Question: Beauville Furniture Corporation produces sofas,
Beauville Furniture Corporation produces sofas, recliners, and lounge chairs. Beauville is located in a medium-sized community in the southeastern part of the United States. It is a major employer in the community. In fact, the economic well-being of the community is tied very strongly to Beauville. Beauville operates a sawmill, a fabric plant, and a furniture plant in the same community.
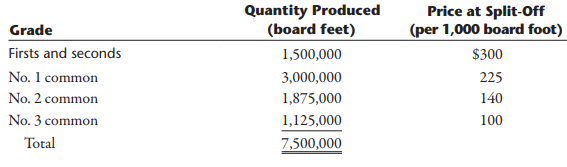
The sawmill buys logs from independent producers. The sawmill then processes the logs into four grades of lumber: firsts and seconds, No. 1 common, No. 2 common, and No. 3 common. All costs incurred in the mill are common to the four grades of lumber. All four grades of lumber are used by the furniture plant. The mill transfers everything it produces to the furniture plant, and the grades are transferred at cost. Trucks are used to move the lumber from the mill to the furniture plant. Although no outside sales exist, the mill could sell to external customers, and the selling prices of the four grades are known.
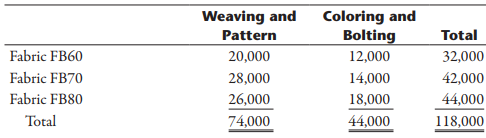
The fabric plant is responsible for producing the fabric that is used by the furniture plant. To produce three totally different fabrics (identified by fabric ID codes FB60, FB70, and FB80, respectively), the plant has three separate production operations—one for each fabric. Thus, production of all three fabrics occurs at the same time in different locations in the plant. Each fabric’s production operation has two processes: the weaving and pattern process and the coloring and bolting process. In the weaving and pattern process, yarn is used to create yards of fabric with different designs. In the next process, the fabric is dyed, cut into 25-yard sections, and wrapped around cardboard rods to form 25-yard bolts. The bolts are transported by forklift to the furniture plant’s Receiving Department. All of the output of the fabric plant is used by the furniture plant (to produce the sofas and chairs). For accounting purposes, the fabric is transferred at cost to the furniture plant.
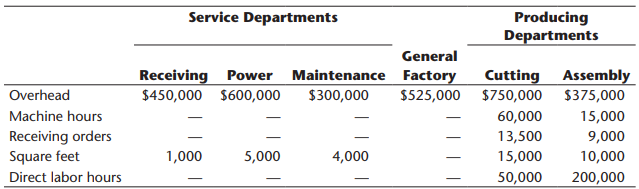
The furniture plant produces orders for customers on a special-order basis. The customers specify the quantity, style, fabric, lumber grade, and pattern. Typically, jobs are large (involving at least 500 units). The plant has two production departments: Cutting and Assembly. In the Cutting Department, the fabric and wooden frame components are sized and cut. Other components are purchased from external suppliers and are removed from stores as needed for assembly. After the fabric and wooden components are finished for the entire job, they are moved to the Assembly Department. The Assembly Department takes the individual components and assembles the sofas (or chairs).
Beauville Furniture has been in business for over two decades and has a good reputation. However, during the past five years, Beauville experienced eroding profits and declining sales. Bids were increasingly lost (even aggressive bids) on the more popular models. Yet, the company was winning bids on some of the more-difficult-to-produce items. Lance Hays, the owner and manager, was frustrated. He simply couldn’t understand how some of his competitors could sell for such low prices. On a common sofa job involving 500 units, Beauville’s bids were running $25 per unit, or $12,500 per job more than the winning bids (on average). Yet, on the more difficult items, Beauville’s bids were running about $60 per unit less than the next closest bid. Gisela Berling, vice president of finance, was assigned the task of preparing a cost analysis of the company’s product lines. Lance wanted to know if the company’s costs were excessive. Perhaps the company was being wasteful, and it was simply costing more to produce furniture than it was costing its competitors.
