Classify each as prevention (P), appraisal (A), internal failure (IF), or external failure (EF).
> Abbott Business Services (ABS) generated revenue of $637,800 processing accounts payable and payroll transactions for clients. ABS reports the following information about resources in two functions: Required a. Compute the cost of unused resource capacit
> The Shipping Department at Nashville Fabricators reports the following information about resources: Required Compute the cost of unused resource capacity in the Shipping Department at Nashville Fabricators.
> What are examples of two nonvalue-added activities that could be found in each of the following service organizations: (a) a health clinic and (b) a bank?
> Refer to Exercise 10-46. Sales revenue totaled $74,000. a. Prepare a traditional income statement like the one in Exhibit 10.11. b. Prepare an activity-based income statement like the one in Exhibit 10.12. Exercise 10-46:
> Boston Home Center (BHC) offers customers the use of a truck at $40 per trip to take purchased merchandise home. BHC reports the following information about the trucks it has for customer usage: Required Compute the cost of unused operation and administr
> Refer to Exercise 10-44. Sales revenue from lathe work totaled $17,900. Required a. Prepare a traditional income statement like the one in Exhibit 10.11. b. Prepare an activity-based income statement like the one in Exhibit 10.12. Exercise 10-44:
> Refer to Exercise 10-42. Sales revenue from truck repair totaled $32,000. Required a. Prepare a traditional income statement like the one in Exhibit 10.11. b. Prepare an activity-based income statement like the one in Exhibit 10.12. Exercise 10-42:
> Byron Truck Repair uses a specialized hydraulic lift to work on trucks and busses. Data on the lift and its usage follow: Required Compute the cost of unused resource capacity in operation and maintenance for Byron Truck Repair.
> Refer to the data in Exercise 10-40. Required a. Assume all else remains the same. What bid by Ewers would make Ellery indifferent between buying from Ewer or Bramford? b. Why, given the information, do you think Ellery continues to buy fabric from Bramf
> Refer to the data in Exercise 10-38. Required Assume all else remains the same. What percentage of late deliveries by Bacon would make WES indifferent between buying from Bacon Electronics and Hessel Audio and Video? Exercise 10-38:
> Watko Entertainment Systems (WES) buys audio and video components for assembling home entertainment systems from two suppliers, Bacon Electronics and Hessel Audio and Video. The components are delivered in cartons. If the cartons are delivered late, the
> Refer to the data in Exercise 10-36. Required Assume all else remains the same. What percentage of metal from Chopin Yards that requires further processing would make Rex Metal Fabricators indifferent between buying from Chopin Yards and Joe Company? Ex
> Rex Metal Fabricators (RMF) buys scrap metal and produces components for buildings and other structures. The purchase contracts specify an average quality level of 90 percent. That is, 90 percent of the metal must be ready for use without further process
> In the context of job costing, what are projects? What additional costing issues are there with projects?
> Heintz Products uses activity-based costing to account for product costs. The plant manager has estimated the following cost drivers and rates. Direct materials costs were $480,000 and direct labor costs were $320,000 during November, when the plant fini
> Refer to the information in Exercise 9-36. Required a. Compute the unit costs for the two products, G-09 and G-35, using the current costing system at Heidelberg (using machine-hours as the allocation basis). b. Compute the unit costs for the two product
> Using the data in Exercise 8-41, compute the cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and for conversion costs for February using the FIFO method. Exercise 8-41:
> The following cost information is available for July for the Crest Plant at Calvert Company: Materials are added at the beginning of the process. The following quantities have been recorded: ∙ Beginning inventory, 40,000 partially compl
> In computing the cost per equivalent unit, the weighted-average method considers a. Current costs less costs in beginning WIP inventory. b. Current costs plus the cost of ending WIP inventory. c. Current costs plus costs in beginning WIP inventory. d. Cu
> Refer to the data in Exercise 8-34. Required a. Compute the equivalent units for the conversion cost calculation for March assuming Shirley Processing, Inc. uses the weighted-average method. b. Compute the cost per equivalent unit for materials and conve
> Hedwig Optical makes three models of binoculars: Travel, Sport, and Pro. The models differ by the size of the casing and the quality of the optics. The binoculars are produced in two departments. The Assembly Department purchases components from vendors
> Devereaux Cycles makes three models of scooter: Commuter, Sport, and X-treme. The scooters are produced in four departments: Assembly, Detailing, Customization, and Packaging. All three models are started in Assembly, where all materials are assembled. T
> Shirley Processing, Inc. (SPI) makes adhesive tape and uses a FIFO process costing system. The following information shows the physical flow of units and costs for the month of March: Required a. Compute the equivalent units for the materials and convers
> What are three common sources of improprieties in job costing?
