Question: Queensland Company reports the following operating
Queensland Company reports the following operating results for the month of April.
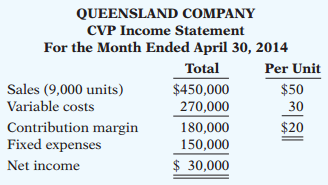
Management is considering the following course of action to increase net income: Reduce the selling price by 4%, with no changes to unit variable costs or fixed costs. Management is confident that this change will increase unit sales by 20%. Using the contribution margin technique, compute the break-even point in units and dollars and margin of safety in dollars:
(a) Assuming no changes to selling price or costs, and
(b) Assuming changes to sales price and volume as described above. Comment on your findings.
Transcribed Image Text:
QUEENSLAND COMPANY CVP Income Statement For the Month Ended April 30, 2014 Total Per Unit $450,000 270,000 $50 Sales (9,000 units) Variable costs 30 Contribution margin Fixed expenses 180,000 150,000 $20 Net income $ 30,000
> After graduating, you might decide to start a small business. As discussed in this chapter, owners of any business need to know how to calculate the cost of their products. In fact, many small businesses fail because they don’t accurately calculate their
> The gross earnings of the factory workers for Vargas Company during the month of January are $66,000. The employer’s payroll taxes for the factory payroll are $8,000. The fringe benefits to be paid by the employer on this payroll are $6,000. Of the total
> Information for Markowis Corporation is given in BE19-7. If the company has fixed costs of $213,000, how many units of each model must the company sell in order to break even?
> Markowis Corporation sells three different models of mosquito “zapper.” Model A12 sells for $50 and has variable costs of $40. Model B22 sells for $100 and has variablecosts of $70. Model C124 sells for $400 and has variable costs of $300. The sales mix
> For Kosko Company actual sales are $1,200,000 and break-even sales are $960,000. Compute (a) the margin of safety in dollars and (b) the margin of safety ratio.
> For Ortega Company, variable costs are 60% of sales, and fixed costs are $210,000. Management’s net income goal is $60,000. Compute the required sales needed to achieve management’s target net income of $60,000. (Use the mathematical equation approach.)
> Dilts Company has a unit selling price of $400, variable costs per unit of $250, and fixed costs of $210,000. Compute the break-even point in units using (a) the mathematical equation and (b) contribution margin per unit.
> Wesland Corp. had total variable costs of $175,000, total fixed costs of $120,000, and total revenues of $250,000. Compute the required sales in dollars to break even.
> Burns Company incurred the following costs during the year: direct materials $20 per unit; direct labor $14 per unit; variable manufacturing overhead $15 per unit; variable selling and administrative costs $8 per unit; fixed manufacturing overhead $128,0
> Information concerning The Rock Company is provided in BE19-16. What are the total product costs for the company under absorption costing? BE19-16: Direct materials …………………………………………….$14,400 Direct labor …………………………………………………..$25,600 Fixed manufacturing
> The Rock Company produces basketballs. It incurred the following costs during the year. Direct materials …………………………………………….$14,400 Direct labor …………………………………………………..$25,600 Fixed manufacturing overhead ……………………..$12,000 Variable manufacturing overhead …
> Many of you will work for a small business. Some of you will even own your own business. In order to operate a small business, you will need a good understanding of managerial accounting, as well as many other skills. Much information is available to ass
> The degree of operating leverage for Montana Corp. and APK Co. are 1.6 and 5.4, respectively. Both have net incomes of $50,000. Determine their respective contribution margins
> Sam’s Shingle Corporation is considering the purchase of a new automated shingle-cutting machine. The new machine will reduce variable labor costs but will increase depreciation expense. Contribution margin is expected to increase from $200,000 to $240,0
> In Briggs Company, data concerning two products are contribution margin per unit—Product A $12, Product B $15; machine hours required for one unit—Product A 2, Product B 3. Compute the contribution margin per unit of limited resource for each product.
> Acorn Corp. had total variable costs of $180,000, total fixed costs of $170,000, and total revenues of $300,000. Compute the required sales in dollars to break even.
> Rice Company has a unit selling price of $520, variable costs per unit of $286, and fixed costs of $163,800. Compute the break-even point in units using (a) the mathematical equation and (b) contribution margin per unit.
> Radial Inc. had sales of $2,400,000 for the first quarter of 2014. In making the sales, the company incurred the costs and expenses shown below. Prepare a CVP income statement for the quarter ended March 31, 2014. Variable Fixed Cost of goods sold
> Determine the missing amounts. Unit Selling Price Unit Variable Contribution Contribution Margin Ratio (b) ) (d) Costs Margin per Unit 1. $640 $300 $352 (c) (f) (a) $93 2. 3. (e) $325 25%
> Stiever Corp. has collected the following data concerning its maintenance costs for the past 6 months. Compute the variable- and fixed-cost elements using the high-low method. Units Produced Total Cost July August September 18,000 $32,000 32,000 36
> For Hunt Company, a mixed cost is $15,000 plus $18 per direct labor hour. Diagram the behavior of the cost using increments of 500 hours up to 2,500 hours on the horizontal axis and increments of $15,000 up to $60,000 on the vertical axis.
