Question: Use a tree diagram to represent a
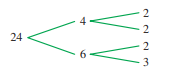
Use a tree diagram to represent a factorization of the given integer into primes, so that there are two branches at each number that is not prime. For example, the factorization 24 = 4 ∙ 6 = (2 ∙ 2) (2∙3) is represented by:
225
> The payoff table for three possible courses of action is given below. Which of the three actions will produce the largest expected value? What is it?
> A single card is drawn from a standard 52-card deck. Let D be the event that the card drawn is a diamond, and let F be the event that the card drawn is a face card. find the indicated probabilities.
> A 5-card hand is dealt from a standard 52-card deck. If the hand contains at least one diamond, you win $10; otherwise, you lose $4. What is the expected value of the game?
> A card is drawn from a standard 52-card deck. If the card is a diamond, you win $10; otherwise, you lose $4. What is the expected value of the game?
> A coin is tossed three times. Suppose you lose $3 if 3 heads appear, lose $2 if 2 heads appear, and win $3 if 0 heads appear. How much should you win or lose if 1 head appears in order for the game to be fair?
> A single die is rolled once. You lose $12 if a number divisible by 3 turns up. How much should you win if a number not divisible by 3 turns up in order for the game to be fair? Describe the process and reasoning used to arrive at your answer.
> On three rolls of a single die, you will lose $10 if a 5 turns up at least once, and you will win $7 otherwise. What is the expected value of the game?
> In Problem 21, for the game to be fair, how much should you lose if a head and a tail turn up? Data from Problem 21: Two coins are flipped. You win $2 if either 2 heads or 2 tails turn up; you lose $3 if a head and a tail turn up. What is the expected v
> Repeat Problem 19 with the same game costing $3.50 for each play. Data from Problem 19: After paying $4 to play, a single fair die is rolled, and you are paid back the number of dollars corresponding to the number of dots facing up. For example, if a 5
> Repeat Problem 17, assuming an unfair coin with the probability of a head being .55 and a tail being .45 Data from Problem 17: A fair coin is flipped. If a head turns up, you win $1. If a tail turns up, you lose $1. What is the expected value of the gam
> In a family with 2 children, excluding multiple births and assuming that a boy is as likely as a girl at each birth, what is the expected number of boys?
> You draw a single card from a standard 52-card deck. If it is an ace, you win $104. Otherwise you get nothing. What is the expected value of the game to you?
> Refer to the description of a standard deck of 52 cards and Figure 4 on page 384. An experiment consists of drawing 1 card from a standard 52-card deck , what is the probability of drawi, Figure 4: A numbered card.
> You draw and keep a single coin from a bowl that contains 120 nickels and 80 quarters. What is the expected value of the game to you?
> Find the probabilities by referring to the tree diagram below.
> write each expression as a quotient of integers, reduced to lowest terms.
> write each expression as a quotient of integers, reduced to lowest terms.
> write each expression as a quotient of integers, reduced to lowest terms.
> In a given county, records show that of the registered voters, 45% are Democrats, 35% are Republicans, and 20% are independents. In an election, 70% of the Democrats, 40% of the Republicans, and 80% of the independents voted in favor of a parks and recre
> A test for tuberculosis was given to 1,000 subjects, 8% of whom were known to have tuberculosis. For the subjects who had tuberculosis, the test indicated tuberculosis in 90% of the subjects, was inconclusive for 7%, and indicated no tuberculosis in 3%.
> In a random sample of 200 women who suspect that they are pregnant, 100 turn out to be pregnant. A new pregnancy test given to these women indicated pregnancy in 92 of the 100 pregnant women and in 12 of the 100 nonpregnant women. If a woman suspects she
> A store sells three types of flash drives: brand A, brand B, and brand C. Of the flash drives it sells, 60% are brand A, 25% are brand B, and 15% are brand C. The store has found that 20% of the brand A flash drives, 15% of the brand B flash drives, and
> A company has rated 75% of its employees as satisfactory and 25% as unsatisfactory. Personnel records indicate that 80% of the satisfactory workers had previous work experience, while only 40% of the unsatisfactory workers had any previous work experienc
> A single card is drawn from a standard 52-card deck. Let D be the event that the card drawn is a diamond, and let F be the event that the card drawn is a face card. find the indicated probabilities.
