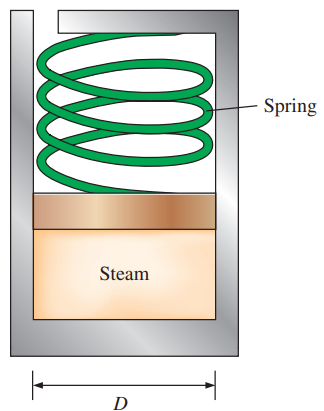
Question: The spring-loaded piston–cylinder device shown
The spring-loaded piston–cylinder device shown in Fig. P4–62 is filled with 0.5 kg of water vapor that is initially at 4 MPa and 400°C. Initially, the spring exerts no force against the piston. The spring constant in the spring force relation F = kx is k = 0.9 kN/cm and the piston diameter is D = 20 cm. The water now undergoes a process until its volume is one-half of the original volume. Calculate the final temperature and the specific enthalpy of the water.
> A piston–cylinder device contains helium gas initially at 100 kPa, 10°C, and 0.2 m3. The helium is now compressed in a polytropic process (PVn = constant) to 700 kPa and 290°C. Determine the heat loss or gain durin
> Saturated water vapor at 200°C is condensed to a saturated liquid at 50°C in a spring-loaded piston–cylinder device. Determine the heat transfer for this process in kJ/kg.
> 1 m3 of saturated liquid water at 200°C is expanded isothermally in a closed system until its quality is 80 percent. Determine the total work produced by this expansion, in kJ.
> Is the boundary work associated with constant-volume systems always zero?
> The combustion in a gasoline engine may be approximated by a constant-volume heat addition process. The cylinder contains the air–fuel mixture before combustion and the combustion gases after it, and both may be approximated as air, an
> A tank contains argon at 600°C and 200 kPa gage. The argon is cooled in a process by heat transfer to the surroundings such that the argon reaches a final equilibrium state at 300°C. Determine the final gage pressure of the argon. Assume atmospheric pres
> The gage pressure of an automobile tire is measured to be 200 kPa before a trip and 220 kPa after the trip at a location where the atmospheric pressure is 90 kPa. Assuming the volume of the tire remains constant at 0.035 m3, determine the percent increas
> Carbon dioxide gas at 3 MPa and 500 K flows steadily in a pipe at a rate of 0.4 kmol/s. Determine (a) the volume and mass flow rates and the density of carbon dioxide at this state. If CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe so that th
> A rigid tank contains an ideal gas at 300 kPa and 600 K. Now half of the gas is withdrawn from the tank and the gas is found at 100 kPa at the end of the process. Determine (a) the final temperature of the gas and (b) the final pressure if no mass was wi
> Consider the flow of air through a wind turbine whose blades sweep an area of diameter D (in m). The average air velocity through the swept area is V (in m/s). On the bases of the units of the quantities involved, show that the mass flow rate of air (in
> Complete the blank cells in the following table of properties of refrigerant-134a. In the last column, describe the condition of refrigerant-134a as compressed liquid, saturated mixture, superheated vapor, or insufficient information, and, if applicable,
> Complete the blank cells in the following table of properties of steam. In the last column, describe the condition of steam as compressed liquid, saturated mixture, superheated vapor, or insufficient information, and, if applicable, give the quality.
> What is the percentage of error involved in treating carbon dioxide at 5 MPa and 25°C as an ideal gas?
> Saturated water vapor at 400°F is heated at constant pressure until its volume has doubled. Determine the final temperature using the ideal-gas equation of state, the compressibility charts, and the steam tables.
> A 0.016773-m3 tank contains 1 kg of refrigerant-134a at 110°C. Determine the pressure of the refrigerant using (a) the ideal-gas equation, (b) the generalized compressibility chart, and (c) the refrigerant tables.
> How does a boiling process at supercritical pressures differ from the boiling process at subcritical pressures?
> Ethane in a rigid vessel is to be heated from 50 psia and 100°F until its temperature is 540°F. What is the final pressure of the ethane as predicted by the compressibility chart?
