Question: The following reaction was attempted during the
The following reaction was attempted during the total synthesis of crispine A, a cytotoxic alkaloid isolated from a Mongolian thistle. Propose a plausible mechanism for the formation of compound 2 from amine 1.
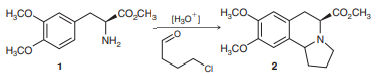
Transcribed Image Text:
H,CO. co.CH3 (H30") H,CO. co,CH, H;Co NH2 H,CO N. 1 2
> Identify how you would make hexylamine from each of the following compounds: a. 1-Bromohexane b. 1-Bromopentane c. Hexanoic acid d. 1-Cyanopentane
> Identify how you would make each of the following compounds from 1-hexanol: a. Hexylamine b. Heptylamine c. Pentylamine
> Draw the structure of the major product obtained when aniline is treated with each of the following reagents: a. Excess Br2 b. PhCH2COCl, py c. Excess methyl iodide d. NaNO2 and HCl followed by H3PO2 e. NaNO2 and HCl followed by CuCN
> Each pair of compounds below will undergo an acid-base reaction. In each case, identify the acid, identify the base, draw curved arrows that show the transfer of a proton, and draw the products. HO. (a) (b)
> Draw all tertiary amines with the molecular formula C5H13N and provide a name for each isomer. Are any of these compounds chiral?
> The isomerization in the previous problem can also occur in basic conditions. Draw a mechanism for the transformation in the presence of catalytic hydroxide.
> For each pair of compounds, identify which compound is more acidic and explain your choice. a. 2,4-Dimethyl-3,5-heptanedione or 4,4-dimethyl-3,5-heptanedione b. 1,2-Cyclopentanedione or 1,3-cyclopentanedione c. Acetophenone or benzaldehyde
> Draw all constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C4H11N and provide a name for each isomer.
> Assign a name for each of the following compounds: NH, (b) -NH2 (c) (a) NH, .N. (d) Br (e) (f)
> Identify the number of chiral centers in each of the following structures: 'N' (a) (b)
> Consider the structure of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), a potent hallucinogen containing three nitrogen atoms. One of these three nitrogen atoms is significantly more basic than the other two. Identify the most basic nitrogen atom in LSD and explain
> Draw the structure of each of the following compounds: a. N-Ethyl-N-isopropylaniline b. N,N-Dimethylcyclopropylamine c. (2R,3S)-3-(N,N-Dimethylamino)-2-pentanamine d. Benzylamine
> For each pair of compounds, identify the stronger base. vS. vs. N. 'N' (a) 'N. (b)
> Cinchocaine is a long-acting local anesthetic used in spinal anesthesia. Identify the most basic nitrogen atom in cinchocaine. N. N. Cinchocaine I-Z
> Clomipramine is marketed under the trade name Anafranil and is used in the treatment of obsessive compulsive disorder. a. Identify which nitrogen atom in clomipramine is more basic and justify your choice. b. Draw the form of clomipramine that is expec
> Spermine is a naturally occurring compound that contributes to the characteristic odor of semen. Classify each nitrogen atom in spermine as primary, secondary, or tertiary NH2 H,N H Spermine I-Z Z-
> How would you use NMR spectroscopy to distinguish between the following compounds? 'N' 'N (a) (b) N.
> Propose a plausible mechanism for the following isomerization and explain the driving force behind this reaction. In other words, explain why the equilibrium favors the product. он H30 ÓH
> How would you use IR spectroscopy to distinguish between the following compounds? 'N' (a) (b)
> Predict the product obtained when pyrrole is treated with a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid at 0ºC.
> Pyridine undergoes electrophilic aromatic substitution at the C3 position. Justify this regiochemical outcome by drawing resonance structures of the intermediate produced from attack at C2, at C3, and at C4.
