Question: On January 2, Year 4, Brady Ltd.
On January 2, Year 4, Brady Ltd. purchased 80% of the outstanding shares of Partridge Ltd. for $4,320,000. Partridge's statement of financial position and the fair values of its identifiable assets and liabilities for that date were as follows:

The patents had a remaining useful life of ten years on the acquisition date. The bonds were issued on January 1, Year 4, and mature on December 31, Year 13. Goodwill impairment losses were recorded as follows:
• Year 4: $31,000
• Year 6: $18,000
Partridge declared and paid dividends of $110,000 in Year 6.
On December 31, Year 6, the financial statements of the two companies were as follows:
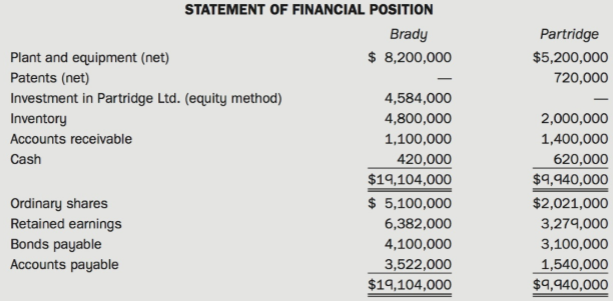

Required:
(a) Prepare consolidated financial statements on December 31, Year 6.
(b) Assume that Brady is a private entity, uses ASPE, and chooses to use the cost method to account for its investment in Partridge. Which items on Brady's separate-entity financial statements would have amounts different from those shown? Compute the cost method balances of these items.
(c) Calculate the current ratio, debt-to-equity ratio, and return on total shareholders' equity for Brady's Year 6 financial statements assuming that the
(i) equity method was used to report its investment in Partridge;
(ii) cost method was used to report its investment in Partridge; and
(iii) consolidated statements were used to report the business combination with Partridge.
Round percentages to one decimal point and other ratios to two decimal points.
(d) Briefly explain which of the different reporting methods in (c) report the highest
(i) Liquidity
(ii) (iii) Risk of insolvency Profitability
(e) Prepare the consolidated financial statements using the worksheet approach.
Transcribed Image Text:
Carrying Amount Fair Value $4,600,000 $4,600,000 Plant and equipment (net) Patents (net) 1,100,000 1,620,000 Inventory 2,100,000 2,320,000 Accounts receivable 1,600,000 1,600,000 Cash 520,000 $9,920,000 520,000 Ordinary shares Retained earnings $2,021,000 2,620,000 10% bonds payable 3,100,000 3,420,000 Accounts payable 2,179,000 $9,920,000 2,179,000 STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION Brady Partridge Plant and equipment (net) $ 8,200,000 $5,200,000 Patents (net) 720,000 Investment in Partridge Ltd. (equity method) 4,584,000 Inventory 4,800,000 2,000,000 Accounts receivable 1,100,000 1,400,000 Cash 420,000 $19,104,000 $ 5,100,000 620,000 $9,940,000 Ordinary shares $2,021,000 Retained earnings Bonds payable Accounts payable 6,382,000 3,279,000 4,100,000 3,100,000 3,522,000 $19,104,000 1,540,000 $9,940,000 INCOME STATEMENTS Sales $10,100,000 $5,100,000 equity method income 136,000 10,236,000 5,100,000 2,910,000 Cost of goods purchased 6,950,000 Change in inventory 72,000 120,000 Depreciation expense 920,000 402,000 Patent amortization expense Interest expense 120,000 490,000 310,000 Other expenses 700,000 870,000 Income taxes 620,000 9,752,000 484,000 160,000 4,892,000 $ 208,000 Profit $
> Pure Company purchased 70% of the ordinary shares of Gold Company on January 1, Year 6, for $483,000 when the latter company's accumulated depreciation, ordinary shares and retained earnings were $75,000, $500,000 and $40,000, respectively. Non-controlli
> Income statements of M Cop. and K Co. for the year ended December 31, Year 9, are presented below: Additional Information • M Co. uses the equity method to account for its investment in K Co. • M Co. acquired its 80%
> On January 1, Year 4, Goodkey Co. acquired all of the common shares of Jingya. The condensed income statements for the two companies for January Year 5, were as follows: The following transactions occurred in January, Year 5, and are properly reflected
> The balance sheets of Forest Company and Garden Company are presented below as at December 31, Year 8. Additional Information: • Forest acquired 90% of Garden for $207,900 on July 1, Year 1, and accounts for its investment under the c
> On December 31, Year 2, HABS Inc. sold equipment to NORD at its fair value of $2,000,000 and recorded a gain of $500,000. This was HABS's only income (other than any investment income from NORD) during the year. NORD reported income (other than any inves
> Hanna Corporation owns 80% of the outstanding voting stock of Fellow Inc. At the date of acquisition, Fellow's retained earnings were $2,100,000. On December 31, Year 2, Hanna Inc. sold equipment to Fellow at its fair value of $2,000,000 and recorded a g
> The comparative consolidated income statements of a parent and its 75%-owned subsidiary were prepared incorrectly as at December 31 and are shown in the following table. The following items were overlooked when the statements were prepared: â€
> Peggy Company owns 75% of Sally Inc. and uses the cost method to account for its investment. The following data were taken from the Year 4 income statements of the two companies: On January 1, Year 2, Sally sold equipment to Peggy at a gain of $15,000.