Gisela prepared herself by reading recent literature on cost management and product costing and attending several conferences that explored the same issues. She then reviewed the costing procedures of the company’s mill and two plants and did a preliminary assessment of their soundness. The production costs of the mill were common to all lumber grades and were assigned using the physical units method. Since the output and production costs were fairly uniform throughout the year, the mill used an actual costing system. Although Gisela had no difficulty with actual costing, she decided to explore the effects of using the sales-value-at-split-off method. Thus, cost and production data for the mill were gathered so that an analysis could be conducted. The two plants used normal costing systems. The fabric plant used process costing, and the furniture plant used job-order costing. Both plants used plantwide overhead rates based on direct labor hours. Based on her initial reviews, she concluded that the costing procedures for the fabric plant were satisfactory. Essentially, there was no evidence of product diversity. A statistical analysis revealed that about 90 percent of the variability in the plant’s overhead cost could be explained by direct labor hours. Thus, the use of a plantwide overhead rate based on direct labor hours seemed justified. What did concern her, though, was the material waste that she observed in the plant. Maybe a standard cost system would be useful for increasing the overall cost efficiency of the plant. Consequently, as part of her report to Lance, she decided to include a description of the fabric plant’s costing procedures—at least for one of the fabric types. She also decided to develop a standard cost sheet for the chosen fabric. The furniture plant, however, was a more difficult matter. Product diversity was present and could be causing some distortions in product costs. Furthermore, statistical analysis revealed that only about 40 percent of the variability in overhead cost was explained by the direct labor hours. She decided that additional analysis was needed so that a sound product costing method could be recommended. One possibility would be to increase the number of overhead rates. Thus, she decided to include departmental data so that the effect of moving to departmental rates could be assessed. Finally, she also wanted to explore the possibility of converting the sawmill and fabric plant into profit centers and changing the existing transfer pricing policy.
With the cooperation of the cost accounting manager for the mill and each plant’s controller, she gathered the following data for last year:
Sawmill:
Joint manufacturing costs: $900,000
Fabric Plant:
Budgeted overhead: $1,200,000 (50% fixed)
Practical volume (direct labor hours): 120,000 hours
Actual overhead: $1,150,000 (50% fixed)
Actual hours worked:
Departmental data on Fabric FB70 (actual costs and actual outcomes):
Proposed standard cost sheet for Fabric FB70 (for the Coloring and Bolting Department only):

Furniture Plant:
Departmental data (budgeted):
After some discussion with the furniture plant controller, Gisela decided to use machine hours to calculate the overhead rate for the Cutting Department and direct labor hours for the Assembly Department rate (the Cutting Department was more automated than the Assembly Department). As part of her report, she wanted to compare the effects of plantwide rates and departmental rates on the cost of jobs. She wanted to know if overhead costing could be the source of the pricing problems the company was experiencing.
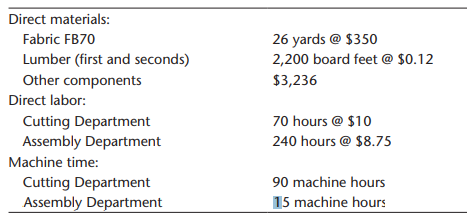
To assess the effect of the different overhead assignment procedures, Gisela decided to examine two prospective jobs. One job, Job A500, could produce 500 sofas, using a frequently requested style and Fabric FB70. Bids on this type of job were being lost more frequently to competitors. The second job, Job B75, would produce 75 specially designed recliners. This job involved a new design and was more difficult for the workers to build. It involved some special cutting requirements and an unfamiliar assembly. Recently, the company seemed to be winning more bids on jobs of this type. To compute the costs of the two jobs, Gisela assembled the following information on the two jobs:
Job A500:
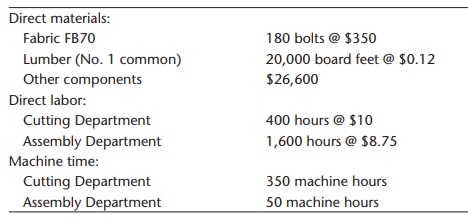
Job B75:
Required:
1.
a. Complete the following table by calculating the sawmill’s cost per board foot for each grade using both the physical units method and the sales-value-at-split-off method (round to three decimal places):
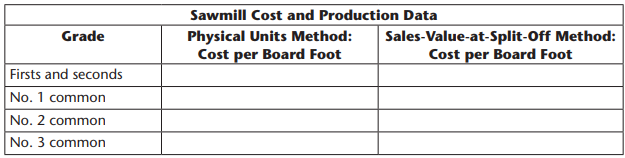
b. Given that the sawmill provides lumber at cost to the furniture plant, using the sales-value-at-split-off method (select: increases, decreases) the cost of Job A500 by $________ and (select: increases, decreases) the cost of Job B75 by $__________.
c. The physical units method, often used in the lumber industry, essentially assumes that it costs (select: the same, more) to produce each board foot (select: regardless of, depending on) the grade. Thus, (select: the same, a higher) cost of lumber would be assigned to a sofa or chair (select: regardless of, depending on) which grade is used. This approach has some drawbacks. Intuitively, the higher grades should cost (select: the same, more). Certainly, if the company was buying this input from suppliers, there would be (select: a cost difference, no cost difference) for sofas and chairs (select: regardless of, depending on) the grade of lumber purchased, because the higher grades have a (select: higher, lower) selling price.