> For Lodes Company, the relevant range of production is 40–80% of capacity. At 40% of capacity, a variable cost is $4,000 and a fixed cost is $6,000. Diagram the behavior of each cost within the relevant range assuming the behavior is linear.
> Howser Company’s fixed overhead costs are $4 per unit, and its variable overhead costs are $8 per unit. In the first month of operations, 50,000 units are produced, and 48,000 units are sold. Write a short memo to the chief financial officer explaining w
> Deines Corporation has fixed costs of $480,000. It has a unit selling price of $6, unit variable costs of $4.40, and a target net income of $1,500,000. Compute the required sales in units to achieve its target net income.
> For Stevens Company, actual sales are $1,000,000 and break-even sales are $840,000. Compute (a) the margin of safety in dollars and (b) the margin of safety ratio.
> For Flynn Company, variable costs are 70% of sales, and fixed costs are $195,000. Management’s net income goal is $75,000. Compute the required sales in dollars needed to achieve management’s target net income of $75,000. (Use the contribution margin app
> Mendle and Kiner is an architectural firm that is contemplating the installation of activity-based costing. The following activities are performed daily by staff architects. Classify these activities as value-added or non–value-added: (a) designing and d
> Rich Novelty Company identified the following activities in its production and support operations. Classify each of these activities as either value-added or non value added. (a) Machine setup. (d) Moving work in process. (b) Design engineering.
> Weisman, Inc. uses activity-based costing as the basis for information to set prices for its six lines of seasonal coats. Compute the activity-based overhead rates using the following budgeted data for each of the activity cost pools. Expected Use o
> Mordica Company identifies three activities in its manufacturing process: machine setups, machining, and inspections. Estimated annual overhead cost for each activity is $150,000, $325,000, and $87,500, respectively. The cost driver for each activity and
> Mason Company manufactures four products in a single production facility. The company uses activity-based costing. The following activities have been identified through the company’s activity analysis: (a) inventory control, (b) machine setups, (c) emplo
> Storrer Co. identifies the following activities that pertain to manufacturing overhead: materials handling, machine setups, factory machine maintenance, factory supervision, and quality control. For each activity, identify an appropriate cost driver.
> Kwik Pix is a large digital processing center that serves 130 outlets in grocery stores, service stations, camera and photo shops, and drug stores in 16 nearby towns. Kwik Pix operates 24 hours a day, 6 days a week. Classify each of the following activit
> LRF Printing provides printing services to many different corporate clients. Although LRF bids most jobs, some jobs, particularly new ones, are negotiated on a “cost-plus” basis. Costplus means that the buyer is willing to pay the actual cost plus a retu
> Spin Cycle Company uses three activity pools to apply overhead to its products. Each activity has a cost driver used to allocate the overhead costs to the product. The activities and related overhead costs are as follows: product design $40,000; machinin
> Trammell, Inc. operates 20 injection molding machines in the production of tool boxes of four different sizes, named the Apprentice, the Handyman, the Journeyman, and the Professional. Classify each of the following costs as unit-level, batch-level, prod
> At December 31, balances in Manufacturing Overhead are Shimeca Company— debit $1,200, Garcia Company—credit $900. Prepare the adjusting entry for each company at December 31, assuming the adjustment is made to cost of goods sold.
> Preprah Engineering Contractors incurred service salaries and wages of $32,000 ($24,000 direct and $8,000 indirect) on an engineering project. The company applies overhead at a rate of 25% of direct labor. Record the entries to assign service salaries an
> In March, Stinson Company completes Jobs 10 and 11. Job 10 cost $20,000 and Job 11 $30,000. On March 31, Job 10 is sold to the customer for $35,000 in cash. Journalize the entries for the completion of the two jobs and the sale of Job 10.
> During the first quarter, Roland Company incurs the following direct labor costs: January $40,000, February $30,000, and March $50,000. For each month, prepare the entry to assign overhead to production using a predetermined rate of 80% of direct labor c
> Marquis Company estimates that annual manufacturing overhead costs will be $900,000. Estimated annual operating activity bases are direct labor cost $500,000, direct labor hours 50,000, and machine hours 100,000. Compute the predetermined overhead rate f
> Data pertaining to job cost sheets for Knox Company are given in BE15-3 and BE15-4. Prepare the job cost sheets for each of the three jobs. (Note: You may omit the column for Manufacturing Overhead.) Data given in BE15-3: In January, Knox Company requis
> Factory labor data for Knox Company is given in BE15-2. During January, time tickets show that the factory labor of $6,000 was used as follows: Job 1 $2,200, Job 2 $1,600, Job 3 $1,400, and general factory use $800. Prepare a summary journal entry toreco
> In January, Knox Company requisitions raw materials for production as follows: Job 1 $900, Job 2 $1,400, Job 3 $700, and general factory use $600. Prepare a summary journal entry to record raw materials used.