> SENS Ltd. acquired equipment on January 1, Year 1, for $500,000. The equipment was depreciated on a straight-line basis over an estimated useful life of 10 years. On January 1, Year 3, SENS sold this equipment to MEL Corp., its parent company, for $420,0
> Identify the main factors to be used when ranking the importance of issues to be resolved.
> On January 1, Year 4, Handy Company (Handy) purchased 70% of the outstanding common shares of Dandy Limited (Dandy) for $13,300. On that date, Dandy's shareholders' equity consisted of common shares of $1,250 and retained earnings of $6,500. The financia
> Financial statements of Champlain Ltd. and its 80%. owned subsidiary Samuel Ltd. as at December 31, Year 8, are presented below. Additional Information • Champlain acquired 8,000 ordinary shares of Samuel on January 1, Year 4, for $1
> Shown below are selected ledger accounts from the trial balance of a parent and its subsidiary as of December 31, Year 10. Additional Information • P Company purchased its 90% interest in S Company in Year 2, on the date that S Compan
> On December 31, Year 4, RAV Company purchased 60% of the outstanding common shares of ENS Company for $1,260,000. On that date, ENS had common shares of $500,000 and retained earnings of $130,000. In negotiating the purchase price, it was agreed that rec
> Palmer Corporation owns 70% of the ordinary shares of Scott Corporation and uses the equity method to account for its investment. Scott purchased $80,000 par of Palmer's 10% bonds from outsiders on October 1, Year 5, for $72,000. Palmer's bond liability
> Parent Co. owns 75% of Sub Co. and uses the cost method to account for its investment. The following are summarized income statements for the year ended December 31, Year 7. Additional Information: • On July 1, Year 7, Parent purchase
> Alpha Corporation owns 90% of the ordinary shares of Beta Corporation and uses the equity method to account for its investment. On January 1, Year 4, Alpha purchased $160,000 of Beta's 10% bonds for $150,064. Beta's bond liability on this date consisted
> X Company owns 80% of Y Company and uses the equity method to account for its investment. On January 1, Year 2, the investment in Y Company account had a balance of $86,900, and Y Company's common shares and retained earnings totaled $100,000. The unamor
> Yosef Corporation acquired 90% of the outstanding voting stock of Randeep Inc. on January 1, Year 6. During Year 6, intercompany sales of inventory of $45,000 (original cost of $27,000) were made. Only 20% of this inventory was still held within the cons
> Explain the difference between report recipient and primary users as they are described in the framework for analyzing a case and which users should be given priority in financial reporting.
> On January 1, Year 8, Fazli Co. acquired all of the common shares of Gervais. The following transactions occurred in January and February, Year 8: • On January 10, Gervais purchased $10,000 of inventory from outsiders. • On January 20, Gervais sold $6,00
> On January 1, Year 3, the Most Company purchased 80% of the outstanding voting shares of the Least Company for $1.6 million in cash. On that date, Least's balance sheet and the fair values of its identifiable assets and liabilities were as follows: On
> L Co. owns a controlling interest in M Co. and Q Co. L Co. purchased an 80% interest in M Co. at a time when M Co. reported retained earnings of $500,000. L Co. purchased a 70% interest in Q Co. at a time when Q Co. reported retained earnings of $50,000.