> Carbon dioxide gas enters a pipe at 3 MPa and 500 K at a rate of 2 kg/s. CO2 is cooled at constant pressure as it flows in the pipe, and the temperature of the CO2 drops to 450 K at the exit. Determine the volume flow rate and the density of carbon dioxi
> Ethylene is heated at constant pressure from 5 MPa and 20°C to 200°C. Using the compressibility chart, determine the change in the ethylene’s specific volume as a result of this heating.
> Determine the specific volume of nitrogen gas at 10 MPa and 150 K based on (a) the idea-gas equation and (b) the generalized compressibility chart. Compare these results with the experimental value of 0.002388 m3/kg, and determine the error involved in e
> What is the weight of a 1-kg substance in N, kN, kg·m/s2, kgf, lbm·ft/s2, and lbf?
> One of the most amusing things a person can experience is that in certain parts of the world, a still car in neutral can go uphill when its brakes are released. Such occurrences are even broadcast on TV. Can this really happen, or is it bad eyesight? How
> Determine the specific volume of superheated water vapor at 3.5 MPa and 450°C based on (a) the ideal-gas equation, (b) the generalized compressibility chart, and (c) the steam tables. Determine the error involved in the first two cases.
> Reconsider Prob. 4–83. Solve the problem using appropriate software. Compare the specific volume of water for the three cases at 15 MPa over the temperature range of 350 to 600°C in 25°C intervals. Plot the percent error involved in the ideal-gas approxi
> Determine the specific volume of superheated water vapor at 15 MPa and 350°C using (a) the ideal-gas equation, (b) the generalized compressibility chart, and (c) the steam tables. Also determine the error involved in the first two cases.
> Refrigerant-134a at 400 psia has a specific volume of 0.1384 ft3/lbm. Determine the temperature of the refrigerant based on (a) the ideal-gas equation, (b) the generalized compressibility chart, and (c) the refrigerant tables.
> Determine the specific volume of refrigerant-134a vapor at 0.9 MPa and 70°C based on (a) the ideal-gas equation, (b) the generalized compressibility chart, and (c) data from tables. Also, determine the error involved in the first two cases.
> What is the physical significance of the compressibility factor Z?
> A househusband is cooking beef stew for his family in a pan that is (a) uncovered, (b) covered with a light lid, and (c) covered with a heavy lid. For which case will the cooking time be the shortest? Why?
> In an informative article in a magazine it is stated that tires lose roughly 1 psi of pressure for every 10°F drop in outside temperature. Investigate whether this is a valid statement.
> A rigid tank contains 20 lbm of air at 20 psia and 70°F. More air is added to the tank until the pressure and temperature rise to 25 psia and 90°F, respectively. Determine the amount of air added to the tank.
> A rigid tank whose volume is unknown is divided into two parts by a partition. One side of the tank contains an ideal gas at 927°C. The other side is evacuated and has a volume twice the size of the part containing the gas. The partition is no
> A man goes to a traditional market to buy a steak for dinner. He finds a 12-oz steak (1 lbm = 16 oz) for $5.50. He then goes to the adjacent international market and finds a 300-g steak of identical quality for $5.20. Which steak is the better buy?
> A mass of 0.1 kg of helium fills a 0.2 m3 rigid vessel at 350 kPa. The vessel is heated until the pressure is 700 kPa. Calculate the temperature change of helium (in °C and K) as a result of this heating.
> A mass of 10 g of oxygen fill a weighted piston–cylinder device at 20 kPa and 100°C. The device is now cooled until the temperature is 0°C. Determine the change of the volume of the device during this cooling
> A 1-m3 tank containing air at 10°C and 350 kPa is connected through a valve to another tank containing 3 kg of air at 35°C and 150 kPa. Now the valve is opened, and the entire system is allowed to reach thermal equilibrium with the surroundings, which ar
> Reconsider Prob. 4–72. Using appropriate software, investigate the effect of the balloon diameter on the mass of helium contained in the balloon for the pressures of (a) 100 kPa and (b) 200 kPa. Let the diameter vary from 5 m to 15 m. Plot the mass of he
> A spherical balloon with a diameter of 9 m is filled with helium at 27°C and 200 kPa. Determine the mole number and the mass of the helium in the balloon.