The relative sales value method assigns (select: the same, a higher) cost to grades that have a (select: lower, higher) market value. Thus, the cost assigned to sofas and chairs (select: would differ, be the same) (select: according to, regardless of) the grade of lumber used.
d. Review the data analytic concepts and metrics found in Exhibits 2.5 and 2.6, pp. 37, 40. What are the data analytic models being considered for the Sawmill? Which of the data analytic types is being used in Part a of Requirement 1? And for Part b? Part c? Note: More than one data analytic type may apply. Which of the data analytic models in play would you recommend for assigning the joint manufacturing sawmill costs? Explain.
2. Calculate the following for the fabric plant:
a. The plantwide overhead rate
b. The amount of under- or overapplied overhead
3.
a. Using the weighted average method, complete the following information regarding the Weaving and Pattern production process:
i. Physical flow schedule (measured in yards)
ii. Equivalent units schedule (measured in yards)
iii. Unit cost
iv. Cost of goods transferred out
b. To convert the output of the Weaving and Pattern Department to the output of the Coloring and Bolting Department, yards transferred is (select: multiplied, divided) by _____.
c. Using the weighted average method, complete the following for the Coloring and Bolting Department:
i. Physical flow schedule (measured in bolts)
ii. Equivalent units schedule (measured in bolts)
iii. Unit cost
4. Currently, the three types of fabrics are produced simultaneously in different locations of the fabric plant using similar processes. Process costing methods are used to determine the unit cost of each fabric. Historically, the plant has never fully utilized any of the three processes. The maximum historical utilization of the capacity has been about 50 percent. Juana Sandoval, the fabric plant manager, is confident that the three operations can be consolidated in a way that there would be sufficient capacity to produce all three fabrics while capturing significant savings by reducing labor and overhead costs. In fact, total direct labor and variable overhead costs would be reduced by 25 percent and fixed overhead costs by 50 percent. Production of the three fabrics can be managed by using a batch production approach; however, one problem is that the yarn used for each fabric differs significantly in cost. Conversion activity is the same for each fabric regardless of the type of yarn. The cost accounting manager has assembled the following budgeted annual data for each process that reflects the expected reductions:

a. Calculate the conversion rate for each process using direct labor hours (round to whole dollars):
Weaving and Pattern Process: $______ per hour
Coloring and Bolting Process: $_______ per hour
b. Assume a batch of 400 bolts of FB70 is produced. The cost of yarn requisitioned for the batch is $40,000. The batch used 2,550 direct labor hours in Weaving and Pattern and 1,200 hours in Coloring and Bolting. In Coloring and Bolting, another $10,000 of materials (dyes) were requisitioned for the batch. Calculate the cost per bolt for the production run of 400 bolts (round to the nearest cent).
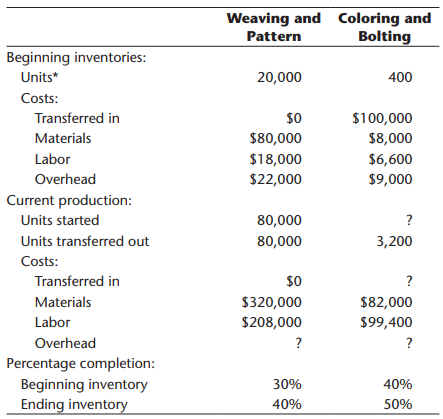
5. In the Coloring and Bolting Department, 400,000 ounces of other materials were purchased and used to produce Fabric FB70’s output of the period.
a. Using the proposed standard cost sheet for Fabric FB70, calculate the following variances for the Coloring and Bolting Department (round actual unit costs and prices to three decimal places; round variances to the nearest dollar):
i. Materials price variance (for other materials only)
ii. Materials usage variance (for other materials only)
iii. Labor rate variance
iv. Labor efficiency variance
In calculating the variances, which method did you use to compute the actual output of the period—FIFO or weighted average? Explain.
