Question: Oki Products, Ltd., has observed the following
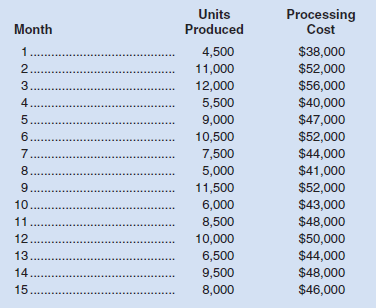
Oki Products, Ltd., has observed the following processing costs at various levels of activity over the last 15 months:
Required:
1. Prepare a scatter graph using the above data. Plot cost on the vertical axis and activity on the horizontal axis. Fit a line to your plotted points using a ruler.
2. Using the quick-and-dirty method, what is the approximate monthly fixed cost? The approximate variable cost per unit processed? Show your computations.
Transcribed Image Text:
Units Produced Processing Cost Month 4,500 $38,000 $52,000 $56,000 $40,000 $47,000 $52,000 $44,000 $41,000 $52,000 $43,000 $48,000 $50,000 $44,000 $48,000 $46,000 1... 11,000 3... 12,000 4.. 5,500 5 9,000 6... 10,500 7. 7,500 8... 5,000 9. 11,500 10.. 6,000 11. 8,500 12.. 10,000 13.. 6,500 14.. 9,500 15.. 8,000
> You have just been hired by Ogden Company to fill a new position that was created in response to rapid growth in sales. It is your responsibility to coordinate shipments of finished goods from the factory to distribution warehouses located in various par
> Swift Company was organized on March 1 of the current year. After five months of start-up losses, management had expected to earn a profit during August. Management was disappointed, however, when the income statement for August also showed a loss. Augus
> Various costs associated with the operation of factories are given below: 1. Electricity to run production equipment. 2. Rent on a factory building. 3. Cloth used to make drapes. 4. Production superintendent’s salary. 5. Wages of l
> Wollogong Group Ltd. of New South Wales, Australia, acquired its factory building about 10 years ago. For several years, the company has rented out a small annex attached to the rear of the building. The company has received a rental income of $30,000 pe
> Listed below are costs found in various organizations. 1. Property taxes, factory. 2. Boxes used for packaging detergent produced by the company. 3. Salespersons’ commissions. 4. Supervisor’s salary, factory. 5. D
> The Devon Motor Company produces motorcycles. During April, the company purchased 8,000 batteries at a cost of $10 per battery. Devon withdrew 7,600 batteries from the storeroom during the month. Of these, 100 were used to replace batteries in motorcycle
> The following cost and inventory data are taken from the accounting records of Mason Company for the year just completed: Costs incurred: Direct labor cost ........................................ $70,000 Purchases of raw materials..................... $
> Below are listed various costs that are found in organizations. 1. Hamburger buns in a Wendy’s outlet. 2. Advertising by a dental office. 3. Apples processed and canned by Del Monte. 4. Shipping canned apples from a Del Monte plant
> What are the arguments in favor of treating fixed manufacturing overhead costs as product costs?