> If U1 and U2 are two mutually exclusive events whose union is the equally likely sample space S and if E is an arbitrary event in S such that P(E)(0, show that
> a player is dealt two cards from a 52-card deck. If the first card is black, the player returns it to the deck before drawing the second card. If the first card is red, the player sets it aside and then draws the second card. If the second card drawn is
> a player is dealt two cards from a 52-card deck. If the first card is black, the player returns it to the deck before drawing the second card. If the first card is red, the player sets it aside and then draws the second card. If the second card drawn is
> a player is dealt two cards from a 52-card deck. If the first card is black, the player returns it to the deck before drawing the second card. If the first card is red, the player sets it aside and then draws the second card. What is the probability of d
> A box contains 10 balls numbered 1 through 10. Two balls are drawn in succession without replacement. If the second ball drawn has the number 4 on it, what is the probability that the first ball had a smaller number on it? An even number on it?
> Two balls are drawn in succession from an urn containing m blue balls and n white balls (m ≥ 2 and n ≥ 2). Discuss the validity of each statement. If the statement is always true, explain why. If not, give a counterexamp
> Refer to the following probability tree: Suppose that c = d = e = f . Discuss the dependence or independence of events M and N.
> urn 1 contains 7 red and 3 white balls. Urn 2 contains 4 red and 5 white balls. A ball is drawn from urn 1 and placed in urn 2. Then a ball is drawn from urn 2. If the ball drawn from urn 2 is white, what is the probability that the ball drawn from urn
> An urn contains 4 red and 5 white balls. Two balls are drawn in succession without replacement. If the second ball is red, what is the probability that the first ball was red?
> one of two urns is chosen at random, with one as likely to be chosen as the other. Then a ball is withdrawn from the chosen urn. Urn 1 contains 1 white and 4 red balls, and urn 2 has 3 white and 2 red balls. If a red ball is drawn, what is the probabili
> Refer to the description of a standard deck of 52 cards and Figure 4 on page 384. An experiment consists of drawing 1 card from a standard 52-card deck , what is the probability of drawing. Figure 4: A black card.
> one of two urns is chosen at random, with one as likely to be chosen as the other. Then a ball is withdrawn from the chosen urn. Urn 1 contains 1 white and 4 red balls, and urn 2 has 3 white and 2 red balls. If a white ball is drawn, what is the probabi
> Use the probabilities in the first tree diagram to find the probability of each branch of the second tree diagram.
> Find the probabilities by referring to the tree diagram below. P(B | D)
> Find the probabilities by referring to the tree diagram below. P(D)
> Find the probabilities by referring to the tree diagram below. P(B)
> Find the probabilities by referring to the following tree diagram and using Bayes’ formula. Round answers to three decimal places. P(W|C′)
> Find the probabilities by referring to the following tree diagram and using Bayes’ formula. Round answers to three decimal places. P(U|C′)
> Find the probabilities by referring to the following tree diagram and using Bayes’ formula. Round answers to three decimal places. P(V|C′)
> Find the probabilities referring to the following Venn diagram and using Bayes’ formula (assume that the simple events in S are equally likely): P(U2 | R’)
> Find the probabilities referring to the following Venn diagram and using Bayes’ formula (assume that the simple events in S are equally likely): P(U2 | R)
> A single card is drawn from a standard 52-card deck. Let D be the event that the card drawn is a diamond, and let F be the event that the card drawn is a face card. find the indicated probabilities.
> Find the probabilities by referring to the tree diagram below.
> Find the probabilities by referring to the tree diagram below.
