Question: Problems are mixed—some may require use
Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever ln g(x) is involved.
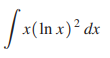
> use Table 1 to find each indefinite integral.
> use Table 1 to find each indefinite integral.
> use Table 1 to find each indefinite integral.
> use substitution techniques and Table 1 to find each indefinite integral.
> use substitution techniques and Table 1 to find each indefinite integral.
> use substitution techniques and Table 1 to find each indefinite integral.
> write each function as a sum of terms of the form axn , where a is a constant.
> use substitution techniques and Table 1 to find each indefinite integral.
> use substitution techniques and Table 1 to find each indefinite integral.
> use substitution techniques and Table 1 to find each indefinite integral.
> Show that Simpson’s rule with n = 1 (so there are 2 subintervals) gives the exact value of ∫5 1 (3x2 - 4x + 72 dx.
> Show that Simpson’s rule with n = 3 (so there are 6 subintervals) gives the exact value of ∫5 -1 (3 - 2x) dx.
> Let ((x) = 10 - 3x and suppose that the interval [5, 75] is partitioned into 35 subintervals of length 2. Without calculating T35, explain why the trapezoidal rule gives the negative of the exact area between the graph of f and the x axis from x = 5 to x
> Use Simpson’s rule with n = 4 (so there are 2n = 8 subintervals) to approximate and use the fundamental theorem of calculus to find the exact value of the definite integral.
> Use the trapezoidal rule with n = 5 to approximate ∫111 x3 dx and use the fundamental theorem of calculus to find the exact value of the definite integral.
> Use Table 1 in Appendix C to find the antiderivative. //
> Use Table 1 in Appendix C to find the antiderivative. //
> use the chain rule to find the derivative of each function.
> could the given matrix be the transition matrix of an absorbing Markov chain?
> Use Table 1 in Appendix C to find the antiderivative. //
> Use Table 1 in Appendix C to find each indefinite integral //
> Use Table 1 in Appendix C to find each indefinite integral //
> Use Table 1 in Appendix C to find each indefinite integral //
> Use Table 1 in Appendix C to find each indefinite integral //
> Use Table 1 in Appendix C to find each indefinite integral //
> Use Table 1 in Appendix C to find each indefinite integral //
> Find the derivative of (x) and the indefinite integral of g(x).
> Find the derivative of (x) and the indefinite integral of g(x).
> Find the derivative of (x) and the indefinite integral of g(x).
> write each function as a sum of terms of the form axn , where a is a constant.
> A student enrolled in a steno typing class progressed at a rate of N′(t) = (t + 10)e-0.1t words per minute per week t weeks after enrolling in a 15- week course. If a student had no knowledge of steno typing (that is, if the student could stenotype at
> After a person takes a pill, the drug contained in the pill is assimilated into the bloodstream. The rate of assimilation t minutes after taking the pill is R(t) = te-0.2t Find the total amount of the drug that is assimilated into the bloodstream durin
> Interpret the results of Problem 84 with both a graph and a description of the graph. Data from Problem 84: Find the producers’ surplus (to the nearest dollar) at a price level of p = $26 for the price–supply equation p = S(x) = 5 ln (x + 1) Use x com
> Find the producers’ surplus (to the nearest dollar) at a price level of p = $26 for the price–supply equation p = S(x) = 5 ln (x + 1) Use x computed to the nearest higher unit.
> The rate of change of the monthly sales of a new basketball game is given by S′(t) = 350 ln (t + 1) S(0) = 0 where t is the number of months since the game was released and S(t) is the number of games sold each month. Find S(t). When, to the nearest m
> Interpret the results of Problem 78 with both a graph and a description of the graph. Data from Problem 78: Find the Gini index of income concentration for the Lorenz curve with equation y = x2ex - 1
> Find the Gini index of income concentration for the Lorenz curve with equation y = x2ex - 1
> Find the interest earned at 4.15%, compounded continuously, for 4 years for a continuous income stream with a rate of flow of ((t) = 1,000 - 250t
> Interpret the results of Problem 72 with both a graph and a description of the graph.
> An oil field is estimated to produce oil at a rate of R1t2 thousand barrels per month t months from now, as given by R(t) = 10te-0.1t Use an appropriate definite integral to find the total production (to the nearest thousand barrels) in the first year
> use the chain rule to find the derivative of each function.
> use absolute value on a graphing calculator to find the area between the curve and the x axis over the given interval. Find answers to two decimal places.
> use absolute value on a graphing calculator to find the area between the curve and the x axis over the given interval. Find answers to two decimal places.
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> write each function as a sum of terms of the form axn , where a is a constant.
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> Problems are mixed—some may require use of the integration by-parts formula along with techniques we have considered earlier; others may require repeated use of the integration-by-parts formula. Assume that g(x) > 0 whenever lnÂ
> illustrate each integral graphically and describe what the integral represents in terms of areas. Problem 22
> illustrate each integral graphically and describe what the integral represents in terms of areas. Problem 20
> The integral can be found in more than one way. First use integration by parts, then use a method that does not involve integration by parts. Which method do you prefer?