> The pressure gage on a 2.5-m3 oxygen tank reads 500 kPa. Determine the amount of oxygen in the tank if the temperature is 28°C and the atmospheric pressure is 97 kPa.
> A 400-L rigid tank contains 5 kg of air at 25°C. Determine the reading on the pressure gage if the atmospheric pressure is 97 kPa.
> What is the difference between the critical point and the triple point?
> A mass of 1 lbm of argon is maintained at 200 psia and 100°F in a tank. What is the volume of the tank?
> A 100-L container is filled with 1 kg of air at a temperature of 27°C. What is the pressure in the container?
> The weight of bodies may change somewhat from one location to another as a result of the variation of the gravitational acceleration g with elevation. Accounting for this variation using the relation g = a − bz where a = 9.807 m/s2 and b = 3.32 × 10−6 s−
> What is the specific volume of oxygen at 25 psia and 80°F?
> Propane and methane are commonly used for heating in winter, and the leakage of these fuels, even for short periods, poses a fire danger for homes. Which gas leakage do you think poses a greater risk for fire? Explain.
> What is the difference between mass and molar mass? How are these two related?
> Under what conditions is the ideal-gas assumption suitable for real gases?
> A piston–cylinder device initially contains steam at 3.5 MPa, superheated by 5°C. Now, steam loses heat to the surroundings and the piston moves down, hitting a set of stops, at which point the cylinder contains saturated liq
> A piston–cylinder device initially contains 50 L of liquid water at 40°C and 200 kPa. Heat is transferred to the water at constant pressure until all liquid is vaporized. (a) What is the mass of the water? (b) What is the final temperature? (c) Determine
> A rigid tank initially contains 1.4 kg saturated liquid water at 200°C. At this state, 25 percent of the volume is occupied by water and the rest by air. Now heat is supplied to the water until the tank contains saturated vapor only. Determine (a) the vo
> Is it true that water boils at higher temperature at higher pressure? Explain.
> Water is being heated in a vertical piston–cylinder device. The piston has a mass of 40 kg and a cross-sectional area of 150 cm2. If the local atmospheric pressure is 100 kPa, determine the temperature at which the water starts boiling.
> The reactive force developed by a jet engine to push an airplane forward is called thrust, and the thrust developed by the engine of a Boeing 777 is about 85,000 lbf. Express this thrust in N and kgf.
> A piston–cylinder device initially contains 1.4 kg saturated liquid water at 200°C. Now heat is transferred to the water until the volume quadruples and the cylinder contains saturated vapor only. Determine (a) the volume of
> A piston–cylinder device contains 0.6 kg of steam at 300°C and 0.5 MPa. Steam is cooled at constant pressure until one-half of the mass condenses. (a) Show the process on a T-v diagram. (b) Find the final temperature. (c) Determine the volume change.
> 10 kg of R-134a fill a 0.7-m3 weighted piston–cylinder device at a pressure of 200 kPa. The container is now heated until the temperature is 30°C. Determine the initial temperature and final volume of the R-134a.
> One kilogram of water fills a 150-L rigid container at an initial pressure of 2 MPa. The container is then cooled to 40°C. Determine the initial temperature and the final pressure of the water.
> Reconsider Prob. 4–53E. Using appropriate software, investigate the effect of initial pressure on the quality of water at the final state. Let the pressure vary from 100 psia to 300 psia. Plot the quality against initial pressure, and discuss the results
> Superheated water vapor at 180 psia and 500°F is allowed to cool at constant volume until the temperature drops to 250°F. At the final state, determine (a) the pressure, (b) the quality, and (c) the enthalpy. Also, show the process on a T-v diagram with
> A 5-ft3 rigid tank contains a saturated mixture of refrigerant-134a at 50 psia. If the saturated liquid occupies 20 percent of the volume, determine the quality and the total mass of the refrigerant in the tank.