> You are the management accountant for Williams Company. Your company does custom carpentry work and uses a job order cost system. Williams sends detailed job cost sheets to its customers, along with an invoice. The job cost sheets show the date materials
> During January, its first month of operations, Knox Company accumulated the following manufacturing costs: raw materials $4,000 on account, factory labor $6,000 of which $5,200 relates to factory wages payable and $800 relates to payroll taxes payable, a
> Determine the missing amounts. Unit Selling Unit Variable Contribution Contribution Margin per Unit (a) $300 $330 Price Costs Margin Ratio $180 (c) (f) 1. $250 $500 (e) (b) (d) 2. 3. 30%
> Eye Spy Corporation manufactures and sells three different types of binoculars. They are referred to as Good, Better, and Best binoculars. Grinding and polishing time is limited. More time is required to grind and polish the lenses used in the Better and
> Snow Cap Springs produces and sells water filtration systems for homeowners. Information regarding its three models is shown below. The company’s total fixed costs to produce the filtration systems are $165,480. (a) Determine the sale
> Presto Company makes radios that sell for $30 each. For the coming year, management expects fixed costs to total $220,000 and variable costs to be $18 per unit. (a) Compute the break-even point in dollars using the contribution margin (CM) ratio. (b) Com
> Flynn Industries has three activity cost pools and two products. It expects to produce 3,000 units of Product BC113 and 1,500 of Product AD908. Having identified its activity cost pools and the cost drivers for each pool, Flynn accumulated the following
> The assembly department has the following production data for the cur Materials are entered at the beginning of the process. The ending work in process units are 70% complete as to conversion costs. Compute the equivalent units of production for (a) m
> Kopa Company manufactures CH-21 through two processes: Mixing and Packaging. In July, the following costs were incurred. Units completed at a cost of $21,000 in the Mixing Department are transferred to the Packaging Department. Units completed at a cos
> In March, Kelly Company had the following unit production costs: materials $10 and conversion costs $8. On March 1, it had zero work in process. During March, Kelly transferred out 22,000 units. As of March 31, 4,000 units that were 40% complete as to co
> Many politicians, scientists, economists, and businesspeople have become concerned about the potential implications of global warming. The largest source of the emissions thought to contribute to global warming is from coal-fired power plants. The cost o
> During the current month, Reyes Corporation completed Job 310 and Job 312. Job 310 cost $60,000 and Job 312 cost $50,000. Job 312 was sold on account for $90,000. Journalize the entries for the completion of the two jobs and the sale of Job 312.
> Milner Company is working on two job orders. The job cost sheets showthe following. Prepare the three summary entries to record the assignment of costs to Work in Process from the data on the job cost sheets. Job 201 Job 202 Direct materials $7,200
> During the current month, Tomlin Company incurs the following manufacturing costs. (a) Purchased raw materials of $16,000 on account. (b) Incurred factory labor of $40,000. Of that amount, $31,000 relates to wages payable and $9,000 relates to payroll ta
> What approach should be used to calculate the breakeven point of a company that has many products?
> Describe the features of a CVP income statement that make it more useful for management decision making than the traditional income statement that is prepared for external users.
> Distinguish between a traditional income statement and a CVP income statement.
> (a) What is the major rationale for the use of variable costing? (b) Discuss why variable costing may not be used for financial reporting purposes.
> How does the replacement of manual labor with automated equipment affect a company’s cost structure? What implications does this have for its operating leverage and break-even point?
> In the long run, will net income be higher or lower under variable costing compared to absorption costing?
> (a) Describe the philosophy and approach of just-in time processing. (b) Identify the major elements of JIT processing.
> Ger Corporation manufactures two products with the following characteristics. If Ger’s machine hours are limited to 2,000 per month, determine which product it should produce. Contribution Margin Machine Hours per Unit $42 $35 Req
> How does a company decide whether to use a job order or a process cost system?
> What is the relevance of the classification of levels of activity to ABC?
> In what ways is the application of ABC to service industries the same as its application to manufacturing companies?
> Matt Litkee is confused about under- and overapplied manufacturing overhead. Define the terms for Matt, and indicate the balance in the manufacturing overhead account applicable to each term.
