Question: Two springs are connected in series so
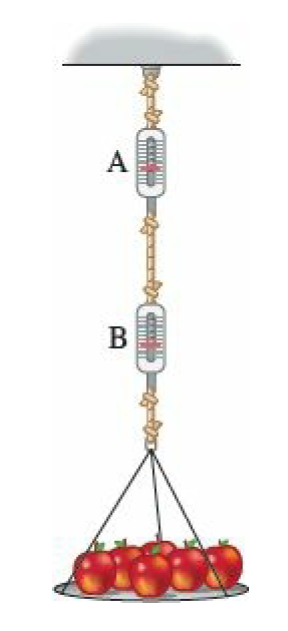
Two springs are connected in series so that spring scale A hangs from a hook on the ceiling and a second spring scale, B, hangs from the hook at the bottom of scale A. Apples weighing 120 N hang from the hook at the bottom of scale B. What are the readings on the upper scale A and the lower scale B? Ignore the weights of the ropes and scales.
> A student's head is bent over her physics book. The head weighs 50.0 N and is supported by the muscle force Fm exerted by the neck extensor muscles and by the contact force Fc exerted at the atlantooccipital joint. Given that the magnitude of Fm is 60.0
> A large wrecking ball of mass m is resting against a wall. It hangs from the end of a cable that is attached at its upper end to a crane that is just touching the wall. The cable makes an angle of θ with the wall. Ignoring friction between t
> Two canal workers pull a barge along the narrow waterway at a constant speed. One worker pulls with a force of 105 N at an angle of 28° with respect to the forward motion of the barge, and the other worker, on the opposite tow path, pulls at an angle of
> A tire swing hangs at a constant 12° angle to the vertical when a stiff breeze is blowing. In terms of the tire's weight W, (a) what is the magnitude of the horizontal force exerted on the tire by the wind? (b) What is the tension in the rope supporting
> By what percentage does the weight of an object change when it is moved from the equator at sea level, where the effective value of g is 9.784 N/kg, to the North Pole where g = 9.832 N/kg?
> The tallest spot on Earth is Mt. Everest, which is 8850 m above sea level. If the radius of Earth to sea level is 6370 km, how much does the gravitational field strength change between the sea level value at that location (9.826 N/kg) and the top of Mt.
> Spring scale A is attached to the ceiling. A 10.0 kg object is suspended from the scale. A second spring scale, B, is hanging from a hook at the bottom of the 10.0 kg object and a 4.0 kg object hangs from the second spring scale. (a) What are the readin
> A 50.0 kg crate is suspended between the floor and the ceiling using two spring scales, one attached to the ceiling and one to the floor. If the lower scale reads 120 N, what is the reading of the upper scale? Ignore the weights of the scales.
> What is the distinction between a vector and a scalar quantity? Give two examples of each.
> In the sport of curling, a player slides a 20.0 kg granite stone down a 38 m long ice rink. Draw FBDs for the stone (a) while it sits at rest on the ice; (b) while it slides down the rink; (c) during a head-on collision with an opponent's stone that was
> Four identical spring scales, A, B, C, and D are used to hang a 220.0 N sack of potatoes. (a) Assume that the scales have negligible weights and that all four scales show the same reading. What is the reading of each scale? (b) Suppose that each scale
> A box full of books rests on a wooden floor. The normal force the floor exerts on the box is 250 N. (a) You push horizontally on the box with a force of 120 N, but it refuses to budge. What can you say about the coefficient of static friction between the
> A book that weighs 10 N is at rest in six different situations. Blue arrows indicate forces exerted on the book by an object that is not shown. Rank the situations according to the magnitude of the normal force on the 10 N book due to the table, from sma
> A box sits on a horizontal wooden ramp. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the ramp is 0.30. You grab one end of the ramp and slowly lift it up, keeping the other end of the ramp on the ground. What is the angle between the ramp and t
> A binary star system consists of two stars of masses M1 and 4.0M1 a distance d apart. Is there any point where the net gravitational field due to the two stars is zero? If so, where is that point?
> Using the masses and mean distances found in Appendix B, calculate the net gravitational force on the Moon (a) during a lunar eclipse (Earth between Moon and Sun) and (b) during a solar eclipse (Moon between Earth and Sun).
