Question: Dave and Sharon Sampson recently established a
Dave and Sharon Sampson recently established a plan to save $300 per month (or $3,600 per year) for their children’s education. Their oldest child is six years old and will begin college in twelve years. They will invest the $300 in a savings account that they expect will earn interest of about 2% per year over the next twelve years. The Sampsons wonder how much additional money they would accumulate if they could earn 5% per year on the savings account instead of 2%. They also wonder how their savings would accumulate if they could save $400 per month (or $4,800 per year) instead of $300 per month.
1. Help the Sampsons determine how much they will have for the children’s education by calculating how much $3,600 in annual savings will accumulate to if they earn interest of (a) 2% and (b) 5%. Next, determine how much $4,800 in annual savings will accumulate to if they earn interest of (a) 2% and (b) 5%.
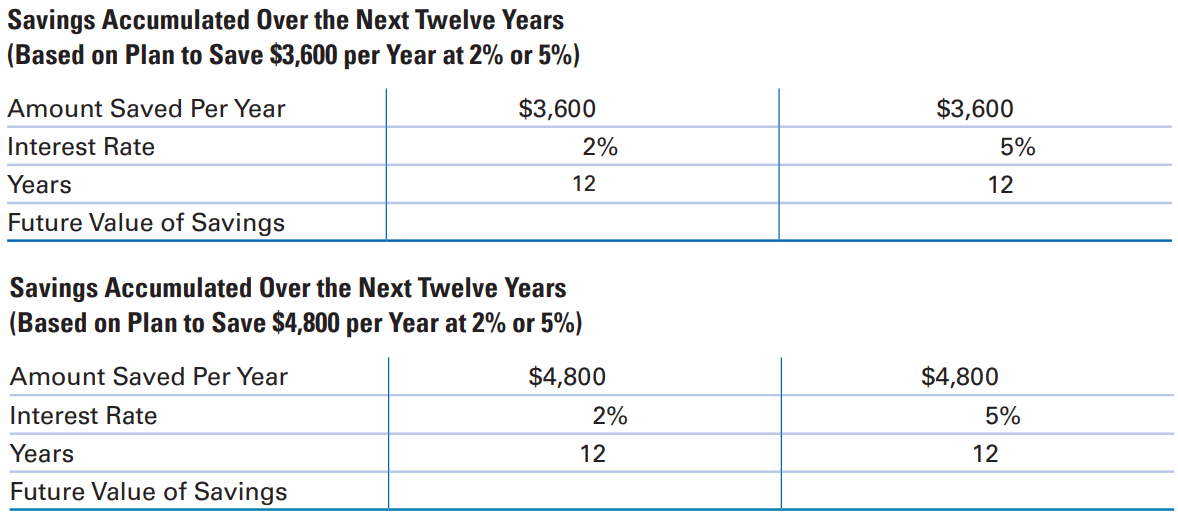
2. What is the impact of the higher interest rate of 5% (instead of 2%) on the Sampsons’ accumulated savings?
3. What is the impact of the higher savings of $4,800 (instead of $3,600) on their accumulated savings?
4. If the Sampsons set a goal to save $70,000 for their children’s college education in twelve years, how would you determine the yearly savings necessary to achieve this goal? How much would they have to save by the end of each year to achieve this goal, assuming a 5% annual interest rate?

> Income Method. Nancy is a widow with two teenage children. Nancy’s gross income is $4,000 per month, and taxes take about 25% of her income. Using the income method, Nancy calculates she will need to purchase about eight times her disposable income in li
> Impact of College Choice on Net Worth. Remi and Raina will both receive $100,000 from their grandfather when they graduate college next month. Remi went to a public university and accumulated $25,000 in total student loan debt. Raina attended a private c
> Copayment. Nareem’s hospital stay cost $7,575 and his insurance requires a copayment of $500. How much will his insurance pay for his hospital bill?
> COBRA. Susan recently quit working for a local firm and has yet to find a new job. She knows she can maintain her health insurance from her old employer due to COBRA. How much will it likely cost her for health insurance if she previously paid $200 per m
> Stop-Loss Provision. Pete’s health insurance policy specifies that he should pay 30% of expenses associated with a long-term illness, and he has a stop-loss provision of $35,000 in his policy. If Pete incurs expenses of $60,000, how much would he owe?
> Refinancing. Doug and Lynn bought their home three years ago. They have a mortgage payment of $601.69. Interest rates have recently fallen, and they can lower their mortgage payments to $491.31 if they refinance. What would their annual savings be if the
> Tax Savings. Matt paid mortgage interest of $4,330 during his first year in the condo. His property taxes were $600, and his homeowner’s insurance was $460. If Matt is in a 24% marginal tax rate bracket, what were his tax savings for his first year assum
> Annual Costs of Renting. Teresa rents her apartment for $850 per month, utilities not included. When she moved in, she paid a $700 security deposit using money from her savings account that was paying 3% interest. Her renter’s insurance costs her $80 per
> Tax Savings. This month you made a mortgage payment of $700, of which $600 was an interest payment and $100 a payment of the loan principal. You are in the 24% marginal tax bracket and you will itemize instead of taking the standard deduction. What are t
> Ethical Dilemma. Mia would like to purchase a specific home and knows that she can afford the home, but her income is slightly lower than the amount needed to qualify for the mortgage. She is a waitress and makes much of her income from tips, so she can
> Computing a Mortgage Payment. N’Cho just purchased a home for $135,000. He put 10% down and financed the remainder for thirty years at 4.8%. How much is his monthly principal and interest payment?