b. Prepare the journal entries for materials and labor:
i. Purchase of 400,000 ounces of other materials
ii. Usage of 400,000 ounces of other materials
iii. Assignment of direct labor costs
c. Assume that the standard hours allowed for the actual total output of the fabric plant are 115,000. Calculate the following variances (round to whole dollar):
i. Fixed overhead spending variance
ii. Fixed overhead volume variance
iii. Variable overhead spending variance
iv. Variable overhead efficiency variance
6. Suppose that the fabric plant has 500 bolts of FB70 in beginning finished goods inventory. The current-year plan is to have 1,000 bolts of FB70 in finished goods inventory at the end of the year. This fabric has an external market price of $400 per bolt. If the fabric plant is set up as a profit center, it could sell 3,000 bolts per year to outside customers and supply 2,000 bolts per year internally to Beauville’s furniture plant. If the fabric plant were designated as a profit center, the plant would transfer all goods internally at market price. Using the proposed standard cost sheet (as needed) and any other relevant data, prepare the following for Fabric FB70:
a. Sales budget
b. Production budget
c. Direct labor budget
d. Cost of goods sold budget
7. Calculate the following overhead rates for the furniture plant: (1) plantwide rate and (2) departmental rates. Use the direct method for assigning service costs to producing departments.
8. For each of the overhead rates computed in Requirement 7, calculate unit bid prices for Jobs A500 and B75. Assume that the company’s aggressive bidding policy is unit cost plus 50 percent. Did departmental overhead rates have any effect on Beauville’s winning or losing bids? What recommendation would you make? Explain. Now, adjust the costs and bids for departmental rate bids using the proposed standard costs for the Coloring and Bolting Department. Did this make a difference? What does this tell you?
9. Suppose that the fabric plant is set up as a profit center. Bolts of Fabric FB70 sell for $400 (or can be bought for $400 from outside suppliers). The fabric plant and the furniture plant both have excess capacity. Assume that Job A500 is a special order. The fabric and furniture plants have sufficient excess capacity to satisfy the demands of Job A500. What is the minimum transfer price for a bolt of FB70? If the maximum transfer price is $400, by how much do the fabric plant’s profits increase if the two profit centers negotiate a transfer price that splits the joint benefit?
> Cherise Ortega, marketing manager for Romer Company, was puzzled by the outcome of two recent bids. The company’s policy was to bid 150 percent of the full manufacturing cost. One job (labeled Job 97-28) had been turned down by a prospe
> Escuha Company produces two type of calculators: scientific and business. Both products pass through two producing departments. The business calculator is by far the most popular. The following data have been gathered for these two products: Required: 1.
> Refer to the data given in Problem 4-34 and suppose that the expected activity costs are reported as follows (all other data remain the same): Other overhead activities: The per unit overhead cost using the 14 activity-based drivers is $110.80 and $77.90
> For Reducir, Inc. Based on a recent internal study, the following information was also gathered and made available. The unit time information was gathered to allow the company to use TDABC. Cycle time was also calculated using historical production data.
> Refer to Brief Exercise 7-3. Now assume that Chekov Company uses the reciprocal method to allocate support department costs. Required: 1. Calculate the allocation ratios (rounded to four significant digits) for the four departments using the reciprocal m
> Reducir, Inc., produces two different types of hydraulic cylinders. Reducir produces a major subassembly for the cylinders in the Cutting and Welding Department. Other parts and the subassembly are then assembled in the Assembly Department. The activitie
> Refer to the data in Problem 4-32. The clinic has identified three types of patients: those with no heart disease, those with mild heart disease, and those with severe heart disease. The following additional data are provided: Required: 1. Using the acti
> The Bienestar Cardiology Clinic has two major activities: diagnostic and treatment. The two activities use four resources: nursing, medical technicians, cardiologists, and equipment. Detailed interviews have provided the work distribution matrix shown be
> Autotech Manufacturing is engaged in the production of replacement parts for automobiles. One plant specializes in the production of two parts: Part #127 and Part #234. Part #127 produced the highest volume of activity, and for many years it was the only
> Glencoe First National Bank operated for years under the assumption that profitability can be increased by increasing dollar volumes. Historically, First National’s efforts were directed toward increasing total dollars of sales and tota
> Glencoe Medical Clinic operates a cardiology care unit and a maternity care unit. Cara Abadi, the clinic’s administrator, is investigating the charges assigned to cardiology patients. Currently, all cardiology patients are charged the s
> Fisico Company produces exercise bikes. One of its plants produces two versions: a standard model and a deluxe model. The deluxe model has a wider and sturdier base and a variety of electronic gadgets to help the exerciser monitor heartbeat, calories bur
> Primera Company produces two products and uses a predetermined overhead rate to apply overhead. Primera currently applies overhead using a plantwide rate based on direct labor hours. Consideration is being given to the use of departmental overhead rates