> The integral can be found in more than one way. First use integration by parts, then use a method that does not involve integration by parts. Which method do you prefer?
> use the chain rule to find the derivative of each function.
> The integral can be found in more than one way. First use integration by parts, then use a method that does not involve integration by parts. Which method do you prefer?
> Problems are mixed some require integration by parts, and others can be solved with techniques considered earlier. Integrate as indicated, assuming x > 0 whenever the natural logarithm function is involved.
> Problems are mixed some require integration by parts, and others can be solved with techniques considered earlier. Integrate as indicated, assuming x > 0 whenever the natural logarithm function is involved.
> Problems are mixed some require integration by parts, and others can be solved with techniques considered earlier. Integrate as indicated, assuming x > 0 whenever the natural logarithm function is involved.
> Problems are mixed some require integration by parts, and others can be solved with techniques considered earlier. Integrate as indicated, assuming x > 0 whenever the natural logarithm function is involved.
> Problems are mixed some require integration by parts, and others can be solved with techniques considered earlier. Integrate as indicated, assuming x > 0 whenever the natural logarithm function is involved.
> Problems are mixed some require integration by parts, and others can be solved with techniques considered earlier. Integrate as indicated, assuming x > 0 whenever the natural logarithm function is involved.
> Problems are mixed some require integration by parts, and others can be solved with techniques considered earlier. Integrate as indicated, assuming x > 0 whenever the natural logarithm function is involved.
> If you want to use integration by parts to find ∫(5x – 7)(x – 1)4 dx, which is the better choice for u: μ = 5x - 7 or u = (x – 1)4 ? Explain your choice and then integrate
> integrate by parts. Assume that x > 0 whenever the natural logarithm function is involved.
> write each function as a sum of terms of the form axn , where a is a constant.
> integrate by parts. Assume that x > 0 whenever the natural logarithm function is involved.
> Find the derivative of (x) and the indefinite integral of g(x).
> evaluate each definite integral to two decimal places.
> Find real numbers b and c such that (x) = ebect.
> Find real numbers b and c such that (x) = ebect.
> Find real numbers b and c such that (x) = ebect.
> Find real numbers b and c such that (x) = ebect.
> Repeat Problem 85, using quadratic regression to model both sets of data. Data from Problem 85: The following tables give price–demand and price–supply data for the sale of soybeans at a grain market, where x is the n
> Find the consumers’ surplus and the producers’ surplus at the equilibrium price level for the given price– demand and price–supply equations. Include a graph that identifies the cons
> Find the consumers’ surplus and the producers’ surplus at the equilibrium price level for the given price– demand and price–supply equations. Include a graph that identifies the cons
> identify the absorbing states for each transition diagram, and determine whether or not the diagram represents an absorbing Markov chain.
> Find the consumers’ surplus and the producers’ surplus at the equilibrium price level for the given price– demand and price–supply equations. Include a graph that identifies the cons
> Find the consumers’ surplus and the producers’ surplus at the equilibrium price level for the given price– demand and price–supply equations. Include a graph that identifies the cons
> Interpret the results of Problem 74 with both a graph and a description of the graph.
> Find the producers’ surplus at a price level of p = $55 for the price–supply equation
> Interpret the results of Problem 70 with both a graph and a description of the graph.
> Find the consumers’ surplus at a price level of p = $120 for the price–demand equation
> Refer to Problem 67. Find the present value of a continuous income stream at 7.65%, compounded continuously for 12 years, if the rate of flow is f1t2 = 1,000e0.03t . Data from Problem 67: A business is planning to purchase a piece of equipment that will
> Compute the interest earned in Problem 62 Data from Problem 66: Find the future value at 3.5% interest, compounded continuously for 10 years, of the continuous income stream with the rate of flow function.
> Compute the interest earned in Problem 60. Data from Problem 60: Find the future value at 6.25% interest, compounded continuously for 4 years, of the continuous income stream with the rate of flow function of Problem 56. Data From Problem 56: The rate
> Find the future value at 3.5% interest, compounded continuously for 10 years, of the continuous income stream with the rate of flow function of Problem 58. Data from Problem 58: The rate of flow (t) of a continuous income stream is a linear function, d
> identify the absorbing states in the indicated transition matrix.
> Find the future value at 6.25% interest, compounded continuously for 4 years, of the continuous income stream with the rate of flow function of Problem 56. Data From Problem 56: The rate of flow of a continuous income stream is a linear function, i
> The rate of flow (t) of a continuous income stream is a linear function, decreasing from $12,000 per year when t = 0 to $9,000 per year when t = 10. Find the total income produced in the first 10 years.
> The rate of flow f1t2 of a continuous income stream is a linear function, increasing from $4,000 per year when t = 0 to $6,000 per year when t = 4. Find the total income produced in the first 4 years.
> Refer to Problem 53. Which is the better investment if the rate of the income from the business is (t) = 2,250? Data from Problem 53: An investor has $10,000 to invest in either a bond that matures in 5 years or a business that will produce a continuou
> Refer to Problem 51. Which investment is the better choice over the next 10 years? Data from Problem 51: An investor is presented with a choice of two investments: an established clothing store and a new computer store. Each choice requires the same ini