> Find the ratio of Earth's gravitational force on a satellite when it is on the ground to the gravitational force exerted when the satellite is orbiting at an altitude of 320 km.
> (a) What is the magnitude of the gravitational force that Earth exerts on the Moon? (b) What is the magnitude of the gravitational force that the Moon exerts on Earth? See Appendix B for necessary information.
> An astronaut stands at a position on the Moon such that Earth is directly overhead and releases a Moon rock that was in her hand. (a) Which way will it fall? (b) What is the gravitational force exerted by the Moon on a 1.0 kg rock resting on the Moon's s
> How far above the surface of Earth does an object have to be in order for it to have the same weight as it would have on the surface of the Moon? (Ignore any effects from Earth's gravity for the object on the Moon's surface or from the Moon's gravity for
> During a balloon ascension, wearing an oxygen mask, you measure the weight of a 5.00 kg object and find that the value of the gravitational field strength at your location is 9.792 N/kg. How high above sea level, where the gravitational field strength wa
> The coefficient of static friction between a block and a horizontal floor is 0.40, while the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.15. The mass of the block is 5.0 kg. A horizontal force is applied to the block and slowly increased. (a) What is the value
> At what altitude above Earth's surface would your weight be half of what it is at Earth's surface?
> Two cars are headed toward each other in opposite directions along a narrow country road. The cars collide head-on, crumpling up the hoods of both. Describe what happens to the car bodies in terms of the principle of inertia. Does the rear end of the car
> Find and compare the weight of a 65 kg man on Earth with the weight of the same man on (a) Mars, where g = 3.7 N/kg; (b) Venus, where g = 8.9 N/kg; and (c) Earth's Moon, where g = 1.6 N/kg.
> Find the altitudes above Earth's surface where Earth's gravitational field strength would be (a) two-thirds and (b) one-third of its value at the surface. Hint: First find the radius for each situation; then recall that the altitude is the distance from
> What is the approximate magnitude of the gravitational force exerted by the Sun on the Voyager 1 spacecraft when they are separated by 17 billion kilometers? The spacecraft has a mass of 722 kg.
> (a) Calculate your weight in newton’s. (b) What is the weight in newton of 250 g of cheese? (c) Name a common object whose weight is about 1 N.
> A woman who weighs 600 N sits on a chair with her feet on the floor and her arms resting on the chair's armrests. The chair weighs 100 N. Each armrest exerts an upward force of 25 N on her arms. The seat of the chair exerts an upward force of 500 N. (a)
> A hanging plant is suspended by a cord from a hook in the ceiling. Draw an FBD for each of these: (a) the system consisting of plant, soil, and pot; (b) the cord; (c) the hook; (d) the system consisting of plant, soil, pot, cord, and1hook. Label each for
> A skydiver, who weighs 650 N, is falling at a constant speed with his parachute open. Consider the apparatus that connects the parachute to the skydiver to be part of the parachute. The parachute pulls upward on the skydiver with a force of 620 N. Consid
> A skydiver, who weighs 650 N, is falling at a constant speed with his parachute open. Consider the apparatus that connects the parachute to the skydiver to be part of the parachute. The parachute pulls upward on the skydiver with a force of 620 N. (a) Id
> A toy freight train consists of an engine and three identical cars. The train is moving to the right at constant speed along a straight, level track. Three spring scales are used to connect the cars as follows: spring scale A is located between the engin
> Tamar wants to cut down a dead poplar tree with her chain saw, but she does not want it to fall onto the nearby gazebo. Yoojin, a physicist, suggests they tie a rope taut from the poplar to an oak tree and then pull sideways on the rope as shown in the f
> While trying to decide where to hang a framed picture, you press it against the wall to keep it from falling. The picture weighs 5.0 N, and you press against the flat frame with a force of 6.0 N at an angle of 40° from the vertical. (a) What
> The coefficient of static friction between block A and a horizontal floor is 0.45, and the coefficient of static friction between block B and the floor is 0.30. The mass of each block is 2.0 kg, and they are connected together by a cord. (a) If a horizo
> When you hold up a 50 N object in your hand, with your forearm horizontal and your palm up, the upward force exerted by your biceps is much larger than 50 N—perhaps as much as 5000 N. How can that be? What other forces are acting on you
> You grab a book and give it a quick push across the top of a horizontal table. After a short push, the book slides across the table, and because of friction, comes to a stop. (a) Draw an FBD of the book while you are pushing it. (b) Draw an FBD of the
> You want to hang a 15 N picture as in the figure (a) using some very fine twine that will break with more than 12 N of tension. Can you do this? What if you have it as illustrated in Figure (b)?
