Question: W. W. Grainger, Inc., is a leading
W. W. Grainger, Inc., is a leading supplier of maintenance, repair, and operating (MRO) products to businesses and institutions in the United States, Canada, and Mexico, with an expanding presence in Japan, India, China, and Panama. The company works with more than 3,000 suppliers and runs an extensive Website (www .grainger.com) where Grainger offers nearly 900,000 products. The products range from industrial adhesives used in manufacturing, to hand tools, janitorial supplies, lighting equipment, and power tools. When something is needed by one of its 1.8 million customers, it is often needed quickly, so quick service and product availability are key drivers to Grainger’s success. Your assignment involves studying U.S. distribution in Grainger’s supply chain. Grainger works with over 250 suppliers in the China and Taiwan region. These suppliers produce products to Grainger’s specifications and ship to the United States using ocean freight carriers from four major ports in China and Taiwan. From these ports, product is shipped to U.S. entry ports in either Seattle, Washington, or Los Angeles, California. After passing through customs, the 20- and 40-foot containers are shipped by rail to Grainger’s central distribution center in Kansas City, Kansas. The containers are unloaded and quality is checked in Kansas City. From there, individual items are sent to regional warehouses in nine U.S. locations, a Canadian site, and Mexico.
Grainger: U.S. Distribution
In the United States, approximately 40 percent of the containers enter in Seattle, Washington, and 60 percent at the Los Angeles, California, port. Containers on arrival at the port cities are inspected by federal agents and then loaded onto rail cars for movement to the Kansas City distribution center. Variable costs for processing at the port are $5.00 per cubic meter (CBM) in both Los Angeles and Seattle. The rate for shipping the containers to Kansas City is $0.0018 per CBM per mile. In Kansas City, the containers are unloaded and processed through a quality assurance check. This costs $3.00 per CMB processed. A very small percentage of the material is actually sent back to the supplier, but errors in quantity and package size are often found that require accounting adjustments. Items are stored in the Kansas City distribution center, which serves nine warehouses in the United States. Items are also sent to warehouses in Canada and Mexico, but for the purposes of this study we focus on the United States. The nine warehouses each place orders at the distribution center that contains all the items to be replenished. Kansas City picks each item on the order, consolidates the items onto pallets, and ships the items on 53-foot trucks destined to each warehouse. Truck freight costs $0.0220 per CBM per mile. The demand forecasts for the items purchased from China/Taiwan for next year in cubic meters, as well as the shipping distances, are given in the following table.
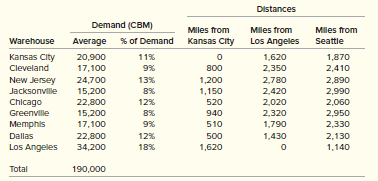
Although a high percentage of demand was from warehouses either south or east of Kansas City, the question has surfaced concerning the 18 percent that will be shipped to Kansas City and then shipped back to the Los Angeles warehouse. This double-transportation could potentially be eliminated if a new distribution center were built in Los Angeles. The idea might be to ship material arriving at the Seattle port by rail to a new Los Angeles distribution center, which would be located at the current location of the Los Angeles warehouse. It is estimated that the Los Angeles facility could be upgraded at a one-time cost of $1,500,000 and then operated for $350,000 per year. In the new Los Angeles distribution center, containers would be unloaded and processed through a quality assurance check, just as is now done in Kansas City. The variable cost for doing this would be $5.00 per CBM processed, which includes the cost to move the containers from the Los Angeles port to the distribution center. After the material is processed in Los Angeles, the amount needed to replenish the Los Angeles warehouse (approximately 18 percent) would be kept and the rest sent by rail to Kansas City. It would then be directly stocked in the Kansas City distribution center and used to replenish the warehouses. Grainger expects that very little would need to be shipped back to the Los Angeles warehouse after the new system has been operating for six months. Grainger management feels that it may be possible to make this change, but it is not sure if it would actually save any money and whether it would be a good strategic change.