> Mortgage Insurance. Justin’s new FHA mortgage is for $131,500. How much will his overall mortgage increase with an upfront fee of 1.5%? How much will his total mortgage be with the upfront mortgage insurance fee added? Will Justin always pay mortgage ins
> Future Value. How much will you have in 36 months if you invest $75 a month at 3% annual interest?
> Down Payment and Loan Payments. Lucas wants to buy a used car that will cost $5,500. How much will his monthly payment be if he puts $2,500 down and finances the remainder at 5% for two years?
> Ethical Dilemma. Chen recently graduated from college and accepted a job in a new city. Furnishing his apartment has proved more costly than he anticipated. To enable him to make purchases, he applied for and received a credit card with a $5,000 credit l
> Interest on Credit Cards. Eileen wants a car that costs $7,000. How long would it have taken Eileen to save for the outright purchase of the car if she did not have any credit card debt and used the interest payments to save for the purchase of the car?
> Credit Card Interest. Margie has had a tough month. First, she had dental work that cost $700. Next, she had her car transmission rebuilt, which cost $1,400. She put both of these unexpected expenses on her credit card. If she does not pay her credit car
> Interest Charged. You just borrowed $5,500 and are charged a simple interest rate of 9%. How much interest do you pay each year?
> Annualized T-bill Rate. Brenda purchased a $30,000, ninety-day T-bill for $29,850. What will Brenda’s return be when the T-bill matures? What will her annualized rate be?
> Return on T-bills. Lauren purchased a $40,000 T-bill for $39,200. A few months later, Lauren sold the T-bill for $39,700. What was Lauren’s return on the T-bill?
> Return on T-bills. Dave has $20,000 excess cash to invest. He can purchase a $20,000 T-bill for $19,800 or two $10,000 T-bills for $9,850 each. Which will give him the better return?
> T-bill Return. Troy paid $9,800 for a T-bill with a face value of $10,000. What is Troy’s return if he holds the T-bill to maturity?
> Interest Earned. Claire has invested $10,000 in an eighteen-month CD that pays 2.25%. How much interest will Claire receive at maturity?
> Future Value. Kyle has $1,000 in cash received for high school graduation gifts from various relatives. He wants to invest it in a certificate of deposit (CD) so that he will have a down payment on a car when he graduates from college in five years. His
> Value of CD. Travis has invested $3,000 in a threemonth CD at 1.25%. How much will Travis have when the CD matures?
> Interest Earned. Lisa is depositing $2,500 in a six-month CD that pays 1.75% interest. How much interest will she accrue if she holds the CD until maturity?
> Ethical Dilemma. Jason is in his mid-fifties and was raised by parents of the Depression era. As a result, he is very risk adverse. He recently came into a very large amount of money, and he wants to put it where it will be safe, but where it will earn h
> Fractional Year Investment Return. Jill placed $10,000 in a ninety-day CD that offered an annualized return of 1.20%. How much interest will she earn on this CD?
> Investment Return. Thomas can invest $10,000 by purchasing a one-year T-bill for $9,775, or he can place the $10,000 in a twelve-month CD paying 2.5%. Which investment will provide a higher return? In addition to return, what else should Thomas consider
> Interest Earned. On June 1, Mia deposited $4,000 in an MMDA that pays 2% interest. On October 31, Mia invested $2,000 in a three-month CD that pays 1.75%. At the end of the year, how much interest will Mia have earned, assuming she hasn’t taken anything
> Interest Earned. Teresa has just opened a NOW account that pays 1.5% interest. If she maintains a minimum balance of $500 for the next twelve months, how much interest will she earn?
> Ethical Dilemma. Jill just finished reconciling her account balance and discovered the bank made a $567 error in her favor. She double-checked her numbers and is certain the bank made an error, and the difference is not a miscalculation on her part. Jill
> Risk Premium. Spencer is considering investing $5,000 in higher risk debt securities that pay 7% for a ten-year period of time. What is the risk premium on that investment assuming he can earn 2.5% on a one-year CD? What does the size of the risk premium
> Impact on Taxes. Daniel has a marginal tax rate of 24%. He suddenly realizes that he neglected to include a $1,000 tax deduction. How will this oversight affect his taxes?