> Kimball Company has developed the following cost formulas: Material usage: Ym = $80X; r = 0.95 Labor usage (direct): Yl = $20X; r = 0.96 Overhead activity: Yo = $350,000 + $100X; r = 0.75 Selling activity: Ys = $50,000 + $10X; r = 0.93 Where; X = Direct
> Big Mike’s, a large hardware store, has gathered data on its overhead activities and associated costs for the past 10 months. Nizam Sanjay, a member of the controller’s department, believes that overhead activities and
> Refer to Brief Exercise 7-3. Now assume that Chekov Company uses the sequential method to allocate support department costs. The support departments are ranked in order of highest cost to lowest cost. Required: 1. Calculate the allocation ratios (rounded
> St. Teresa’s Medical Center (STMC) offers a number of specialized medical services, including neuroscience, cardiology, and oncology. STMC’s strong reputation for quality medical care allowed it to branch out into othe
> Rolertyme Company manufactures roller skates. With the exception of the rollers, all parts of the skates are produced internally. Neeta Booth, president of Rolertyme, has decided to make the rollers instead of buying them from external suppliers. The com
> Thames Assurance Company sells a variety of life and health insurance products. Recently, Thames developed a long-term care policy for sale to members of university and college alumni associations. Thames estimated that the sale and service of this type
> Harriman Industries manufactures engines for the aerospace industry. It has completed manufacturing the first unit of the new ZX-9 engine design. Management believes that the 1,000 labor hours required to complete this unit are reasonable and is prepared
> The Lockit Company manufactures door knobs for residential homes and apartments. Lockit is considering the use of simple (single-driver) and multiple regression analyses to forecast annual sales because previous forecasts have been inaccurate. The new sa
> Randy Harris, controller, has been given the charge to implement an advanced cost management system. As part of this process, he needs to identify activity drivers for the activities of the firm. During the past four months, Randy has spent considerable
> Friendly Bank is attempting to determine the cost behavior of its small business lending operations. One of the major activities is the application activity. Two possible activity drivers have been mentioned: application hours (number of hours to complet
> Weber Valley Regional Hospital has collected data on all of its activities for the past 16 months. Data for cardiac nursing care follow: Required: 1. Using the high-low method, calculate the variable rate per hour and the fixed cost for the nursing care
> DeMarco Company is developing a cost formula for its packing activity. Discussion with the workers in the Packing Department has revealed that packing costs are associated with the number of customer orders, the size of the orders, and the relative fragi
> The management of Wheeler Company has decided to develop cost formulas for its major overhead activities. Wheeler uses a highly automated manufacturing process, and power costs are a significant manufacturing cost. Cost analysts have decided that power c
> Chekov Company has two support departments, Human Resources and General Factory, and two producing departments, Fabricating and Assembly. The costs of the Human Resources Department are allocated on the basis of number of employees, and the costs of Gene
> Vasani House Company produces numerous fabrics for use in automobile, airplane, and boat seats. For last year, Vasani House reported the following: Last year, Vasani House produced 6,800 units and sold 7,000 units at $250 per unit. Required: 1. Prepare a
> Mason, Durant, and Santos (MDS) is a tax services firm. The firm is located in Oklahoma City and employs 15 professionals and eight staff. The firm does tax work for small businesses and well-to-do individuals. The following data are provided for the las
> Allright Test Design Company creates, produces, and sells Internet-based CPA and CMA review courses for individual use. Davis Webber, head of human resources, is convinced that question development employees must have strong analytical and problem-solvin
> Spencer Company produced 200,000 cases of sports drinks during the past calendar year. Each case of 1-liter bottles sells for $36. Spencer had 2,500 cases of sports drinks in finished goods inventory at the beginning of the year. At the end of the year,
> The actions listed next are associated with either an activity-based operational control system or a traditional operational control system: a. Budgeted costs for the maintenance department are compared with the actual costs of the maintenance department
> The following items are associated with a traditional cost accounting information system, an activity-based cost accounting information system, or both (i.e., some elements are common to the two systems): a. Usage of direct materials b. Direct materials
> Wright Plastic Products is a small company that specialized in the production of plastic dinner plates until several years ago. Although profits for the company had been good, they have been declining in recent years because of increased competition. Man
> Brody Company makes industrial cleaning solvents. Various chemicals, detergent, and water are mixed together and then bottled in 10-gallon drums. Brody provided the following information for last year: Last year, Brody completed 100,000 units. Sales reve
> Foto-Fast Copy Shop provides a variety of photocopying and printing services. On June 5, the owner invested in some computer-aided photography equipment that enables customers to reproduce a picture or illustration, input it digitally into the computer,