> As part of the effort to create new anti-cancer drugs that selectively target cancer cells, scientists are developing light-activated compounds such as trans-PST-1, which can be prepared from compound A, shown below. Upon irradiation with blue light, tra
> Identify the reactants you would use to prepare each of the following azo dyes via an azo coupling reaction: -NO2 -NH2 но HO3S (a) so,H (b) (c)
> Propose an efficient synthesis for each of the following transformations: NO2 Br Br NH2 CN (b) OH OH (c) (d) Br -F
> Predict the major product obtained when each of the following amines is treated with a mixture of NaNO2 and HCl: NH2 y-H NH (a) (b) (c) (d)
> Phencyclidine (PCP) was originally developed as an anesthetic for animals, but it has since become an illegal street drug because it is a powerful hallucinogen. Treatment of PCP with excess methyl iodide followed by aqueous silver oxide gives the followi
> Draw the major product that is expected when each of the following compounds is treated with excess methyl iodide followed by aqueous silver oxide and heat: a. Cyclohexylamine b. (R)-3-Methyl-2-butanamine c. N,N-Dimethyl-1-phenylpropan-2-amine
> Using acetic acid as your only source of carbon atoms, show how you could make N-ethyl acetamide. OH Zーエ
> Identify all of the different β-hydroxyaldehydes that are formed when a mixture of benzaldehyde and hexanal is treated with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
> Starting with nitrobenzene and using any other reagents of your choice, outline a synthesis of para-chloroaniline.
> When aniline is treated with a mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid, the expected nitration product (para-nitroaniline) is obtained in poor yield. Instead, the major product from nitration is meta-nitroaniline. Apparently, the amino group is protonat
> Neuroscience research has led chemists to explore compound 3 below and other related structures as potential drug candidates to treat obesity and depression. As part of this effort, compound 3 was prepared from compound 1. Show reagents that might be use
> Starting with sodium azide as your source of nitrogen and using any other reagents of your choice, show how you would prepare each of the compounds in Problem 22.16.
> Starting with potassium phthalimide as your source of nitrogen and using any other reagents of your choice, show how you would prepare each of the compounds in Problem 22.16.
> Using ammonia as your source of nitrogen, show the reagents you would use to prepare each of the following amines: 'N. H -NH2 -N (a) (b) (c) N. 'N' (d) (e) (f)
> Methamphetamine is used in some formulations for the treatment of attention deficit disorder and can be prepared by reductive amination using phenylacetone and methylamine. Draw the structure of methamphetamine.
> Show two different ways of preparing each of the following compounds via a reductive amination: H (a) (b) - (c) (d) (e)
> Fluorescent compounds emit light when excited, and some fluorescent compounds have been used for the detection, or sensing, of small molecules, metals, and changes in pH, among other things. Dapoxylsulfonic acid (DSA) is a fluorescent molecule that respo
> Using a Gabriel synthesis, show how you would make each of the following compounds: NH2 NH2 NH2 (a) (b) (c) (d) NH2
> Draw all four β-hydroxyaldehydes that are formed when a mixture of acetaldehyde and pentanal is treated with aqueous sodium hydroxide.
> The following compound cannot be prepared from an alkyl halide or a carboxylic acid using the methods described in this section. Explain why each synthesis cannot be performed. NH2
> Draw the structure of an alkyl halide or carboxylic acid that might serve as a precursor in the preparation of each of the following amines: NH2 NH2 (a) NH2 (b) (c)
> For each of the following compounds, draw the form that predominates at physiological pH: H CI CHs Sertraline (Zoloft) An antidepressant (a) NH2 OH NH2 Amantadine Used in the treatment Phenylpropanolamine (b) of Parkinson's disease (c) A nasal decong
> When (E)-4-amino-3-buten-2-one is treated with molecular hydrogen in the presence of platinum, the resulting amine is more basic than the reactant. Draw the reactant and the product and explain why the product is a stronger base than the reactant.
> Rank the following compounds in terms of increasing basicity: N. Br
> For each of the following pairs of compounds, identify which compound is the stronger base: N- (a) (b) (c) (d)
> Identify whether each of the following compounds is expected to be water soluble: -NH, -NH, -NH2 H,N- (c) (a) (b)
> Rank this group of compounds in order of increasing boiling point. H NH2
> Propose a plausible mechanism for the following transformation and justify the stereochemical outcome: R. R. CO,Me Heat "CO,Me MEOH Meo" OH он
> The racemization process described in the previous problem also occurs in acidic conditions. Draw a mechanism for the racemization process in aqueous acid.