Specific questions to address in your analysis:
1. Relative to the U.S. distribution network, calculate the cost associated with running the existing
system. Assume that 40 percent of the volume arrives in Seattle and 60 percent in Los Angeles and that the port processing fee for federal processing at both locations is $5.00 per CBM. Assume
that everything is transferred to the Kansas City distribution center by rail, where it is unloaded
and quality-checked. Assume that all volume is then transferred by truck to the nine existing warehouses in the United States.
2. Consider the idea of upgrading the Los Angeles warehouse to include a distribution center capable of processing all the volume coming into the United States. Assume that containers coming into Seattle to be done at all port locations) and then immediately shipped by rail in their original containers to Los Angeles. All volume would be unloaded and quality-checked in Los Angeles (the quality check cost $5.00 per CBM when done in Los Angeles). Eighteen percent of the volume would then be kept in Los Angeles for distribution through that warehouse and the rest transshipped by rail to the Kansas City warehouse. Assume the cost to transship by rail is $0.0018 per CBM per mile. The material sent to Kansas City would not need to go through the “unload and quality check process,†and would be stored directly in the Kansas City distribution center. Assume that the remaining volume would be transferred by truck to the eight remaining warehouses in the United States at a cost of $0.0220 per CBM per mile.
3. What should be done based on your analytics analysis of the U.S. distribution system? Should the new Los Angeles distribution center be added? Is there any obvious change that Grainger might make to have this option be more attractive?
4. Is this strategically something that Grainger should do? What has the company not considered that may be important?
Transcribed Image Text:
Distances Demand (CBM) Mles from Miles from Miles from % of Demand Kansas City Los Angeles Seattle Warehouse Average Kansas City 20,900 11% 1,620 1,870 Cleveland 17,100 9% 800 2,350 2,410 New Jersey 24,700 13% 1,200 2,780 2,890 Jacksonville 15,200 8% 1,150 2,420 2,990 Chicago 22,800 12% 520 2,020 2,060 Greenville 15,200 8% 940 2,320 2,950 Memphis 17,100 9% 510 1,790 2,330 Dallas 22,800 12% 500 1,430 2,130 Los Angeles 34,200 1,140 18% 1,620 Total 190,000
> Next week, Super Discount Airlines has a flight from New York to Los Angeles that will be booked to capacity. The airline knows from past history that an average of 25 customers (with a standard deviation of 15) cancel their reservation or do not show fo
> Expando, Inc. is considering the possibility of building an additional factory that would produce a new addition to its product line. The company is currently considering two options. The first is a small facility that it could build at a cost of $6 mill
> You work for Nokia in its global cell phone group. You have been made project manager for the design of a new cell phone. Your supervisors have already scoped the project, so you have a list showing the work breakdown structure, and this includes major p
> The local supermarket buys lettuce each day to ensure really fresh produce. Each morning, any lettuce that is left from the previous day is sold to a dealer that resells it to farmers who use it to feed their animals. This week, the supermarket can buy f
> The R&D department is planning to bid on a large project for the development of a new communications system for commercial planes. The accompanying table shows the activities, times, and sequences required: a. Draw the network diagram. b. What is th
> To support the manufacture of desktop computers for their customers, Dell needs to order all the parts that go into the computer, such as hard drives, motherboards and memory modules. Obviously the demand for these items is driven by the production sche
> “The nice thing about inventory models is that you can pull one off the shelf and apply it so long as your cost estimates are accurate.” Comment.
> What tool is used to ensure that all tasks in a project has the right mix of project team members assigned to it?
> Describe the benefits of using an ERP system.
> Explain how an ERP system can improve the evaluation and analysis of performance metrics.
> From the standpoint of the scheduling process, how are resource limitations treated in an MRP application and how are they treated in a synchronous manufacturing application?
> Briefly describe how supply chain planning and control is managed in an ERP system.
> Are the ERP systems discussed in the chapter appropriate for use in all firms? Explain.
> Why is the cash-to-cash cycle time such an important supply chain performance measure?
> An assembly line makes two models of trucks: a Buster and a Duster. Busters take 12 minutes each and Dusters take 8 minutes each. The daily output requirement is 24 of each per day. Develop a perfectly balanced mixed-model sequence to satisfy demand.