> Firenza Company manufactures specialty tools to customer order. Budgeted overhead for the coming year is: Purchasing $40,000 Setups 37,500 Engineering 45,000 Other 40,000 Previously, Sanjay Bhatt, Firenza Company’s controller, had appli
> The expected costs for the Maintenance Department of Stazler, Inc., for the coming year include: Fixed costs (salaries, tools): $64,900 per year Variable costs (supplies): $1.35 per maintenance hour The Assembly and Packaging departments expect to use ma
> During May, the following transactions were completed and reported by Sylvana Company: a . Materials purchased on account, $60,100. b. Materials issued to production to fill job-order requisitions: direct materials, $51,000; indirect materials, $8,950. c
> Lawanna Davis graduated from State U with a major in accounting five years ago. She obtained a position with a well-known professional services firm upon graduation and has become one of their outstanding performers. In the course of her work, she has de
> Garcia Industries produces tool and die machinery for manufacturers. The company expanded vertically in 20x1 by acquiring one of its suppliers of alloy steel plates, Keimer Steel Company. To manage the two separate businesses, the operations of Keimer ar
> Reddy Industries is a vertically integrated firm with several divisions that operate as decentralized profit centers. Reddy’s Systems Division manufactures scientific instruments and uses the products of two of Reddy’s
> For each of the following scenarios, determine whether the specified variable would increase, decrease, or remain the same. Explain your choice. 1. If sales and average operating assets for Kayman Company for Year 2 are identical to their values in Year
> At the end of 20x1, Mejorar Company implemented a low-cost strategy to improve its competitive position. Its objective was to become the low-cost producer in its industry. A Balanced Scorecard was developed to guide the company toward this objective. To
> Carson Wellington, president of Mallory Plastics, was considering a report sent to him by Emily Sorensen, vice president of operations. The report was a summary of the progress made by an activity-based management system that was implemented three years
> CableTech Bell Corporation (CTB) operates in the telecommunications industry. CTB has two divisions: the Phone Division and the Cable Service Division. The Phone Division manufactures telephones in several plants located in the Midwest. The product lines
> Elena Chavez is founder and CEO of Willowbank, Inc., which owns and operates several assisted-living facilities. The facilities are apartment-style buildings with 25 to 30 one- or two-bedroom apartments. While each apartment has its own complete kitchen,
> Jack Aerospace Technologies (JAT) researches, designs, manufactures, delivers, and services numerous product part components to the world’s largest aircraft companies. JAT produces approximately 120 aircraft products using numerous proc
> Refer to Brief Exercise 7-10. (Round percentages to four significant digits and cost allocations to the nearest dollar.) Required: 1. Calculate the total revenue, total costs, and total gross profit the company will earn on the sale of L-Ten, Triol, and
> Each of the following scenarios requires the use of accounting information to carry out one or more of the following managerial activities: (1) planning, (2) control and evaluation, (3) continuous improvement, or (4) decision making. a. MANAGER: At t
> Bill Christensen, the production manager, was grumbling about the new quality cost system the plant controller wanted to put into place. “If we start trying to track every bit of spoiled material, we’ll never get any work done. Everybody knows when they
> If I can increase my reported profit by $2 million, the actual earnings per share will exceed analysts’ expectations, and stock prices will increase. The stock options that I am holding will become more valuable. The extra income will also make me eligib
> Consider the following actions associated with a cost management information system: a. Eliminating a non-value-added activity b. Determining how much it costs to perform a heart transplant c. Calculating the cost of inspecting components from an outside
> Hepworth Communications produces cell phones. One of the four major electronic components is produced internally. The other three components are purchased from external suppliers. The electronic components and other parts are assembled (by the Assembly D
> Classify each of the following actions as either being associated with the financial accounting information system (FS) or the cost management information system (CMS): a. Determining the total compensation of the CEO of a public company b. Issuing a qua
> Refer to the data given in Exercise 10-8. Required: 1. Compute the residual income for each of the opportunities. (Round to the nearest dollar.) 2. Compute the divisional residual income (rounded to the nearest dollar) for each of the following four alte
> At the end of Year 2, the manager of the Canned Foods Division is concerned about the division’s performance. As a result, he is considering the opportunity to invest in two independent projects. The first is juice boxes for elementary
> Allard, Inc., presented two years of data for its Frozen Foods Division and its Canned Foods Division. Required: 1. Compute the ROI and the margin and turnover ratios for each year for the Frozen Foods Division. (Round your answers to four significant di
> A company manufactures three products, L-Ten, Triol, and Pioze, from a joint process. Each production run costs $12,900. None of the products can be sold at split-off, but must be processed further. Information on one batch of the three products is as fo
> Arbus Company provided the following information: Turnover 1.4 Operating assets $120,000 Operating income 6,720 Required: 1. What is ROI? 2. What is margin?