> A box containing a new TV weighs 350 N. Phineas is pushing horizontally on it with a force of 150 N, but it doesn't budge. (a) Identify all the forces acting on the crate. Describe each as: (type of force) exerted on the crate by (object). (b) Identify
> A bike is hanging from a hook in a garage. Consider the following forces: (1) the force of Earth pulling down on the bike, (2) the force of the bike pulling up on Earth, and (3) the force of the hook pulling up on the bike. (a) Which two forces are equa
> A freight train consists of an engine and several identical cars on level ground. Determine whether each of these statements is correct or incorrect and explain why. (a) If the train is moving at constant speed, the engine must be pulling with a force g
> An ideal pulley is hung from the ceiling by a rope. A block of mass M is suspended by another rope that passes over the pulley and is attached to the wall. The rope fastened to the wall makes a right angle with the wall. Ignore the masses of the rope and
> A 45 N lithograph is supported by two wires. One wire makes a 25° angle with the vertical and the other makes a 15° angle with the vertical. Find the tension in each wire.
> A 2.0 kg ball tied to a string fixed to the ceiling is pulled to one side by a force F. Just before the ball is released and allowed to swing back and forth, (a) how large is the force F that is holding the ball in position and (b) what is the tension in
> A crow perches on a clothesline midway between two poles. Each end of the rope makes an angle of θ below the horizontal where it connects to the pole. If the weight of the crow is W, what is the tension in the rope? Ignore the weight of the
> The drawing shows a wire attached to two back teeth and stretched across a front tooth. The purpose of this arrangement is to apply a force F to the front tooth. (The figure has been simplified by drawing the wire as if it ran straight from the front too
> A 200.0 N sign is suspended from a horizontal strut of negligible weight. The force exerted on the strut by the wall is horizontal. Draw an FBD to show the forces acting on the strut. Find the tension T in the diagonal cable supporting the strut.
> Two boxes with different masses are tied together on a frictionless ramp surface. What is the tension in each of the cords?
> A spring scale hangs from a cord that is attached to a hook in the ceiling. A 10 kg object hangs from a second cord connected to the bottom of the scale. The weights of the cords and the scale are negligible. (a) What is the reading of the scale? (b) T
> You are pulling a suitcase through the airport at a constant speed by exerting a force of 25.0 N at angle 30.0° from the vertical. What is the force of friction acting on the suitcase?
> (a) What assumptions do you make when you call the reading of a bathroom scale your “weight”? What does the scale really tell you? (b) Under what circumstances might the reading of the scale not be equal to your weight?
> An 85 kg skier is sliding down a ski slope at a constant velocity. The slope makes an angle of 11° above the horizontal direction. Ignore air resistance. (a) What is the force of kinetic friction acting on the skier? (b) What is the coefficient of kineti
> An 80.0 N crate of apples sits at rest on a ramp that runs from the ground to the bed of a truck. The ramp is inclined at 20.0° to the ground. (a) What is the normal force exerted on the crate by the ramp? (b) The interaction partner of this normal for
> Mechanical advantage is the ratio of the force required without the use of a simple machine to that needed when using the simple machine. Compare the force to lift an object with that needed to slide the same object up a frictionless incline and show tha
> (a) In Example 2.14, if the movers stop pushing on the safe, can static friction hold the safe in place without having it slide back down? (b) If not, what minimum force needs to be applied to hold the safe in place?
> Before hanging new William Morris wallpaper in her bedroom, Brenda sanded the walls lightly to smooth out some irregularities on the surface. The sanding block weighs 2.0 N and Brenda pushes on it with a force of 3.0 N at an angle of 30.0° with respect t
> A crate of artichokes is on a ramp that is inclined 10.0° above the horizontal. Give the direction of the normal force and the friction force acting on the crate in each of these situations. (a) The crate is at rest. (b) The crate is sliding up the ramp.