> Operations and supply chain ___________________________ leverages the vast amount of data in enterprise resource planning systems to make decisions related to managing resources.
> What are the three types of projects based on the amount of change involved?
> Your company assembles five different models of a motor scooter that is sold in specialty stores in the United States. The company uses the same engine for all five models. You have been given the assignment of choosing a supplier for these engines for t
> One of your Taiwanese suppliers has bid on a new line of molded plastic parts that is currently being assembled at your plant. The supplier has bid $0.10 per part, given a forecast you provided of 200,000 parts in year 1; 300,000 in year 2; and 500,000 i
> U.S. Airfilter has hired you as a supply chain consultant. The company makes air filters for residential heating and air-conditioning systems. These filters are made in a single plant located in Louisville, Kentucky, in the United States. They are distri
> What tool is used to reflect the particular needs of each stakeholder group in a performance measurement system?
> Almost certainly you have seen vending machines being serviced on your campus and elsewhere. On a predetermined schedule the vending company checks each machine and fills it up with various products. Which category of inventory model is this an exampl
> Dunstreet’s Department Store would like to develop an inventory ordering policy with a 95 percent probability of not stocking out. To illustrate your recommended procedure, use as an example the ordering policy for white percale sheets. Demand for white
> Schedule the following activities using CPM: a. Draw the network path. b. What is the critical path? c. How many weeks will it take to complete the project? d. Which activities have slack, and how much? АСTIVITY IMMEDIATE PREDECESSOR TIME (WEEKS) A
> The McDonald’s fast-food restaurant on campus sells an average of 4,000 quarter-pound hamburgers each week. Hamburger patties are resupplied twice a week, and on average the store has 350 pounds of hamburger in stock. Assume that the hamburger patties co
> The owner of a large machine shop has just finished its financial analysis from the prior fiscal year. Following is an excerpt from the final report: a. Compute the inventory turnover ratio (ITR). b. Compute the weeks of supply (WS). Net revenue $37
> Discuss the concept of “drum-buffer-rope.”
> What do you call the average total value of all items held in inventory for a firm, at cost?
> Which supply chain efficiency measure is more appropriate when the majority of inventory is held in distribution channels?
> What is the term used for the act of moving some of a company’s internal activities and decision-making processes to outside providers?
> One product that Staples sells a lot of is copy paper. According to Lee’s Uncertainty Framework, what supply chain strategy is appropriate for this product?
> The Dorton University president has asked the OSCM department to assign eight biology professors (A, B, C, D, E, F, G, and H) to eight offices (numbered 1 to 8 in the diagram) in the new biology building. The following distances and two-way flows are g
> Sony Electronics produces a wide variety of electronic products for the consumer marketplace, like laptop computers, PlayStation game consoles and tablet computers. What type of products would these be considered in Lee’s Uncertainty Framework?
> What type of plant tour is designed to determine the “leanness” of a plant in just 30 minutes?
> A manufacturing shop is designed to operate most efficiently at an output of 550 units per day. In the past month the plant produced 490 units. What was their capacity utilization rate last month?
> AlwaysRain Irrigation, Inc., would like to determine capacity requirements for the next four years. Currently two production lines are in place for making bronze and plastic sprinklers. Three types of sprinklers are available in both bronze and plastic:
> What type of chart compares the current project schedule with the original baseline schedule so that deviations from the original plan can be easily noticed?
> As a manager, which learning percentage would you prefer (other things being equal), 110 percent or 60 percent? Explain.
> List some occupations or sporting events where the ending is a dominant element in evaluating success.
> Sometimes a company may need to purchase goods or services that are unique, very complex, and/or extremely expensive. These would not be routine purchases, but there may be a number of vendors that could supply what is needed. What process would be use
> Measures of product development success can be organized in what three categories?
> What term refers to the development and management of supplier relationships to acquire goods and services in a way that helps achieve the immediate needs of a business?
> Which category of lifetime product costs is sometimes overemphasized, leading to a failure to fully recognize the total cost of ownership?