> Fermat, Inc., has acquired two new companies, one in consumer products and the other in financial services. Fermat’s top management believes that the executives of the two newly acquired companies can be most quickly assimilated into the parent company i
> The following selected data pertain to the Argent Division for last year: Sales $1,000,000 Variable costs $ 624,000 Traceable fixed costs $ 100,000 Average invested capital $1,500,000 Imputed interest rate 15% Required: 1. How much is the residual income
> Consider the data for each of the following four independent companies: Required: 1. Calculate the missing values in the above table. (Round rates to four significant digits.) 2. Assume that the cost of capital is 9 percent for each of the four firms. Co
> A multinational corporation has a number of divisions, two of which are the North American Division and the Pacific Rim Division. Data on the two divisions are as follows: Round all rates of return to four significant digits. Required: 1. Compute residua
> Asgard Farms, Inc., has a number of divisions that produce jams and jellies, condiments, and glassware. The Glassware Division manufactures a variety of bottles that can be sold externally (to soft-drink and juice bottlers) or internally to Asgard Farm’s
> Xenold, Inc., manufactures and sells cooktops and ovens through three divisions: Home, Restaurant, and Specialty. Each division is evaluated as a profit center. Data for each division for last year are as follows (numbers in thousands): The income tax ra
> Brewster Company manufactures elderberry wine. Last year, Brewster earned operating income of $192,000 after income taxes. Capital employed equaled $2.3 million. Brewster is 45 percent equity and 55 percent 10-year bonds paying 6 percent interest. Brewst
> Janson, Inc., uses a standard costing system. The predetermined overhead rates are calculated using practical capacity. Practical capacity for a year is defined as 100,000 units requiring 20,000 standard direct labor hours. Budgeted overhead for the year
> Madison Company uses the following rule to determine whether direct labor efficiency variances ought to be investigated. A direct labor efficiency variance will be investigated anytime the amount exceeds the lesser of $12,000 or 10 percent of the standar
> The expected costs for the Maintenance Department of Stazler, Inc., for the coming year include: Fixed costs (salaries, tools): $64,900 per year Variable costs (supplies): $1.35 per maintenance hour Estimated usage by: Assembly Department 4,500 Fabricati
> Samson Company produces paper towels. The company has established the following direct materials and direct labor standards for one case of paper towels: Paper pulp (4 lbs. @ $0.30) $ 1.20 Labor (1.8 hrs. @ $18) 32.40 Total prime cost $33.60 During the f
> Redfield Company uses two types of direct labor for the manufacturing of its products: fabricating and assembly. Redfield has developed the following standard mix for direct labor, where output is measured in units. During the second week in April, Redfi
> Chypre, Inc., purchased the amount used of each direct material input on May 2 for the following actual prices: solvent mix for $5.20 per gallon, and aromatic compound for $8,010 per gallon. Required: 1. Compute and journalize the direct materials price
> Chypre, Inc., produces a cologne mist using a solvent mix (water and pure alcohol) and aromatic compounds (the scent base) that it sells to other companies for bottling and sale to consumers. Chypre developed the following standard cost sheet: On May 2,
> Refer to the data in Exercise 9-15. Required: 1. Compute overhead variances using a two-variance analysis. 2. Compute overhead variances using a three-variance analysis. 3. Illustrate how the two- and three-variance analyses are related to the four-varia
> Oerstman, Inc., uses a standard costing system and develops its overhead rates from the current annual budget. The budget is based on an expected annual output of 120,000 units requiring 480,000 direct labor hours. (Practical capacity is 500,000 hours.)