> Reconsider Prob. 4–50. Using appropriate software, investigate the effect of pressure on the total mass of water in the tank. Let the pressure vary from 0.1 MPa to 1 MPa. Plot the total mass of water against pressure, and discuss the re
> A piston–cylinder device contains 0.005 m3 of liquid water and 0.9 m3 of water vapor in equilibrium at 600 kPa. Heat is transferred at constant pressure until the temperature reaches 200°C. (a) What is the initial temperature
> If the pressure of a substance is increased during a boiling process, will the temperature also increase or will it remain constant? Why?
> Solve this system of three equations with three unknowns using appropriate software: x2y − z = 1 x − 3y0.5 + xz = −2 x + y − z = 2
> A rigid tank with a volume of 1.8 m3 contains 40 kg of saturated liquid–vapor mixture of water at 90°C. Now the water is slowly heated. Determine the temperature at which the liquid in the tank is completely vaporized. Also, show the process on a T-v dia
> Water is boiled in a pan covered with a poorly fitting lid at a specified location. Heat is supplied to the pan by a 2-kW resistance heater. The amount of water in the pan is observed to decrease by 1.19 kg in 30 min. If it is estimated that 75 percent o
> Repeat Prob. 4–46 for a location at 2000-m elevation where the standard atmospheric pressure is 79.5 kPa. Data from Prob. 4-46: Water is boiled at 1 atm pressure in a 25-cm-internal-diameter stainless steel pan on an electric range. If it is observed th
> Water is boiled at 1 atm pressure in a 25-cm-internal-diameter stainless steel pan on an electric range. If it is observed that the water level in the pan drops by 10 cm in 45 min, determine the rate of heat transfer to the pan.
> A person cooks a meal in a 30-cm-diameter pot that is covered with a well-fitting lid and lets the food cool to the room temperature of 20°C. The total mass of the food and the pot is 8 kg. Now the person tries to open the pan by lifting the lid up. Assu
> Saturated steam coming off the turbine of a steam power plant at 40°C condenses on the outside of a 3-cm-outer-diameter, 35-m-long tube at a rate of 70 kg/h. Determine the rate of heat transfer from the steam to the cooling water flowing through the pipe
> Water initially at 200 kPa and 300°C is contained in a piston–cylinder device fitted with stops. The water is allowed to cool at constant pressure until it exists as a saturated vapor and the piston rests on the stops. Then t
> 100 kg of R-134a at 200 kPa are contained in a piston–cylinder device whose volume is 12.322 m3. The piston is now moved until the volume is one-half its original size. This is done such that the pressure of the R-134a does not change. Determine the fina
> 10 kg of R-134a at 300 kPa fills a rigid container whose volume is 14 L. Determine the temperature and total enthalpy in the container. The container is now heated until the pressure is 600 kPa. Determine the temperature and total enthalpy when the heati
> Repeat Prob. 4–39 for a location at an elevation of 1500 m where the atmospheric pressure is 84.5 kPa and thus the boiling temperature of water is 95°C. Data from Prob. 4-39: Water is to be boiled at sea level in a 30-cm-dia
> Solve this system of three equations with three unknowns using appropriate software: 2x − y + z = 7 3x2 + 3y = z + 3 xy + 2z = 4
> What is the difference between saturated liquid and compressed liquid?
> Water is to be boiled at sea level in a 30-cm-diameter stainless steel pan placed on top of a 3-kW electric burner. If 60 percent of the heat generated by the burner is transferred to the water during boiling, determine the rate of evaporation of water.
> How much error would one expect in determining the specific enthalpy by applying the incompressible-liquid approximation to water at 3000 psia and 400°F?
> The temperature in a pressure cooker during cooking at sea level is measured to be 250°F. Determine the absolute pressure inside the cooker in psia and in atm. Would you modify your answer if the place were at a higher elevation?