> Enaminoesters (also called vinylogous carbamates), such as compound 4 below, can serve as building blocks in the synthesis of nitrogen heterocycles. Compound 4 was prepared from compound 1 in a one-pot method (the entire transformation took place in one
> Piperazinone derivatives, such as compound 4, are being investigated for their potential use in the treatment of migraines as well as a variety of other diseases, including hypertension and sepsis. The following two-step synthetic procedure was developed
> Dogs are used by police and emergency personnel to detect a variety of things, including drugs, explosives, and humans (both as missing persons and as deceased bodies). Canines that are trained to detect human remains (aka, cadaver dogs) can be trained u
> Draw the structure of each of the following compounds: a. Cyclohexylmethylamine b. Tricyclobutylamine c. 2,4-Diethylaniline d. (1R,2S)-2-Methylcyclohexanamine e. ortho-Aminobenzaldehyde
> Assign a name for each of the following compounds: NH2 (a) NH2 (b) (c) NH2 но, NH2 (d) (e) (f)
> When the following compound is treated with concentrated HCl at 100ºC for several hours, hydrolysis occurs, producing one of the 20 naturally occurring amino acids. Identify which one. H,N Ine
> We saw in Section 25.6 that DCC can be used to form a peptide bond. We explored the mechanism, and we saw that DCC activates the COOH group so that it readily undergoes nucleophilic acyl substitution. An alternative method for activating a COOH group inv
> Proton NMR spectroscopy provides evidence for the restricted rotation of a peptide bond. For example, N,N dimethylformamide exhibits three signals in its proton NMR spectrum at room temperature. Two of those signals are observed upfield, at 2.9 and 3.0
> Compound A is a D-aldopentose. When treated with sodium borohydride, compound A is converted into an alditol that exhibits three signals in its 13C NMR spectrum. Compound A undergoes a Kiliani–Fischer synthesis to produce two aldohexoses, compounds B and
> Compound X is a d-aldohexose that can adopt a β-pyranose form with only one axial substituent. Compound X undergoes a Wohl degradation to produce an aldopentose, which is converted into an optically active alditol when treated with sodium borohydride. Fr
> When optically active (S)-2-methylcyclopentanone is treated with aqueous base, the compound loses its optical activity. Explain this observation and draw a mechanism that shows how racemization occurs.
> A carboxylic acid with the molecular formula C5H10O2 is treated with thionyl chloride to give compound A. Compound A has only one signal in its 1 H NMR spectrum. Draw the structure of the product that is formed when compound A is treated with excess ammo
> Draw a plausible mechanism for the following transformation: te H,0 * но
> Using acetonitrile (CH3CN) and CO2 as your only sources of carbon atoms, identify how you could prepare each of the following compounds: OH OH он OH (a) (b) (c) (d)
> Starting with benzene and using any other reagents of your choice, devise a synthesis for acetaminophen: но Acetaminophen (Tylenol) エーZ
> Propose an efficient synthesis for each of the following transformations: OH (a) `NH (b) (c) S. (d) OMe H. COOH (e) OH
> meta-Hydroxybenzoyl chloride is not a stable compound, and it polymerizes upon preparation. Show a mechanism for the polymerization of this hypothetical compound.
> Identify what monomers you would use to produce the following polymer: Zーエ Zーエ Zーエ Zーエ
> Draw the structure of the polymer produced when the following two monomers are allowed to react with each other: OH CI но
> Dexon (below) is a polyester that is spun into fibers and used for surgical stitches that dissolve over time, eliminating the need for a follow-up procedure to remove the stitches. The ester groups are slowly hydrolyzed by enzymes present in the body, an
> Pivampicillin is a penicillin prodrug: The prodrug ester group (in red) enables a more rapid delivery of the prodrug to the bloodstream, where the ester group is subsequently hydrolyzed by enzymes, releasing the active drug. a. Draw the structure of th
> When 2-hepten-4-one is treated with LDA, a proton is removed from one of the gamma (γ) positions. Identify which γ position is deprotonated and explain why the γ proton is the most acidic proton in the compound.
> Draw the structure of the diol that is produced when the following carbonate is heated under aqueous acidic conditions: H20 ? O: Heat
> Ethyl trichloroacetate is significantly more reactive toward hydrolysis than ethyl acetate. Explain this observation.