> X Co. acquired 75% of Y Co. on January 1, Year 3, when Y Co. had common shares of $100,000 and retained earnings of $70,000. The acquisition differential was allocated as follows on this date: Since this date the following events have occurred: Year 3
> The income statements for Paste Company and its subsidiaries, Waste Company, and Baste Company were prepared for the year ended December 31, Year 9, and are shown below: Additional Information • Paste purchased its 80% interest in Was
> On January 1, Year 1, Spike Ltd. purchased land from outsiders for $200,000. On December 31, Year 1, Pike Co. acquired all of the common shares of Spike. The fair value of Spike's land on this date was $230,000. On December 31, Year 2, Spike sold its lan
> The consolidated income statement of a parent and its 90%-owned subsidiary appears below. It was prepared by an accounting student before reading this chapter. The following items were overlooked when the statement was prepared: • The
> Fast Ltd. is a public company that prepares its consolidated financial statements in accordance with IFRS. Its net income in Year 2 was $200,000, and shareholders' equity at December 31, Year 2, was $1,800,000. Mr. Lombardi, the major shareholder, has ma
> IAS 16 Property, Plant, and Equipment requires assets to be initially measured at cost. Subsequently, assets may be carried at cost less accumulated depreciation, or they can be periodically revalued upward to current value and carried at the revalued am
> Part A On January 1, Year 5, Anderson Corporation paid $650,000 for 20,000 (20%) of the outstanding shares of Carter Inc. The investment was considered to be one of significant influence. In Year 5, Carter reported profit of $95,000; in Year 6, its prof
> List the six steps of the case framework.
> On January 1, Year 7, the Vine Company purchased 60,000 of the 80,000 ordinary shares of the Devine Company for $80 per share. On that date, Devine had ordinary shares of $3,440,000, and retained earnings of $2,170,000. When acquired, Devine had inventor
> On January 2, Year 5, Road Ltd. acquired 70% of the outstanding voting shares of Runner Ltd. The acquisition differential of $520,000 on that date was allocated in the following manner: The Year 9 income statements for the two companies were as follows
> The partial trial balances of P Co. and S Co. at December 31, Year 10, were as follows: Additional Information • The investment in the shares of S Co. (a 90% interest) was acquired January 2, Year 6, for $90,000. At that time, the sha
> The income statements of Evans Company and Falcon Company for the current year are shown below: The following amounts were taken from the statement of changes in eq_uity for the two companies: Evans owns 80% of the outstanding common shares of Falcon
> On January 1, Year 2, PAT Ltd. acquired 90% of SAT Inc. when SAT's retained earnings were $1,000,000. There was no acquisition differential. PAT accounts for its investment under the cost method. SAT sells inventory to PAT on a regular basis at a markup
> On July 1, Year 5, Big purchased 80% of the outstanding common shares of Little for $122,080. On that date, Little's equipment had a fair value that was $21,600 less than carrying amount. The equipment had accumulated depreciation of $20,000 and an estim
> On January 1, Year 4, Cyrus Inc. paid $914,000 in cash to acquire all of the ordinary shares of Fazli Company. On that date, Fazli's retained earnings were $200,000. All of Fazli's assets and liabilities had fair values equal to carrying amounts except f
> On January 1, Year 4, Grant Corporation bought 8,000 (80%) of the outstanding common shares of Lee Company for $70,000 cash. Lee's shares were trading for $7 per share on the date of acquisition. On that date, Lee had $25,000 of common shares outstanding
> Explain if and when it may be appropriate for an accountant to prepare financial statements for external users that are not in accordance with GAAP.
> Briefly explain the concept of fund accounting.