> Berner Company produces a dark chocolate candy bar. Recently, the company adopted the following standards for one bar of the candy: Direct materials (8.2 oz. @ $0.09) $0.738 Direct labor (0.07 hr. @ $18.00) 1.26 Standard prime cost $1.998 During the firs
> During the year, Vandy Company produced 280,000 components for industrial metal working machinery. Vandy’s direct materials and direct labor standards per unit are as follows: Direct materials (3.70 lbs. @ $6) $22.20 Direct labor (1.80 hr. @ $15) 28.80 R
> Quincy Farms is a producer of items made from farm products that are distributed to supermarkets. For many years, Quincy’s products have had strong regional sales on the basis of brand recognition. However, other companies have been marketing similar pro
> Suppose Gene determines that next year’s Sales Division activities include the following: Research—researching current and future conditions in the industry Shipping—arranging for shipping of mattress
> Jackson Products produces a barbeque sauce using three departments: Cooking, Mixing, and Bottling. In the Cooking Department, all materials are added at the beginning of the process. Output is measured in ounces. The production data for July are as follo
> Next year, Bob’s Bistro expects to produce 50,000 units and sell 50,500 units at a price of $20.00 each. Beginning inventory of finished goods is $13,000, and ending inventory of finished goods is expected to be $10,000. Total selling expense is projecte
> Olympus, Inc., manufactures three models of mattresses: the Sleepeze, the Plushette, and the Ultima. Forecast sales for next year are 15,000 for the Sleepeze, 12,000 for the Plushette, and 5,000 for the Ultima. Gene Dixon, vice president of sales, has pr
> At the end of the year, Engersol, Inc., actually produced 305,000 units of the commercial cleaner and 120,000 of the deluxe model. The actual overhead costs incurred were: Maintenance $ 56,900 Power 10,000 Indirect labor 108,700 Rent 28,000 Required: Pre
> In an attempt to improve budgeting, the controller for Engersol, Inc., has developed a flexible budget for overhead costs. Engersol, Inc., makes two types of products, commercial floor cleaners and household floor cleaners. The company expects to produce
> Ingles Corporation is a manufacturer of tables sold to schools, restaurants, hotels, and other institutions. The table tops are manufactured by Ingles, but the table legs are purchased from an outside supplier. The Assembly Department takes a manufacture
> Del Spencer’s purchases clothing evenly throughout the month. All purchases are on account. On the first of every month, Jana Spencer, Del’s wife, pays for all of the previous month’s purchases. Terms are 2/10, n/30 (i.e., a 2 percent discount can be tak
> Del Spencer is the owner and founder of Del Spencer’s Men’s Clothing Store. Del Spencer’s has its own house charge accounts and has found from past experience that 10 percent of its sales are for cash. The remaining 90 percent are on credit. An aging sch
> Historically, Ragman Company has had no significant bad debt experience with its customers. Cash sales have accounted for 20 percent of total sales, and payments for credit sales have been received as follows: 40 percent of credit sales in the month of t
> LeeAnn Ortiz owns a retail store that sells new and used sporting equipment. LeeAnn has requested a cash budget for October. After examining the records of the company, you find the following: a. Cash balance on October 1 is $980. b. Actual sales for Aug
> Rosita thinks that it may be time to refuse to accept checks and to start accepting credit cards. She is negotiating with VISA/MasterCard and American Express, and she would start the new policy on April 1. Rosita estimates that with the drop in sales fr
> Rosita Flores owns Rosita’s Mexican Restaurant in Tempe, Arizona. Rosita’s is an affordable restaurant near campus and several hotels. Rosita accepts cash and checks. Checks are deposited immediately. The bank charges $0.50 per check; the amount per chec
> Gunnison Company had the following equivalent units schedule and cost information for its Sewing Department for the month of December: Required: 1. Calculate the unit cost for December, using the FIFO method. 2. Calculate the cost of goods transferred ou
> Tiger Drug Store carries a variety of health and beauty aids, including 500-count bottles of vitamins. The sales budget for vitamins for the first six months of the year is presented below. The owner of Tiger Drug believes that ending inventories should
> Video-Forward, Inc., designs and manufactures wearable video cameras. Models A-1, A-2, and A-3 are lightweight video cameras that can be used on arms and headbands. Models A-4 and A-5 have larger memory, better resolution, and more Wi-Fi-related features
> Macchu Company produces stuffed toy animals; one of these is “Andie the Llama.” Each Andie takes 0.30 yard of fabric and eight ounces of polyfiberfill. Fabric costs $3.50 per yard and polyfiberfill is $0.05 per ounce.
> Archer Company produces two products: the custom and the basic. The custom sells for $30, and the basic sells for $8. Projected sales of the two models for the coming four quarters are given below. The president of the company believes that the projected
> Palmgren Company produces consumer products. The sales budget for four months of the year is presented below. Company policy requires that ending inventories for each month be 25 percent of next month’s sales. At the beginning of July,
> Arvin, Inc., produces two products, ins and outs, in a single process. The joint costs of this process were $77,300, and 14,000 units of ins and 36,000 units of outs were produced. Separable processing costs beyond the split-off point were as follows: in
> Refer to Exercise 7-25 and allocate the joint costs using the sales-value-at-split-off method. Data from Exercise 7-25: Alomar Company manufactures four products from a joint production process: barlon, selene, plicene, and corsol. The joint costs for o