> Following are a number of cost terms introduced in the chapter: Variable cost Fixed cost Prime cost Opportunity cost Product cost Sunk cost Conversion cost Period cost Required: Choose the term or terms above that most appropriately describe the cost i
> Northwest Hospital is a full-service hospital that provides everything from major surgery and emergency room care to outpatient clinics. The hospital’s Radiology Department is considering replacing an old inefficient X-ray machine with
> Below are costs and measures of activity in a variety of organizations. Required: Classify each cost as variable or fixed with respect to the indicated measure of activity by placing an X in the appropriate column. Cost Behavior Cost Measure of A
> Lompac Products manufactures a variety of products in its factory. Data for the most recent month’s operations appear below: Beginning raw materials inventory ................ $60,000 Purchases of raw materials........................... $690,000 Ending
> Lompac Products manufactures a variety of products in its factory. Data for the most recent month’s operations appear below: Beginning raw materials inventory ............... $60,000 Purchases of raw materials ......................... $690,000 Ending r
> Suppose that you have been given a summer job as an intern at Issac Aircams, a company that manufactures sophisticated spy cameras for remote-controlled military reconnaissance aircraft. The company, which is privately owned, has approached a bank for a
> The PC Works assembles custom computers from components supplied by various manufacturers. The company is very small and its assembly shop and retail sales store are housed in a single facility in a Redmond, Washington, industrial park. Listed below are
> A number of terms that relate to organizations, the work of management, and the role of managerial accounting are listed below: Budgets Directing and motivating Financial accounting Performance report Precision Controller Feedback Managerial accounting
> Selzik Company makes super-premium cake mixes that go through two processing departments, Blending and Packaging. The following activity was recorded in the Blending Department during July: Production data: Units in process, July 1 (materials 100% comple
> There is often more than one way to improve a performance measure. Unfortunately, some of the actions taken by managers to make their performance look better may actually harm the organization. For example, suppose the marketing department is held respon
> Refer to the data for the Blending Department of Sunspot Beverages, Ltd., in Problem 4–13A. Assume that the company uses the FIFO method rather than the weighted-average method in its process costing system. In Problem 4â€&#
> Refer to the data for Alaskan Fisheries, Inc., in Exercise 4–12. In Exercise 4–12 Alaskan Fisheries, Inc., processes salmon for various distributors. Two departments are involved— Cleaning and Packin
> Jarvene Corporation uses the FIFO method in its process costing system. The following data are for the most recent month of operations in one of the company’s processing departments: Units in beginning inventory ........................
> Refer to the data for Hielta Oy in Exercise 4–7. Assume that the company uses the FIFO method in its process costing system. In Exercise 4–7 Hielta Oy, a Finnish company, processes wood pulp for various manufacturers
> Refer to the data for Pureform, Inc., in Exercise 4–8. In Exercise 4–8 Pureform, Inc., manufactures a product that passes through two departments. Data for a recent month for the first department follow: The beginni
> MediSecure, Inc., produces clear plastic containers for pharmacies in a process that starts in the Molding Department. Data concerning that department’s operations in the most recent period appear below: Beginning work in process: Units in process…......
> Data concerning a recent period’s activity in the Assembly Department, the first processing department in a company that uses process costing, appear below: A total of 26,000 units were completed and transferred to the next processing
> Superior Micro Products uses the FIFO method in its process costing system. Data for the Assembly Department for May appear below: Required: Compute the cost per equivalent unit for materials, labor, overhead, and in total. Materials Labor Overhead
> Refer to the data for Clonex Labs, Inc., in Brief Exercise 4–2. In Brief Exercise 4–2 Clonex Labs, Inc., uses a process costing system. The following data are available for one department for October: The department
> Explain how fixed manufacturing overhead costs are shifted from one period to another under absorption costing.
> High Country, Inc., produces and sells many recreational products. The company has just opened a new plant to produce a folding camp cot that will be marketed throughout the United States. The following cost and revenue data relate to May, the first mont
> During Heaton Company’s first two years of operations, the company reported absorption costing net operating income as follows: The company’s $18 unit product cost is computed as follows: Direct materials............
> Refer to the data in Exercise 5A–6 for Chuck Wagon Grills. Assume in this exercise that the company uses absorption costing. In Exercise 5A–6 Chuck Wagon Grills, Inc., makes a single product—a handmade specialty barbecue grill that it sells for $210. Da
> Chuck Wagon Grills, Inc., makes a single product—a handmade specialty barbecue grill that it sells for $210. Data for last year’s operations follow: Units in beginning inventory…............................... 0 Units produced............................