> Use a tree diagram to represent a factorization of the given integer into primes, so that there are two branches at each number that is not prime. For example, the factorization 24 = 4 ∙ 6 = (2 ∙ 2) (2âˆ
> Use a tree diagram to represent a factorization of the given integer into primes, so that there are two branches at each number that is not prime. For example, the factorization 24 = 4 ∙ 6 = (2 ∙ 2) (2âˆ
> Refer to the data in the following table, obtained in a study to determine the frequency and dependency of IQ ranges relative to males and females. 1,000 people were chosen at random and the following results were recorded: (A) What is the probability o
> In a study to determine frequency and dependency of color-blindness relative to females and males, 1,000 people were chosen at random, and the following results were recorded: (A) Convert this table to a probability table by dividing each entry by 1,0
> To transfer into a particular technical department, a company requires an employee to pass a screening test. A maximum of 3 attempts are allowed at 6-month intervals between trials. From past records it is found that 40% pass on the first trial; of those
> An automobile manufacturer produces 37% of its cars at plant A. If 5% of the cars manufactured at plant A have defective emission control devices, what is the probability that one of this manufacturer’s cars was manufactured at plant A and has a defectiv
> Show that P(A|B) = 1 if B is a subset of A and P(B) ∙ 0.
> A circular spinner is divided into 15 sectors of equal area: 6 red sectors, 5 blue, 3 yellow, and 1 green. , consider the experiment of spinning the spinner once. Find the probability that the spinner lands on: Purple.
> Show that P(A|B) + P(A′|B) = 1.
> Show that if A and B are events with nonzero probabilities in a sample space S, and either P(A|B) = P(A) or P(B|A) = P(B), then events A and B are independent.
> Ann and Barbara are playing a tennis match. The first player to win 2 sets wins the match. For any given set, the probability that Ann wins that set is 2/ 3. Find the probability that (A) Ann wins the match. (B) 3 sets are played. (C) The player who w
> For the experiment in Problem 71, what is the probability that no white balls are drawn? Data from problem71: A box contains 2 red, 3 white, and 4 green balls. Two balls are drawn out of the box in succession without replacement. What is the probability
> Discuss the validity of each statement. If the statement is always true, explain why. If not, give a counterexample.
> Discuss the validity of each statement. If the statement is always true, explain why. If not, give a counterexample.
> Discuss the validity of each statement. If the statement is always true, explain why. If not, give a counterexample.
> Discuss the validity of each statement. If the statement is always true, explain why. If not, give a counter example.
> Refer to the following experiment: 2 balls are drawn in succession out of a box containing 2 red and 5 white balls. Let Ri be the event that the ith ball is red, and let Wi be the event that the ith ball is white. Find the probability that both balls wer
> Refer to the following experiment: 2 balls are drawn in succession out of a box containing 2 red and 5 white balls. Let Ri be the event that the ith ball is red, and let Wi be the event that the ith ball is white. Find the probability that the second bal
> Refer to the Venn diagram below for events A and B in an equally likely sample space S. Find each of the indicated probabilities.
> that at least 2 heads turn up, and let B be the event that all the coins turn up the same. Test A and B for independence if (A) 2 coins are tossed. (B) 3 coins are tossed.
> A card is drawn at random from a standard 52-card deck. Events M and N are M = the drawn card is a diamond. N = the drawn card is even 1face cards are not valued2. (A) Find P(N| M). (B) Test M and N for independence.
> Two cards are drawn in succession from a standard 52-card deck. What is the probability that both cards are red (A) If the cards are drawn without replacement? (B) If the cards are drawn with replacement?
> In 2 throws of a fair die, what is the probability that you will get at least 5 on each throw? At least 5 on the first or second throw?
> For each pair of events (see Problem 49), discuss whether they are independent and whether they are mutually exclusive. (A) E1 and E3 (B) E3 and E4 Data from problem 49: For each pair of events, discuss whether they are independent and whether they ar
> Compute the indicated probabilities in Problems 47 and 48 by referring to the following probability tree:
> Repeat Problem 45 with the following events: E = pointer lands on an odd number F = pointer lands on a prime number Compute the indicated probabilities in Problems 47 and 48 by referring to the following probability tree: Data from problem 45: A pointer
> A fair die is rolled 5 times. (A) What is the probability of getting a 6 on the 5th roll, given that a 6 turned up on the preceding 4 rolls? (B) What is the probability that the same number turns up every time?