> Peach Ltd. acquired 80% of the common shares of Cherry Company on January 1, Year 4. On that date, Cherry had common shares of $710,000 and retained earnings of $410,000. The following is a summary of the changes in Peach's investment account from Januar
> Pen Ltd. acquired an 85% interest in Silk Corp. on December 31, Year 1, for $646,000. On that date, Silk had common shares of $500,000 and retained earnings of $100,000. The imputed acquisition differential was allocated $70,000 to inventory, with the ba
> Summarized balance sheets of Comer Company and its subsidiary Brook Corporation on December 31, Year 4, were as follows: On the date that Comer acquired its interest in Brook, there was no acquisition differential and the carrying amounts of Brook's ne
> On January 1, Year 2, Gros Corporation acquired 70% of the outstanding common shares of Petite Company for a total cost of $84,000. On that date, Petite had $35,000 of common shares and $25,000 of retained earnings. The carrying amounts of each of Petite
> Large Ltd. purchased 70% of Small Company on January 1, Year 6, for $770,000, when the statement of financial position for Small showed common shares of $560,000 and retained earnings of $260,000. On that date, the inventory of Small was undervalued by $
> Balance sheet and income statement data for two affiliated companies for the current year appear on the next page. Additional Information • Albeniz acquired an 80% interest in Bach on January 1, Year 3, for $272,000. On that date, the f
> The following financial statements were prepared on December 31, Year 6. Additional Information Pearl purchased 80% of the outstanding voting shares of Silver for $3,300,000 on July 1, Year 2, at which time Silver's retained earnings were $445,000, an
> Foxx Corp. purchased 75% of the outstanding shares of Rabb Ltd. on January 1, Year 3, at a cost of $117,000. Non-controlling interest was valued at $35,000 by an independent business valuator at the date of acquisition. On that date, Rabb had common shar
> On July 1, Year 4, Aaron Co. purchased 80% of the voting shares of Bondi Ltd. for $543,840. The statement of financial position of Bondi on that date follows. The accounts receivable of Bondi were collected in October Year 4, and the inventory was comple
> When writing the final case report, how much attention, if any, should be given to discussing alternatives?
> On December 31, Year 2, Palm Inc. purchased 80% of the outstanding ordinary shares of Storm Company for $350,000. At that date, Storm had ordinary shares of $240,000 and retained earnings of $64,000. In negotiating the purchase price, it was agreed that
> The following information is available for the assets of Saman Ltd. at December 31, Year 5: Required: (The following 3 parts are independent situations.) Part A. Assume that the total fair value for all of Saman's assets as a group is $1,860. (a) Cal
> The balance sheets of Percy Corp. and Saltz Ltd. on December 31, Year 10, are shown below: The fair values of the identifiable net assets of Saltz Ltd. on December 31, Year 10, were as follows: In addition to the assets identified above, Saltz owned
> On January 1, Year 5, Black Corp. purchased 90% of the common shares of Whyte Inc. On this date, the following differences were observed with regard to specific net assets of Whyte: The non-consolidated and consolidated balance sheets of Black Corp. on
> On December 31, Year 1, P Company purchased 80% of the outstanding shares of S Company for $7,900 cash. The statements of financial position of the two companies immediately after the acq,uisition transaction appear below. Required: (a) Calculate conso
> The balance sheets of E Ltd. and J Ltd. on December 30, Year 6, were as follows: The carrying amounts of J Ltd.'s net assets were equal to fair values on this date except for the following: E Ltd. was identified as the acquirer in the combination.
> On December 31, Year 2, Blue purchased a percentage of the outstanding ordinary shares of Joy. On this date all but two categories of Joy's identifiable assets and liabilities had fair values equal to carrying amounts. Following are the statements of fin
> The balance sheets of Hill Corp. and McGraw Ltd. on December 31, Year 4, were as follows: On December 31, Year 4, Hill purchased 80% of the common shares of McGraw for $288,000 plus a commitment to pay an additional $100,000 in two years if sales grow
> The balance sheets of Petron Co. and See view Co. on June 29, Year 2, were as follows: On June 30, Year 2, Petron Co. purchased 90% of the outstanding shares of See view Co. for $52,200 cash. Legal fees involved with the acquisition were an additional
> The balance sheets of Par Ltd. and Sub Ltd. on December 31, Year 1, are as follows: The fair values of the identifiable net assets of Sub on December 31, Year 1, are as follows: Assume that the following took place on January 1, Year 2. (Par acquired
> How will the investment in a private company be reported under IFRS 9, and how does this differ from lAS 39?