> Whitman Company has just completed its first year of operations. The company’s absorption costing income statement for the year follows: Whitman Company Income Statement Sales (35,000 units × $25 per unit) .................................... $875,000 Co
> Lynch Company manufactures and sells a single product. The following costs were incurred during the company’s first year of operations: Variable costs per unit: Manufacturing: Direct materials.................................................. $6 Direct l
> Jorgansen Lighting, Inc., manufactures heavy-duty street lighting systems for municipalities. The company uses variable costing for internal management reports and absorption costing for external reports to shareholders, creditors, and the government. Th
> Refer to the data in Brief Exercise 5A–1 for Ida Sidha Karya Company. The absorption costing income statement prepared by the company’s accountant for last year appears below (all currency values are in thousands of rupiahs): Sales.......................
> Far North Telecom, Ltd., of Ontario, has organized a new division to manufacture and sell specialty cellular telephones. The division’s monthly costs are shown below: Manufacturing costs: Variable costs per unit: Direct materials.........................
> Tami Tyler opened Tami’s Creations, Inc., a small manufacturing company, at the beginning of the year. Getting the company through its first quarter of operations placed a considerable strain on Ms. Tyler’s personal fi
> What is the basic difference between absorption costing and variable costing?
> Ida Sidha Karya Company is a family-owned company located in the village of Gianyar on the island of Bali in Indonesia. The company produces a handcrafted Balinese musical instrument called a gamelan that is similar to a xylophone. The sounding bars are
> Refer to the data for Lakeshore Hotel in Exercise 5–8. In Exercise 5–8 The Lakeshore Hotel’s guest-days of occupancy and custodial supplies expense over the last seven months were: Guest-days is a
> The Lakeshore Hotel’s guest-days of occupancy and custodial supplies expense over the last seven months were: Guest-days is a measure of the overall activity at the hotel. For example, a guest who stays at the hotel For three days is
> Hoi Chong Transport, Ltd., operates a fleet of delivery trucks in Singapore. The company has determined that if a truck is driven 105,000 kilometers during a year, the average operating cost is 11.4 cents per kilometer. If a truck is driven only 70,000 k
> The following data relating to units shipped and total shipping expense have been assembled by Archer Company, a wholesaler of large, custom-built air-conditioning units for commercial buildings: Required: 1. Using the high-low method, estimate a cost
> Harris Company manufactures and sells a single product. A partially completed schedule of the company’s total and per unit costs over the relevant range of 30,000 to 50,000 units produced and sold annually is given below: Required: 1.
> The Alpine House, Inc., is a large retailer of winter sports equipment. An income statement for the company’s Ski Department for a recent quarter is presented below: Skis sell, on the average, for $750 per pair. Variable selling expen
> The Cheyenne Hotel in Big Sky, Montana, has accumulated records of the total electrical costs of the hotel and the number of occupancy-days over the last year. An occupancy-day represents a room rented out for one day. The hotel’s busin
> Nova Company’s total overhead cost at various levels of activity are presented below: Assume that the total overhead cost above consists of utilities, supervisory salaries, and maintenance. The breakdown of these costs at the 60,000 m
> Classify the following fixed costs as normally being either committed or discretionary: a. Depreciation on buildings. b. Advertising. c. Research. d. Long-term equipment leases. e. Pension payments to the company’s retirees. f. Management development and
> Benoit Company produces three products, A, B, and C. Data concerning the three products follow (per unit): Demand for the company’s products is very strong, with far more orders each month than the company can produce with the availab
> Draw a graph of the relationship between the revenue per theatre on the y -axis and the number of theatres on the x -axis. Describe the relationship. Reven The unbe dolan Movia peh The LEGO Movte 3,775 2,253 3372 3,083 $16,551 Abeus Lasu Nighe RoboCa
> Apple Inc. decides to make iTunes freely available in unlimited quantities. a. Does Apple’s decision change the incentives that people face? b. Is Apple’s decision an example of a microeconomic or a macroeconomic issue?
> Which of the following pairs does not match? a. Labour and wages b. Land and rent c. Entrepreneurship and profit d. Capital and profit
> List some examples of the scarcity that you face.