> Under what conditions is ABC generally the superior overhead costing system?
> How can the agreement of Work in Process Inventory and job cost sheets be verified?
> Peggy Turnbull asks your help in constructing a CVP graph. Explain to Peggy (a) how the break-even point is plotted, and (b) how the level of activity and dollar sales at the break-even point are determined.
> What is the theory of constraints? Provide some examples of possible constraints for a manufacturer.
> Explain the purpose and use of a “materials requisition slip” as used in a job order cost system.
> Adam Antal is confused. He does not understand why rent on his apartment is a fixed cost and rent on a Hertz rental truck is a mixed cost. Explain the difference to Adam.
> Faune Furniture Co. consists of two divisions, Bedroom Division and Dining Room Division. The results of operations for the most recent quarter are: (a) Determine the company’s sales mix. (b) Determine the company’s
> Huegel Hollow Resort has ordered 20 rotomolded kayaks from Current Designs. Each kayak will be formed in the rotomolded oven, cooled, and then the excess plastic trimmed away. Then, the hatches, seat, ropes, and bungees will be attached to the kayak. Dav
> J. P. Alexander claims that the relevant range concept is important only for variable costs. (a) Explain the relevant range concept. (b) Do you agree with J. P.’s claim? Explain.
> John Harbeck is confused about computing physical units. Explain to John how physical units to be accounted for and physical units accounted for are determined.
> Explain the preparation and use of a value-added/ non–value-added activity flowchart in an ABC system.
> What steps are involved in developing an activity based costing system?
> (a) What source documents are used in assigning (1) materials and (2) labor to production in a process cost system? (b) What criterion and basis are commonly used in allocating overhead to processes?
> (a) Scott Winter asks your help in understanding the term “activity index.” Explain the meaning and importance of this term for Scott. (b) State the two ways that variable costs may be defined.
> What has happened in recent industrial history to reduce the usefulness of direct labor as the primary basis for allocating overhead to products?
> What type of industry is likely to use a job order cost system? Give some examples.
> (a) Distinguish between the two types of cost accounting systems. (b) Can a company use both types of cost accounting systems?
> (a) Mary Barett is not sure about the difference between cost accounting and a cost accounting system. Explain the difference to Mary. (b) What is an important feature of a cost accounting system?
> Presented on the next page are variable costing income statements for Logan Company and Morgan Company. They are in the same industry, with the same net incomes, but different cost structures. Compute the break-even point in dollars for each company an
> Electricoil is a division of Meier Products Corporation. The division manufactures and sells an electric coil used in a wide variety of applications. During the coming year, it expects to sell 200,000 units for $9 per unit. Mark Barnes is the division ma
> FAB produces fabrics that are used for clothing and other applications. In 2013, the first year of operations, FAB produced 500,000 yards of fabric and sold 400,000 yards. In 2014, the production and sales results were exactly reversed. In each year, sel
> Peaches and Cream Corporation manufactures cosmetic products that are sold through a network of sales agents. The agents are paid a commission of 16.25% of sales. The income statement for the year ending December 31, 2014, is shown below. The company i
> The following variable costing income statements are available for Lyte Company and Darke Company. Instructions: (a) Compute the break-even point in dollars and the margin of safety ratio for each company. (b) Compute the degree of operating leverage f
> The Eatery is a restaurant in DeKalb, Illinois. It specializes in deluxe sandwiches in a moderate price range. Michael Raye, the manager of The Eatery, has determined that during the last 2 years the sales mix and contribution margin ratio of its offerin
> Keppel Corporation manufactures and sells three different models of exterior doors. Although the doors vary in terms of quality and features, all are good sellers. Keppel is currently operating at full capacity with limited machine time. Sales and produc
> Huber Corporation has collected the following information after its first year of sales. Sales were $1,000,000 on 40,000 units; selling expenses $200,000 (30% variable and 70% fixed); direct materials $327,000; direct labor $190,000; administrative expen
> McCure Corporation had a bad year in 2013, operating at a loss for the first time in its history. The company’s income statement showed the following results from selling 200,000 units of product: net sales $2,400,000; total costs and e
> Mega Electronix carries no inventories. Its product is manufactured only when a customer’s order is received. It is then shipped immediately after it is made. For its fiscal year ended October 31, 2014, Mega’s break-even point was $2.4 million. On sales
> Isaac Corporation has collected the following information after its first year of sales. Sales were $1,800,000 on 100,000 units; selling expenses $400,000 (30% variable and 70% fixed); direct materials $456,000; direct labor $250,000; administrative expe
> Production costs chargeable to the Finishing Department in May at Kim Company are materials $8,000, labor $20,000, overhead $18,000, and transferred-in costs $67,000. Equivalent units of production are materials 20,000 and conversion costs 19,000. Kim us