> A crate of potatoes of mass 18.0 kg is on a ramp with angle of incline 30° to the horizontal. The coefficients of friction are μs = 0.75 and μk = 0.40. Find the normal force (magnitude) and the frictional force (magnitude and direction) on the crate if t
> A crate of potatoes of mass 18.0 kg is on a ramp with angle of incline 30° to the horizontal. The coefficients of friction are μs = 0.75 and μk = 0.40. Find the normal force (magnitude) and the frictional force (magnitude and direction) on the crate if t
> A crate of potatoes of mass 18.0 kg is on a ramp with angle of incline 30° to the horizontal. The coefficients of friction are μs = 0.75 and μk = 0.40. Find the normal force (magnitude) and the frictional force (magnitude and direction) on the crate if t
> A crate of potatoes of mass 18.0 kg is on a ramp with angle of incline 30° to the horizontal. The coefficients of friction are μs = 0.75 and μk = 0.40. Find the normal force (magnitude) and the frictional force (magnitude and direction) on the crate if t
> (a) Is it possible for the sum of two vectors to be smaller in magnitude than the magnitude of either vector? (b) Is it possible for the magnitude of the sum of two vectors to be larger than the sum of the magnitudes of the vectors?
> A person is standing on a bathroom scale. Which of the following is not a force exerted on the scale: a contact force due to the floor, a contact force due to the person's feet, the weight of the person, the weight of the scale?
> When sodium is bombarded with electrons accelerated through a potential difference ΔV, its x - ray spectrum contains emission peaks at 1.04 keV and 1.07 keV. Find the minimum value of ΔV required to produce both of these peaks.
> What minimum accelerating voltage is required to produce an x - ray with a wavelength of 70.0 pm?
> Calculate the minimum - wavelength x - ray that can be produced when a target is struck by an electron that has been accelerated through a potential difference of (a) 15.0 kV and (b) 1.00 x 102 kV. (c) What happens to the minimum wavelength as the potent
> The extremes of the x - ray portion of the electromagnetic spectrum range from approximately 1.0 x 10-8 m to 1.0 x 10-13 m. Find the minimum accelerating voltages required to produce wavelengths at these two extremes.
> Two light sources are used in a photoelectric experiment to determine the work function for a particular metal surface. When green light from a mercury lamp (λ = 546.1 nm) is used, a stopping potential of 0.376 V reduces the photocurrent to zero. (a) Bas
> When monochromatic light of an unknown wavelength falls on a sample of silver, a minimum potential of 2.50 V is required to stop all of the ejected photoelectrons. Determine the (a) Maximum kinetic energy and (b) Maximum speed of the ejected photoelectro
> Lithium, beryllium, and mercury have work functions of 2.30 eV, 3.90 eV, and 4.50 eV, respectively. Light with a wavelength of 4.00 x 102 nm is incident on each of these metals. (a) Which of these metals emit photoelectrons in response to the light? Why?
> The work function for platinum is 6.35 eV. (a) Convert the value of the work function from electron volts to joules. (b) Find the cutoff frequency for platinum. (c) What maximum wavelength of light incident on platinum releases photoelectrons from the pl
> The work function for zinc is 4.31 eV. (a) Find the cutoff wavelength for zinc. (b) What is the lowest frequency of light incident on zinc that releases photoelectrons from its surface? (c) If photons of energy 5.50 eV are incident on zinc, what is the m
> When light of wavelength 3.50 x 102 nm falls on a potassium surface, electrons having a maximum kinetic energy of 1.31 eV are emitted. Find (a) The work function of potassium, (b) The cutoff wavelength, and (c) The frequency corresponding to the cutoff w
> Monochromatic light falls on a screen 1.75 m from two slits separated by 2.10 mm. The first - and second - order bright fringes are separated by 0.552 mm. What is the wavelength of the light?
> The threshold of dark - adapted (scotopic) vision is 4.0 x 10-11 W/m2 at a central wavelength of 5.00 x 102 nm. If light with this intensity and wavelength enters the eye when the pupil is open to its maximum diameter of 8.5 mm, how many photons per seco
> Calculate the energy, in electron volts, of a photon whose frequency is (a) 6.20 x 102 THz, (b) 3.10 GHz, and (c) 46.0 MHz.