> An island economy produces only fish and crabs. Calculate the island’s chained-dollar real GDP in 2014 expressed in 2013 dollars. Ouantiten Fish Crabs 2013 2014 1,000 tonnes 1,100 tonnes 500 tonnes 525 tonnes Prices Fish Crabs 2013
> Tropical Republic produces only bananas and coconuts. The base year is 2013. Calculate real GDP in 2014 in base-year prices. 2013 800 bunches 900 bunches Quanfife 2014 Banans Cocomuts á00 bunches 5o0 bunches ricn Banana 2014 $2 a bunch $á a bunch $1
> Tropical Republic produces only bananas and coconuts. The base year is 2013. Calculate nominal GDP in 2013 and 2014. 2013 800 bunches 900 bunches Quanfife 2014 Banans Cocomuts á00 bunches 5o0 bunches ricn Banana 2014 $2 a bunch $á a bunch $10 a bunc
> Real GDP grew 1 percent in 2013. Business investment increased 3.2 percent, exports grew 1.6 percent, and imports rose by 2.2 percent. Use the flows in the figure below to identify each flow in the news clip. How can GDP have grown by only 1 percent wi
> Use the following data to calculate aggregate expenditure and imports of goods and services: ■ Government expenditure: $20 billion ■ Aggregate income: $100 billion ■ Consumption expenditure: $67 billion ■ Investment: $21 billion ■ Exports of goods and se
> Use the following figure, which illustrates the circular flow model. During 2014, flow A was $13.0 billion, flow B was $9.1 billion, flow D was $3.3 billion, and flow E was –$0.8 billion. Calculate (i) GDP and (ii) government expendi
> Classify each of the following items as a final good or service or an intermediate good or service and identify each item as a component of consumption expenditure, investment, or government expenditure on goods and services: ■ Banking services bought by
> Explain why real GDP might be an unreliable indicator of the standard of living.
> What is PPP and how does it help us to make valid international comparisons of real GDP
> What is a business cycle and what are its phases and turning points?
> Distinguish between real GDP and potential GDP and describe how each grows over time.
> Why does GDP equal aggregate income and also equal aggregate expenditure?
> Define GDP and distinguish between a final good and an intermediate good. Provide examples
> Use the information in Problem 20 to calculate the chained-dollar real GDP in 2014 expressed in 2013 dollars. Problem 20: An economy produces only apples and oranges. The base year is 2013, and the table gives the quantities produced and the prices.
> GDP has proved useful in tracking both shortterm fluctuations and long-run growth. Which isn’t to say GDP doesn’t miss some things. Amartya Sen, at Harvard, helped create the United Nations’ Human Development Index, which combines health and education da
> Answer the following questions. a. Which economy—the Canadian or the U.S.—had the longer and deeper recession in 2008–2009? b. Which economy—the Canadian or the U.S.—had the lower estimated growth rate of potential GDP? c. Why does the news article descr
> India, with the world’s largest population of poor people, created millionaires at the fastest pace in the world in 2007. India added another 23,000 millionaires in 2007 to its 2006 tally of 100,000 millionaires measured in dollars. That is 1 millionaire
> News clip in Problem 22 is as follows: China’s gross domestic product grew 11.4 percent last year and marked a fifth year of double-digit growth. The increase was especially remarkable given that the United States is experiencing a slowdown due to the su
> Oxford analysts report that living standards in Britain are set to rise above those in America for the first time since the nineteenth century. Real GDP per person in Britain will be £23,500 this year, compared with £23,250 in America, but also the U.K.