> What three main categories of costs are considered in figuring total cost of ownership?
> What term refers to the way some companies focus on what they do best and outsource other functions to key partners?
> Many bottled water manufacturers have recently worked with their suppliers to switch over to bottles using much less plastic than before, reducing the amount of plastic that needs to be transported, recycled, and/or disposed of. What sourcing practice i
> What is the term used for a company moving management of the complete cycle of material flow to an outside provider?
> “Project control should always focus on the critical path.” Comment.
> Two of the efficiency ratios mentioned in the chapter are the receivable turnover ratio and the inventory turnover ratio. While they are two completely separate measures, they are very similar in one way. What is the common thread between these two?
> What are the three primary data sources used by the MRP system?
> What motivations typically cause firms to initiate a facilities location or relocation project?
> A firm uses a serial assembly system and needs answers to the following: a. An output of 900 units per shift (7.5 hours) is desired for a new processing system. The system requires product to pass through four stations where the work content at each stat
> A study-aid desk staffed by a graduate student has been established to answer students’ questions and help in working problems in your OSCM course. The desk is staffed eight hours per day. The dean wants to know how the facility is working. Statistics sh
> What kind of layout is used in a physical fitness center?
> Here is a CPM network with activity times in weeks: a. Determine the critical path. b. How many weeks will the project take to complete? c. Suppose F could be shortened by two weeks and B by one week. How would this affect the completion date? (B(5
> An office employs several clerks who create documents and has one operator who enters the document information in a computer system. The group creates documents at a rate of 25 per hour. The operator can enter the information with an average exponentiall
> Customers enter the camera department of a store at the average rate of six per hour. The department is staffed by one employee, who takes an average of six minutes to serve each arrival. Assume this is a simple Poisson arrival, exponentially distributed
> Dave’s Auto Supply custom mixes paint for its customers. The shop performs a weekly inventory count of the main colors used for mixing paint. Determine the amount of white paint that should be ordered using the following information:
> Benny the Barber owns a one-chair shop. At barber college, they told Benny that his customers would exhibit a Poisson arrival distribution and that he would provide an exponential service distribution. His market survey data indicate that customers arriv
> A graphics reproduction firm has four units of equipment that are automatic but occasionally become inoperative because of the need for supplies, maintenance, or repair. Each unit requires service roughly twice each hour, or, more precisely, each unit of
> L Winston Martin (an allergist) has an excellent system for handling his regular patients who come in just for allergy injections. Patients arrive for an injection and fill out a name slip, which is then placed in an open slot that passes into another ro
> What it the major cost trade-off that must be made in managing waiting line situations?
> How much time on average would a server need to spend on a customer to achieve a service rate of 20 customers per hour?
> If the average time between customer arrivals is 8 minutes, what is the hourly arrival rate?
> Rent’R Cars is a multisite car rental company in the city. It is trying out a new “return the car to the location most convenient for you” policy to improve customer service. But this means that the c
> The exponential distribution is often used to model what in a queuing system?
> A local fast-food restaurant wants to analyze its drive-thru window. At this time, the only information known is the average number of customers in the system (4.00) and the average time a customer spends at the restaurant (1.176 minutes). What are the a
> What is the essential requirement for mixed-model lines to be practical?
> A toll tunnel has decided to experiment with the use of a debit card for the collection of tolls. Initially, only one lane will be used. Cars are estimated to arrive at this experimental lane at the rate of 750 per hour. It will take exactly four seconds
> A local service station is open 7 days per week, 365 days per year. Sales of 10W40 grade premium oil average 20 cans per day. Inventory holding costs are $0.50 per can per year. Ordering costs are $10 per order. Lead time is two weeks. Backorders are not
> A construction project is broken down into the following 10 activities: a. Draw the network diagram. b. Find the critical path. c. If activities 1 and 10 cannot be shortened, but activities 2 and 9 can be shortened to a minimum of one week each at a cos
> Bobby, another enterprising barber, is thinking about advertising in the local newspaper because he is idle 45 percent of the time. Currently, customers arrive, on average, every 40 minutes. What does the arrival rate need to be for Bobby to be busy 85 p
> What is the objective of assembly-line balancing? How would you deal with the situation where one worker, although trying hard, is 20 percent slower than the other 10 people on a line?