> Use the table below. Events A, B, and C are mutually exclusive; so are D, E, and F test each pair of events for independence. D and F
> Use the table below. Events A, B, and C are mutually exclusive; so are D, E, and F test each pair of events for independence. C AND F
> A circular spinner is divided into 15 sectors of equal area: 6 red sectors, 5 blue, 3 yellow, and 1 green. , consider the experiment of spinning the spinner once. Find the probability that the spinner lands on: Yellow,red, or green.
> Use the table below. Events A, B, and C are mutually exclusive; so are D, E, and F Test each pair of events for independence. B and E
> Use the table below. Events A, B, and C are mutually exclusive; so are D, E, and F Test each pair of events for independence. A and E
> Use the table below. Events A, B, and C are mutually exclusive; so are D, E, and F compute each probability using formula (1) on page 423 and appropriate table values. P(B|B)
> Use the table below. Events A, B, and C are mutually exclusive; so are D, E, and F compute each probability using formula (1) on page 423 and appropriate table values. P(E|A)
> Use the table below. Events A, B, and C are mutually exclusive; so are D, E, and F Compute each probability using formula (1) on page 423 and appropriate table values P(E|C)
> Use the table below. Events A, B, and C are mutually exclusive; so are D, E, and F Compute each probability using formula (1) on page 423 and appropriate table values. P(C|E)
> Use the table below. Events A, B, and C are mutually exclusive; so are D, E, and F Find each probability directly from the table.
> Use the table below. Events A, B, and C are mutually exclusive; so are D, E, and F Find each probability directly from the table. P (E)
> Find the conditional probability, in a single roll of two fair dice, that. At least one die is a six, given that the sum is odd.
> Find the conditional probability, in a single roll of two fair dice, that. The sum is odd, given that at least one die is a six.
> Refer to the Venn diagram below for events A and B in an equally likely sample space S. Find each of the indicated probabilities.
> Without using a calculator, determine which event, E or F, is more likely to occur.
> Mega Communications Inc. (MCI) is a Canadian-owned public company operating throughout North America. Its core business is communications media, including newspapers, radio, television, and cable. The company’s year-end is December 31. You, a CPA, have r
> Nova Mine Engineering is a junior Canadian company with a variety of operating subsidiaries and other undertakings that provide mine engineering and management services in Canada and in several less-developed countries. One of these subsidiaries is activ
> Pluto Technology Venture (PTV) is an unincorporated joint operation with three current joint operators. A few other prospective investors are awaiting an opportunity to invest in PTV. PTV was organized three months ago to combine the knowledge, assets, a
> On December 31, Year 7, Pepper Company, a public company, agreed to a business combination with Salt Limited, an unrelated private company. Pepper issued 82 of its common shares for all 50 of the outstanding common shares of Salt. This transaction increa
> What is non-controlling interest, and where is it reported in the consolidated balance sheet under the identifiable net assets and fair value enterprise methods?
> Access the 2017 consolidated financial statements for Loblaw Companies Limited by going to investor relations section of the company’s website. Answer the questions below. Round percentages to one decimal point and other ratios to two decimal points. For
> Access the 2017 consolidated financial statements for Barrick Gold Corporation by going to investor relations section of the company’s website. Answer the questions below. For each question, indicate where in the financial statements you found the answer
> Access the 2017 consolidated financial statements for Goldcorp Inc. by going to the investor relations section of the company’s website. Answer the questions below. For each question, indicate where in the financial statements you found the answer and/or
> When accounting for the acquisition of a non–wholly owned subsidiary, the parent can use the fair value enterprise method or the identifiable net assets method to account for the business combination. Access the 2017 consolidated financial statements for
> Access the 2017 consolidated financial statements for Bell Canada Enterprises Inc. by going to the investor relations section of the company’s website. Answer the questions below. Round percentages to one decimal point and other ratios to two decimal poi