> One kilogram of water vapor at 200 kPa fills the 1.1989-m3 left chamber of a partitioned system shown in Fig. P4–36. The right chamber has twice the volume of the left and is initially evacuated. Determine the pressure of the water afte
> One kilogram of R-134a fills a 0.14-m3 weighted piston–cylinder device at a temperature of 26.4°C. The container is now heated until the temperature is 100°C. Determine the final volume of the R-134a.
> Refrigerant-134a at 200 kPa and 25°C flows through a refrigeration line. Determine its specific volume.
> What is the specific volume of R-134a at 20°C and 700 kPa? What is the internal energy at that state?
> What is the specific volume of water at 5 MPa and 100°C? What would it be if the incompressible liquid approximation were used? Determine the accuracy of this approximation.
> What is the specific internal energy of water at 50 kPa and 200°C?
> Solve this system of two equations with two unknowns using appropriate software: x3 − y2 = 5.9 3xy + y = 3.5
> 10 kg of R-134a fill a 1.115-m3 rigid container at an initial temperature of –30°C. The container is then heated until the pressure is 200 kPa. Determine the final temperature and the initial pressure.
> What is the difference between saturated vapor and superheated vapor?
> Determine the vertical force applied by water on the container.
> A piston–cylinder device contains 0.85 kg of refrigerant 134a at –10°C. The piston that is free to move has a mass of 12 kg and a diameter of 25 cm. The local atmospheric pressure is 88 kPa. Now, heat is tra
> Consider a recuperative crossflow heat exchanger (both fluids unmixed) used in a gas turbine system that carries the exhaust gases at a flow rate of 7.5 kg/s and a temperature of 500°C. The air initially at 30°C and flowing at a rat
> Oil in an engine is being cooled by air in a crossflow heat exchanger, where both fluids are unmixed. Oil (cph = 2047 J/kg⋅K) flowing with a flow rate of 0.026 kg/s enters the heat exchanger at 75°C, while air (cpc = 1007J/kg
> Cold water (cp = 4.18 kJ/kg⋅K) enters a crossflow heat exchanger at 14°C at a rate of 0.35 kg/s where it is heated by hot air (cp = 1.0 kJ/kg⋅K) that enters the heat exchanger at 65°C at a rate of
> A crossflow air-to-water heat exchanger with an effectiveness of 0.65 is used to heat water (cp = 4180 J/kg⋅K) with hot air (cp = 1010 J/kg⋅K). Water enters the heat exchanger at 20°C at a rate of 4 kg/s, while air enters at 100°C at a rate of 9 kg/s. If
> A crossflow heat exchanger with both fluids unmixed has an overall heat transfer coefficient of 200 W/m2⋅K and a heat transfer surface area of 400 m2. The hot fluid has a heat capacity of 40,000 W/K, while the cold fluid has a heat capacity of 80,000 W/K
> Air (cp = 1005 J/kg⋅K) enters a crossflow heat exchanger at 20°C at a rate of 3 kg/s, where it is heated by a hot water stream (cp = 4190 J/kg⋅K) that enters the heat exchanger at 70°C at a rate of 1 kg/s. Determine the maximum heat transfer rate and the
> In a one-shell and eight-tube-pass heat exchanger, the temperature of water flowing at rate of 50,000 lbm/h is raised from 70°F to 150°F. Hot air (cp = 0.25 Btu/lbm⋅°F) that flows on the tube side enters the heat exchanger at 600°F and exits at 300°F. If
> Cold water (cp = 4180 J/kg⋅K) enters the tubes of a heat exchanger with two shell passes and 23 tube passes at 14°C at a rate of 3 kg/s, while hot oil (cp = 2200 J/kg⋅K) enters the shell at 200°C at the same mass flow rate. The overall heat transfer coef
> A shell-and-tube heat exchanger with two shell passes and eight tube passes is used to heat ethyl alcohol (cp = 2670 J/kg⋅K) in the tubes from 25°C to 70°C at a rate of 2.1 kg/s. The heating is to be done by water (cp = 4190 J/kg⋅K) that enters the shell