> Demand for an item is 1,000 units per year. Each order placed costs $10; the annual cost to carry items in inventory is $2 each. In what quantities should the item be ordered?
> To support National Heart Week, the Heart Association plans to install a free blood pressure testing booth in El Con Mall for the week. Previous experience indicates that, on average, 10 persons per hour request a test. Assume arrivals are Poisson distri
> Burrito King (a new fast-food franchise opening up nationwide) has successfully automated burrito production for its drive-up fast-food establishments. The Burro-Master 9000 requires a constant 45 seconds to produce a batch of burritos. It has been estim
> What is the most commonly used priority rule for setting queue discipline, likely because it is seen as most fair?
> What is the term used for the situation where a potential customer arrives at a service operation and upon seeing a long line decides to leave?
> Bindley Corporation has a one-year contract to supply motors for all washing machines produced by Rinso Ltd. Rinso manufactures the washers at four locations around the country: New York, Fort Worth, San Diego, and Minneapolis. Plans call for the followi
> Toshihiro Nakamura, manufacturing engineering section manager, is examining the prototype assembly process sheet (shown in Exhibit 8.15) for the newest subnotebook computer model. With every new model introduced, management felt that the assembly line h
> The customer order decoupling point determines the position of what in the supply chain?
> What is the first of the three simple steps in the high-level view of manufacturing?
> UA Hamburger Hamlet (UAHH) places a daily order for its high-volume items (hamburger patties, buns, milk, and so on). UAHH counts its current inventory on-hand once per day and phones in its order for delivery 24 hours later. Determine the number of hamb
> The following diagram represents a process where two components are made at stations A1 and A2 (one component is made at A1 and the other at A2). These components are then assembled at station B and moved through the rest of the process, where some addit
> This exercise is designed to support a plant tour event conducted as part of a class. This questionnaire is focused on assessing the “leanness” of a manufacturing plant. It might be useful to review the material on &a
> AudioCables, Inc., is currently manufacturing an adapter that has a variable cost of $.50 per unit and a selling price of $1.00 per unit. Fixed costs are $14,000. Current sales volume is 30,000 units. The firm can substantially improve the product qualit
> Owen Conner works part-time packaging software for a local distribution company in Indiana. The annual fixed cost is $10,000 for this process, direct labor is $3.50 per package, and material is $4.50 per package. The selling price will be $12.50 per pack
> Aldo Redondo drives his own car on company business. His employer reimburses him for such travel at the rate of 36 cents per mile. Aldo estimates that his fixed costs per year—such as taxes, insurance, and depreciation—are $2,052. The direct or variable
> Define, in a practical sense, what is meant by an exponential service time.
> A manufacturing process has a fixed cost of $150,000 per month. Each unit of product being produced contains $25 worth of material and takes $45 of labor. How many units are needed to break even if each completed unit has a value of $90?
> What’s the relationship between the design of a manufacturing process and the firm’s strategic competitive dimensions?
> What feature in project management information systems can be used to resolve overallocation of project resources?
> What does the product-process matrix tell us? How should the kitchen of a Chinese restaurant be structured?
> What is a customer order decoupling point? Why is it important?
> It is your responsibility, as the new head of the automotive section of Nichols Department Store, to ensure that reorder quantities for the various items have been correctly established. You decide to test one item and choose Michelin tires, XW size 185
> Check out the web sites of the consulting companies listed in the chapter outlines. Which ones impressed you most as a potential client and as a potential employee?
> What two basic questions must be answered by an inventory-control decision rule?
> What was the most complex project that you have been involved in? Give examples of the following as they pertain to the project: the work breakdown structure, tasks, subtasks, and work package. Were you on the critical path? Did it have a good project
> What is meant by a process? Describe its important features.
> Why is it that reducing moves, delays, and storages in a manufacturing process is a good thing? Can they be completed eliminated?