> Boulder Toys manufactures powered, ride-on tractors and other equipment for children. There are three models, increasing in features and detail: XL, XLS, and XLT. All three models start in the Assembly Department, where the raw materials are shaped and c
> Refer to the data in Exercise 8-32. Required Compute the cost per equivalent unit for materials and conversion costs using the FIFO method. Exercise 8-32:
> Beverly Plastics produces a part used in precision machining. The part is produced in two departments: Mixing and Refining. The raw material is introduced into the process in the Mixing Department. The cost of the material fluctuates significantly month
> The following information about the work-in-process inventory pertains to the Remington Plant for the month of July (all materials are added at the beginning of the process): The Remington Plant started 216,000 units and transferred out 200,000 in July.
> Terminal Industries (TI) produces a product using three departments: Mixing, Processing, and Filtering. New material is added only in the Mixing Department. The following information is given for the Processing Department for August. TI uses process cost
> Refer to the data in Exercise 8-45. Required a. Compute the cost of goods transferred out and the cost of ending inventory for March using the FIFO method. b. Is the ending inventory higher or lower under the weighted-average method compared to FIFO? Why
> Refer to the data in Exercise 8-45. Compute the cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and for conversion costs for March using the FIFO method. Exercise 8-45: Bellevue Chemicals had beginning work-in-process inventory of $239,910 on March 1. Of
> Refer to the data in Exercise 8-45. Compute the costs of goods transferred out and the ending inventory for March using the weighted-average method. Exercise 8-45: Bellevue Chemicals had beginning work-in-process inventory of $239,910 on March 1. Of thi
> Bellevue Chemicals had beginning work-in-process inventory of $239,910 on March 1. Of this amount, $101,280 was the cost of direct materials and $138,630 was the cost of conversion. The 24,000 units in the beginning inventory were 45 percent complete wit
> Refer to the data in Exercises 8-41 and 8-43. Compute the cost of goods transferred out and the ending inventory for February using the FIFO method. Exercise 8-41:
> What is a limitation of the direct method of allocating service department costs? The step method?
> At the beginning of the month, Daniel’s Business Services had two incomplete consulting engagements (jobs) that had the following costs assigned from previous months. During the month, Jobs DBS-32 and DBS-35 were completed but not bille
> Refer to the data in Exercise 8-41. Compute the cost of goods transferred out and the ending inventory for February using the weighted-average method. Exercise 8-41:
> Annin Laboratories uses the weighted-average method to account for its work-in-process inventories. The accounting records show the following information for February: Quantity information is obtained from the manufacturing records and includes the follo
> Refer to the data in Exercise 8-37. Compute the cost of goods transferred out and the ending inventory for July using the FIFO method. Exercise 8-37:
> Refer to Exercise 8-37. Compute the cost per equivalent unit for direct materials and for conversion costs for July using the FIFO method. Exercise 8-37:
> What is the basic difference between the allocation of joint costs to (a) joint products and (b) by-products?
> When would a physical quantities method for allocation be preferred?
> Refer to the data in Exercise 8-37. Compute the cost of goods transferred out and the ending inventory for July using the weighted-average method. Exercise 8-37:
> What is the objective of joint cost allocation?
> What criterion should be used to determine the order of allocation from service departments when the step method is used? Explain why.
> What are the similarities and differences among the direct method, the step method, and the reciprocal method of allocating costs?