> The United Nations’ Human Development Index (HDI) is based on real GDP per person, life expectancy at birth, and indicators of the quality and quantity of education. a. Explain why the HDI might be better than real GDP as a measure of economic welfare. b
> An economy produces only apples and oranges. The base year is 2013, and the table gives the quantities produced and the prices. Calculate real GDP in 2013 and 2014 expressed in base-year prices. Quantities 2013 2014 Apples Oranges 60 160 80 220 Pric
> An economy produces only apples and oranges. The base year is 2013, and the table gives the quantities produced and the prices. Calculate nominal GDP in 2013 and 2014. Quantities 2013 2014 Apples Oranges 60 160 80 220 Pricu Apples Oranges 2013 $0.50
> Boeing is producing some components of its new 787 Dreamliner in Japan and is assembling it in the United States. Much of the first year’s production will be sold to ANA (All Nippon Airways), a Japanese airline. Explain how ANA’s activities and its trans
> Boeing is producing some components of its new 787 Dreamliner in Japan and is assembling it in the United States. Much of the first year’s production will be sold to ANA (All Nippon Airways), a Japanese airline. Explain how Boeing’s activities and its tr
> The components and robots for Toyota’s auto assembly lines in Canada are built in Japan. Toyota assembles cars for the Canadian market in Ontario. Explain where these activities appear in Canada’s National Income and Expenditure Accounts.
> In 2014, flow D was $2 trillion, flow E was –$1 trillion, flow A was $10 trillion, and flow C was $4 trillion. Calculate consumption expenditure. HOUSEHOLDS GOVEM TACTOR MAS MARKITS EEST or WORLD EMS
> In 2013, flow A was $1,000 billion, flow C was $250 billion, flow B was $650 billion, and flow E was $50 billion. Calculate investment. HOUSEHOLDS GOVEM TACTOR MAS MARKITS EEST or WORLD EMS
> Classify each of the following items as a final good or service or an intermediate good or service and identify which is a component of consumption expenditure, investment, or government expenditure on goods and services: ■ Banking services bought by Lob
> In Problem 7, a fire destroys some factories that produce gum and the quantity of gum supplied decreases by 40 million packs a week at each price. a. Explain what happens in the market for gum and draw a graph to illustrate the changes. b. If, at the sam
> The following events occur one at a time: (i) The price of crude oil rises. (ii) The price of a car rises. (iii) All speed limits on highways are abolished. (iv) Robots cut car production costs. Explain the effect of each of these events on the market fo
> The demand and supply schedules for gum are: a. Suppose that the price of gum is 70¢ a pack. Describe the situation in the gum market and explain how the price adjusts. b. Suppose that the price of gum is 30¢ a pack. Describe the
> Dairies make low-fat milk from full-cream milk, and in the process they produce cream, which is made into ice cream. The following events occur one at a time: (i) The wage rate of dairy workers rises. (ii) The price of cream rises. (iii) The price of low
> In 2013, the price of corn fell and some corn farmers switched from growing corn in 2014 to growing soybeans. a. Does this fact illustrate the law of demand or the law of supply? Explain your answer. b. Why would a corn farmer grow soybeans?
> Which of the following goods are likely substitutes and which are likely complements? (You may use an item more than once.) coal, oil, natural gas, wheat, corn, pasta, pizza, sausage, skateboard, roller blades, video game, laptop, iPad, cellphone, text m
> The price of food increased during the past year. a. Explain why the law of demand applies to food just as it does to other goods and services. b. Explain how the substitution effect influences food purchases when the price of food rises and other things
> In April 2014, the money price of a litre of milk was $2.01 and the money price of a litre of gasoline was $1.30. Calculate the real price of a litre of gasoline in terms of milk.
> What is the effect on the price and quantity of MP3 players (such as the iPod) if: Any two of the events in questions 1 and 2 occur together? (Draw the diagrams!).
> What is the effect on the price and quantity of MP3 players (such as the iPod) if: More firms produce MP3 players or electronics workers’ wages rise? (Draw the diagrams!).
> What is the effect on the price and quantity of MP3 players (such as the iPod) if: The price of a PC falls or the price of an MP3 download rises? (Draw the diagrams!).
> Why is the equilibrium price the best deal available for both buyers and sellers?
> List all the influences on selling plans, and for each influence, say whether it changes supply.
> What is the law of supply and how do we illustrate it?
> List all the influences on buying plans that change demand, and for each influence, say whether it increases or decreases demand.
> What does the demand curve tell us about the price that consumers are willing to pay?
> What is the law of demand and how do we illustrate it?