> Suppose a star with radius 8.50 x 108 m has a peak wavelength of 685 nm in the spectrum of its emitted radiation. (a) Find the energy of a photon with this wavelength. (b) What is the surface temperature of the star? (c) At what rate is energy emitted fr
> Earth’s average surface temperature is about 287 K. Assuming Earth radiates as a blackbody, calculate λmax for the Earth.
> The radius of our Sun is 6.96 x 108 m, and its total power output is 3.85 x 1026 W. (a) Assuming the Sun’s surface emits as a blackbody, calculate its surface temperature. (b) Using the result of part (a), find λmax for the Sun.
> The temperature of a student’s skin is 33.0°C. At what wavelength does the radiation emitted from the skin reach its peak?
> (a) Lightning produces a maximum air temperature on the order of 104 K, whereas (b) A nuclear explosion produces a temperature on the order of 107 K. Use Wien’s displacement law to find the order of magnitude of the wavelength of the thermally produced p
> Why is it impossible to simultaneously measure the position and velocity of a particle with infinite accuracy?
> Why is an electron microscope more suitable than an optical microscope for “seeing” objects of atomic size?
> If matter has a wave nature, why is this wave - like characteristic not observable in our daily experiences?
> Light of wavelength 6.0 x 102 nm falls on a double slit, and the first bright fringe of the interference pattern is observed to make an angle of 12° with the horizontal. Find the separation between the slits.
> The atoms in a crystal lie in planes separated by a few tenths of a nanometer. Can a crystal be used to produce a diffraction pattern with visible light as it does for x - rays? Explain your answer with reference to Bragg’s law.
> The brightest star in the constellation Lyra is the bluish star Vega, whereas the brightest star in Boötes is the reddish star Arcturus. How do you account for the difference in color of the two stars?
> What effect, if any, would you expect the temperature of a material to have on the ease with which electrons can be ejected from it via the photoelectric effect?
> Which has more energy, a photon of ultraviolet radiation or a photon of yellow light?
> Is light a wave or a particle? Support your answer by citing specific experimental evidence.
> A flat piece of glass is supported horizontally above the flat end of a 10.0 - cm - long metal rod that has its lower end rigidly fixed. The thin film of air between the rod and the glass is observed to be bright when illuminated by light of wavelength 5
> A diffraction pattern is produced on a screen 1.40 m from a single slit, using monochromatic light of wavelength 5.00 x 102 nm. The distance from the center of the central maximum to the first - order maximum is 3.00 mm. Calculate the slit width. Assume
> A plano - convex lens (flat on one side, convex on the other) with index of refraction n rests with its curved side (radius of curvature R) on a flat glass surface of the same index of refraction with a film of index nfilm between them. The lens is illum
> The transmitting antenna on a submarine is 5.00 m above the water when the ship surfaces. The captain wishes to transmit a message to a receiver on a 90.0 - m - tall cliff at the ocean shore. If the signal is to be completely polarized by reflection off
> Three polarizers, centered on a common axis and with their planes parallel to one another, have transmission axes oriented at angles of θ1, θ2, and θ3 from the vertical, as shown in Figure P24.59. Light of intensity
> Two radio antennas separated by d = 3.00 x 102 m, as shown in Figure P24.7, simultaneously broadcast identical signals at the same wavelength. A car travels due north along a straight line at position x = 1.00 x 103 m from the center point between the an
> Figure P24.69 shows a radio - wave transmitter and a receiver, both h = 50.0 m above the ground and d = 6.00 x 102 m apart. The receiver can receive signals directly from the transmitter and indirectly from signals that bounce off the ground. If the grou
> Many cells are transparent and colorless. Structures of great interest in biology and medicine can be practically invisible to ordinary microscopy. An interference microscope reveals a difference in refractive index as a shift in interference fringes to
> Interference effects are produced at point P on a screen as a result of direct rays from a 5.00 x 102 - nm source and reflected rays off a mirror, as shown in Figure P24.67. If the source is L = 1.00 x 102 m to the left of the screen and h = 1.00 cm abov