> Calof Inc. acquires 100% of the common shares of Xiyu Company on January 1, Year 4, for the following consideration: • $275,000 market value of 5,000 shares of its common shares. • A contingent payment of $40,000 cash on January 1, Year 5 if Xiyu gener
> The balance sheets of Bates Co. and Casey Co. on June 30, Year 2 just before the transaction described below, were as follows: On June 30, Year 2, Bates Co. purchased 2,400 (80%) of Casey Co.'s common shares for $48,000 in cash. On that date, Casey's
> The July 31, Year 3, balance sheets of two companies that are parties to a business combination are as follows: In addition to the assets identified above, Ravinder Corp. attributed a value of $100,000 to a major research project that Robin Inc. was wo
> The condensed financial statements for OIL Inc. and ERS Company for the year ended December 31, Year 5, follow: On December 31, Year 5, after the above figures were prepared, OIL issued $252,000 in debt and 12,000 new shares to the owners of ERS for 90
> On January 1, Year 5, FLA Company issued 6,300 ordinary shares to purchase 9,000 ordinary shares of MES Company. Prior to the acquisition, FLA had 180,000 and MES had 10,000 ordinary shares outstanding, which were trading at $5 and $3 per share, respecti
> The balance sheets of Prima Ltd. and Donna Corp. on December 31, Year 5, are shown below: The fair values of the identifiable net assets of Donna Corp. on this date are as follows: In addition to the assets identified above, Donna owned a significant
> The statements of financial position of Pork Co. and Barrel Ltd. on December 31, Year 2, are shown next: Pork acquired 70% of the outstanding shares of Barrel on December 30, Year 2, for $329,000. Direct costs of the acquisition amounted to $12,000. Th
> The July 31, Year 3, balance sheets of two companies that are parties to a business combination are as follows: In addition to the property, plant, and equipment identified above, Red Corp. attributed a value of $100,000 to Sax's assembled workforce. T
> D Ltd. and H Corporation are both engaged in the manufacture of computers. On July 1, Year 5, they agree to a merger, whereby D will issue 300,000 shares with a current market value of $9 each for the net assets of H. Summarized balance sheets of the tw
> The balance sheet of Drake Enterprises as at December 31, Year 5, is as follows: Effective January 1, Year 6, Drake proposes to issue 82,500 common shares (currently trading at $20 per share) for all of the common shares of Hanson Industries. In determ
> How should a private company that has opted to follow ASPE report an investment in an associate?
> The shareholders of Prong Company and Hom Company agreed to a statutory amalgamation under which a share exchange took place. On September 1, Year 5, Prong Company issued 60,000 ordinary shares for all of the ordinary shares of Hom Company, after which H
> The statement of financial position of Bagley Incorporated as at July 31, Year 4, is as follows: On August 1, Year 4, the directors of Bagley considered a takeover offer from Davis Inc., whereby the corporation would sell all of its assets and liabilit
> Three companies, A, L, and M, whose December 31, Year 5, balance sheets appear below, have agreed to combine as at January 1, Year 6. Each of the companies has a very small proportion of an intensely competitive market dominated by four much larger compa
> G Company is considering the takeover of K Company whereby it will issue 7,400 common shares for all of the outstanding shares of K Company. K Company will become a wholly owned subsidiary of G Company. Prior to the acquisition, G Company had 13,000 shar
> The trial balances for Walla Corporation and Au Inc. at December 31, Year 4, just before the transaction described below, were as follows: On December 31, Year 4, Walla purchased all of the outstanding shares of Au Inc. by issuing 20,000 common shares
> The balance sheets of A Ltd. and B Ltd. on December 30, Year 6, are as follows: On December 31, Year 6, A issued 150 common shares for all 60 outstanding common shares of B. The fair value of each of B's common shares was $40 on this date. Required:
> Z Ltd. is a public company with factories and distribution centers located throughout Canada. It has 100,000 common shares outstanding. In past years, it has reported high earnings, but in Year 5, its earnings declined substantially in part due to a loss
> The financial statements for CAP Inc. and SAP Company for the year ended December 31, Year 5, follow: On December 31, Year 5, after the above figures were prepared, CAP issued $314,000 in debt and 12,400 new shares to the owners of SAP to purchase all
> Refer to Problem 11. All of the facts and data are the same except that in the proposed takeover, Myers Company will purchase all of the outstanding common shares of Norris Inc. Required: (a) Prepare the journal entries of Myers for each of the two pro
> Myers Company Ltd. was formed 10 years ago by the issuance of 34,000 common shares to three shareholders. Four years later, the company went public and issued an additional 30,000 common shares. The management of Myers is considering a takeover in which
> Which of the reporting methods described in this chapter would typically report the highest current ratio? Briefly explain.