> Kingsley Products estimated that direct labor for the year would be 64,000 hours. The company also estimated that the fixed overhead cost for the year would be $160,000. They further estimated the variable overhead cost to be $4.00 per direct labor-hour.
> Kenmore Fabrication estimated that direct labor cost for the year would be $640,000. The company also estimated that fixed overhead would be $480,000 and variable overhead would be 35 percent of direct labor cost. Kenmore applies its overhead on the basi
> Louisiana Metals uses a job costing system. The company applies manufacturing overhead using a predetermined rate based on direct labor cost. The following debits (credits) appeared in the Workin- Process Inventory for June. Job LM-12, the only job still
> Bradby Automotive Restoration (BAR) has three service departments (S1, S2, and S3) and two operating departments (P1 and P2). Data on departmental usage of service departments follow: The direct costs for each department in the most recent period were as
> Rohns Manufacturing produces kitchen appliances at its North Roberts plant. The appliances go through two production departments: Fabrication and Assembly. The plant has three service departments: Information Systems Support (ISS), Training, and Administ
> Baldwin Enterprises has two service departments, Personnel and Legal, and two operating divisions, Eastern and Western. Personnel costs are allocated on the basis of employees and Legal costs are allocated on the basis of hours. A summary of Baldwin oper
> Hildale Manufacturing is organized with two service departments (Administration and Maintenance) and two production departments (Assembly and Finishing). The company uses the step method to allocate service department costs, allocating costs from Adminis
> Refer to the information in Exercise 7-36. Required Prepare an entry to allocate over- or underapplied overhead to a. Work in Process. b. Finished Goods. c. Cost of Goods Sold. Exercise 7-36: Marian Manufacturing (2M) applies manufacturing overhead to j
> Greendale Office Products has a warehouse that supplies office products to its store locations. The warehouse has two service departments, Human Resources (HR) and Information Technology (IT), and two operating departments, Packaging and Delivery. The fo
> Tennessee Company manufactures a specialized fitting for industrial machinery at the Stephens Street Facility. The facility has five departments. Two departments (Casting and Finishing) are production departments. The other three departments (Purchasing,
> Refer to the information and data in Problem 10-79. After working with the quality system for one year, the cost analyst revisits the relations for conformance and nonconformance costs. During the year, the quality team worked on lowering the cost of con
> Refer to the information in Problem 10-77. The organic cider business has two seasons, holidays and nonholidays. The holiday season lasts exactly four months (although it feels longer), and the nonholiday season lasts eight months. SOP orders the same am
> Remington Agricultural Products (RAP) produces organic cider with no preservatives. Any production must be sold within a few days, so producing for inventory is not an option. RAP’s single plant has the capacity to make 72,000 cases of cider annually. Cu
> Refer to Problems 10-74 and 10-75. The owner of Terry’s Bakery now believes that there are really three seasons instead of two, the third being the fall and spring (as a combined season). Each of the three seasons lasts exactly four mon
> Refer to the information in Problem 10-74. The pie business in this town has two seasons, summer and winter. Each season lasts exactly six months. Panama Food Mart orders 9,000 pies in the summer and 9,000 pies in the winter. East Street Coffee is closed
> Located in a small town in upstate New York, Terry’s Bakery operates a facility that makes pies for retail sale. The facility has the capacity to make 36,000 pies annually. The plant has only two customers, Panama Food Mart and East Street Coffee. Annual
> Barr Plastics makes parts for a variety of manufacturing applications. Sales last year totaled $3,060,000. Information regarding resources for the month follows. In addition, Barr spent $90,000 on 60 engineering changes with a cost-driver rate of $1,400,
> Consider the information in Problem 10-71. The sales manager of Granger Materials has proposed to the purchasing manager at Carrie Construction that Granger be given an exclusive contract to supply the aggregate. Assume that the total annual demand remai
> Marian Manufacturing (2M) applies manufacturing overhead to jobs based on direct labor costs. For Year 2, 2M estimates its manufacturing overhead to be $421,200 and its direct labor costs to be $810,000. 2M worked on three jobs for the year. Job 2M-1, wh