> Draw a plausible mechanism for each of the following transformations: -он Pyridine (a) 1) NaOH O. OH (Ь) 21 H,0 HO но OH 1) NAOH 2) H,0* HO (c) CI H,N-NH, Excess pyridine .CI H. (d) 1) Excess EtMgBr 2) H,0 OH (e)
> Aspartame (below) is an artificial sweetener used in diet soft drinks and is marketed under many trade names, including Equal and Nutrasweet. In the body, aspartame is hydrolyzed to produce methanol, aspartic acid, and phenylalanine. The production of ph
> Benzyl acetate is a pleasant-smelling ester found in the essential oil of jasmine flowers and is used in many perfume formulations. Starting with benzene and using any other reagents of your choice, design an efficient synthesis for benzyl acetate. B
> Fluphenazine is an antipsychotic drug that is administered as an ester prodrug via intramuscular injection: The hydrophobic tail of the ester is deliberately designed to enable a slow release of the prodrug into the bloodstream, where the prodrug is rap
> Phosgene is highly toxic and was used as a chemical weapon in World War I. It is also a synthetic precursor used in the production of many plastics. a. When vapors of phosgene are inhaled, the compound rapidly reacts with any nucleophilic sites present
> When acetic acid is treated with isotopically labeled water (18O, shown in red) in the presence of a catalytic amount of acid, it is observed that the isotopic label becomes incorporated at both possible positions of acetic acid. Draw a mechanism that ac
> Predict the products that are formed when diphenyl carbonate is treated with excess methyl magnesium bromide. 1) Excess MeMgBr 2) H0"
> DEET is the active ingredient in many insect repellants, such as OFFTM. Starting with meta-bromotoluene and using any other reagents of your choice, devise an efficient synthesis for DEET. Br ?. N,N-Diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET) m-Bromotoluene
> Draw the enolate that is formed when each of the following compounds is treated with LDA: (a) H. (b) OEt (c)
> Identify reagents that can be used to accomplish each of the following transformations: H. OR *NH, | -
> When methyl benzoate bears a substituent at the para position, the rate of hydrolysis of the ester group depends on the nature of the substituent at the para position. Apparently, a methoxy substituent renders the ester less reactive, while a nitro subst
> Propose an efficient synthesis for each of the following transformations: Br (a) OH (b) Br (c) Br (d)
> Starting with benzene and using any other reagents of your choice, show how you would prepare each of the following compounds: OH of 'N. (а) (b) он (c) (d) エーZ
> Identify the reagents you would use to convert 1-bromopentane into each of the following compounds: a. Pentanoic acid b. Hexanoic acid c. Pentanoyl chloride d. Hexanamide e. Pentanamide f. Ethyl hexanoate
> Determine the structures of compounds A through F: но. Na,Cr,0, OH *osH xs NH, B A 1) LIAI(OR);H 2) H20 [H*] EIOH 오
> Identify the carboxylic acid and the alcohol that are necessary in order to make each of the following compounds via a Fischer esterification: (a) (Б)
> Predict the major product(s) for each of the following reactions: 1) xs LIAIH OH 2) H,0 ? 1) SOCI, 2) xs (CH),NH ? Он (b) ? NH, (c) 1) H,0 OMe 2) CH,COCI, pyridine ? (d) OMe 1) DIBAH 2) H,0 LOH ? (f) Pyridine (h)
> Predict the major product(s) formed when cyclopentanecarboxylic acid is treated with each of the following reagents: a. SOCl2 b. LiAlH4 (excess), followed by H2O c. NaOH d. [H+], EtOH
> Predict the major product(s) formed when hexanoyl chloride is treated with each of the following reagents: a. CH3CH2NH2 (excess) b. LiAlH4 (excess), followed by H2O c. CH3CH2OH, pyridine d. H2O, pyridine e. C6H5CO2Na f. NH3 (excess) g. Et2CuLi h.
> Ethyl acetoacetate has three enol isomers. Draw all three.
> Careful measurements reveal that para-methoxybenzoic acid is less acidic than benzoic acid, while meta-methoxybenzoic acid is more acidic than benzoic acid. Explain these observations.
> Identify the reagents you would use to convert each of the following compounds into pentanoic acid: a. 1-Pentene b. 1-Bromobutane
> Identify the reagents you would use to convert pentanoic acid into each of the following compounds: a. 1-Pentanol b. 1-Pentene c. Hexanoic acid
> Draw and name all constitutionally isomeric acid chlorides with the molecular formula C4H7ClO. Then provide a systematic name for each isomer.
> Draw the structures of eight different carboxylic acids with the molecular formula C6H12O2. Then, provide a systematic name for each compound and identify which three isomers exhibit chiral centers.
> Identify the common name for each of the following compounds: (а) (Б) OH (c) H OH (d) HO он