> The following are summarized statements of financial position of three companies as at December 31, Year3: The fair values of the identifiable assets and liabilities of the three companies as at December 31, Year 3, were as follows: On January 2, Yea
> The balance sheets of Abdul Co. and Lana Co. on June 30, Year 2, just before the transaction described below, were as follows: On June 30, Year 2, Abdul Co. purchased all of Lana Co. assets and assumed all of Lana Co. liabilities for $58,000 in cash.
> All facts are the same as in Problem 8 except that COX applies ASPE. Follow the same instructions as those given in the Required: section of Problem 8. Data from Problem 8: COX Limited is a multinational telecommunication company owned by a Canadian b
> COX Limited is a multinational telecommunication company owned by a Canadian businesswoman. It has numerous long-term investments in a wide variety of equity instruments. Some investments have to be measured at fair value at each reporting date. In turn,
> Right Company purchased 25,000 common shares (25%) of ON Inc. on January 1, Year 11, for $250,000. Right uses the eq_uity method to report its investment in ON because it has significant influence in the operating and investing decisions made by ON. Righ
> On January 1, Year 2, Grow Corp. paid $200,000 to purchase 20,000 common shares of UP Inc., which represented an 8% interest in UP. On December 27, Year 2, UP declared and paid a dividend of $0.50 per common share. During Year 2, UP reported net income o
> Her Company purchased 22,000 common shares (20%) of Him Inc. on January 1, Year 4, for $374,000. Additional information on Him for the three years ending December 31, Year 6, is as follows: On December 31, Year 6, Her sold its investment in Him for $50
> Pender Corp. paid $285,000 for a 30% interest in Saltspring Limited on January 1, Year 6. During Year 6, Saltspring paid dividends of $110,000 and reported profit as follows: Pender's profit for Year 6 consisted of $990,000 in sales, expenses of $110,0
> On January 1, Year 5, Blake Corporation purchased 25% of the outstanding common shares of Stergis Limited for $1,850,000. The following relates to Stergis since the acquisition date: Required: (a) Assume that Blake is a public company and the number of
> Baskin purchased 20,000 common shares (20%) of Robbin on January 1, Year 5, for $275,000 and classified the investment as FVTPL. Robbin reported net income of $85,000 in Year 5 and $90,000 in Year 6, and paid dividends of $40,000 in each year. Robbin's s
> Briefly describe the trend in reporting of investments in equity securities over the past 12 years.
> Harmandeep Ltd. is a private company in the pharmaceutical industry. It has been preparing its financial statements in accordance with ASPE. Since it has plans to go public in the next three to five years, it is considering changing to IFRS for the curre
> The summarized trial balances of Phase Limited and Step Limited as of December 31, Year 5, are as follows (amounts in thousands): Phase had acquired the investment in Step in three stages: The January 1, Year 2, acquisition enabled Phase to elect 3 m
> On December 31, Year 6, Ultra Software Limited purchased 70,000 common shares (70%) of a major competitor, Personal Program Corporation (PPC), at $30 per share. Several shareholders who were unwilling to sell at that time owned the remaining common share
> On January 1, Year 8, Panet Company acquired 40,000 common shares of Saffer Corporation, a public company, for $500,000. This purchase represented 8% of the outstanding shares of Saffer. It was the intention of Panet to acquire more shares in the future
> On January 1, Year 4, a Canadian firm, Canuck Enterprises Ltd., borrowed US$208,000 from a bank in Seattle, Washington. Interest of 7.5% per annum is to be paid on December 31 of each year during the four-year term of the loan. Principal is to be repaid