> Present Value. Winners of the Georgia Lotto drawing are given the choice of receiving the winning amount divided equally over twenty years or as a lump-sum cash option amount. The cash option amount is determined by discounting the winning amount at 5% o
> Change in Taxable Income. Using the information in problem 7, if Nick and Nora’s itemized deductions increase by $4,000, how will their taxable income be affected? Data from Problem 7: Taxable Income. Nick and Nora are married and file jointly. They hav
> Taxable Income. Nick and Nora are married and file jointly. They have an adjusted gross income of $47,400. If they have itemized deductions of $22,500, what is their taxable income?
> Itemized Deduction. Dawn’s 2018 adjusted gross income is $16,700. Dawn has $1,800 in unreimbursed medical expenses. How much can Dawn claim as an itemized deduction?
> Itemized Deduction. Emma’s 2018 adjusted gross income is $24,200. She has $1,800 in unreimbursed medical expenses. How much in medical expenses could Emma claim as an itemized deduction?
> Deductions. Emily and Paul are married and will file a joint return for 2018. The standard deduction for their filing status is $24,000. They have the following itemized deductions: Should Emily and Paul itemize their deductions or use the standard deduc
> Capital Gains Tax. Stephen’s salary is $34,000 in 2018. In 2018, he sold stock that he had held for nine months for a gain of $1,900. How much tax must he pay on this capital gain? How much would the tax be if he had held the stock for thirteen months?
> FICA Contributions. Brian makes $27,000 per year. How much can he expect to contribute to FICA taxes in 2018? How much will his employer contribute?
> As a result of watching a financial news network on cable, reading articles in some business magazines, and listening to a coworker tell how her portfolio doubled in value in six months, Brad is now convinced that his financial future lies in the stock m
> Your friend Brad Brooks tells you about his plans to upgrade his auto insurance. Specifically, he would like to add several types of coverage to his policy, such as uninsured motorist coverage and rental car coverage. Recall that Brad is 30 years old. Hi
> Your friend Brad Brooks now has the urge to upgrade his car and housing situations, and he needs your guidance. 1. Brad is interested in purchasing an SUV for $35,000. He has found a buyer who will pay him $15,000 cash for his existing car. This would en
> Your friend Brad Brooks has called you for additional guidance on dealing with his credit card balance of about $8,000. 1. Brad is frustrated with his high credit card balance (with an 18% interest rate). He wants to delay making any more payments on his
> Your friend Brad Brooks has no control of personal finances. Single and 30 years old, he has a good job at a technology company. His monthly disposable income is $4,000. Brad recently moved from his apartment where the rent was $1,400 per month to an exp
> Dave and Sharon Sampson want to determine their taxes for this year. Their combined income will be $65,000 for the entire year. They did not make any individual retirement account (IRA) contributions. The Sampsons are filing jointly. 1. Help the Sampsons
> Ethical Dilemma. When Larry filed his taxes he forgot to include $2,500 in cash income he earned painting a friend’s house. He was going through his checking account records and noticed the cash deposit and realized his mistake. a. Should Larry ignore hi
> The Sampsons realize that the first step toward achieving their financial goals is to create a budget capturing their monthly cash inflows and outflows. Dave and Sharon’s combined disposable (after-tax) income is now about $5,000 per mo
> The Sampsons is a continuing case that occurs at the end of every chapter. You will help the Sampsons develop their financial plan using the key concepts presented in each chapter. You can fill in the blanks on these worksheets electronically at www.pear
> With your help, Dave and Sharon Sampson have now established a financial plan. Among their key financial planning decisions were the following: • Budgeting. They decided to revise their budget to make it possible to start saving. By reducing their spendi
> Dave and Sharon Sampson want to make sure that their family is properly cared for in the event of their death. They recently purchased term life insurance and want to make sure that the funds are allocated to best serve their children in the long run. Sp
> Dave’s employer offers a 401(k) plan, but Dave has not participated in it up to this point. Now he wants to seriously consider contributing. His employer will allow him to invest about $7,000 of his salary per year and match his contrib
> The Sampsons have been evaluating methods for investing money that will ultimately be used to support their children’s college education. They have concluded that a mutual fund is better suited to their needs than investing in individual stocks or indivi
> Over the last month, the Sampsons have been struggling with how to invest their savings to support their children’s college education. They previously considered stocks and bonds and are now seriously considering investing their money in mutual funds. Th
> The Sampsons are considering investing in bonds as a way of saving for their children’s college education. They learn that there are bonds with maturities between twelve and sixteen years, which is exactly when they need the funds for college expenses. D
> Recall that one of the Sampsons’ goals is to invest for their children’s future college education. They are considering investing in several stocks that are rated highly by analysts. 1. Offer advice to the Sampsons about whether they should buy stocks th
> Social Security. Dorinda earned $112,000. How much did she pay in Social Security taxes?
> Recall that the Sampsons have a goal of saving about $300 per month ($3,600 per year) for their children’s college education. They want to estimate how this money would grow over time if they invest it in stock. Dave and Sharon have nev
> The Sampsons want a life insurance policy that will provide for the family in the event of Dave’s death because he is the major breadwinner. Specifically, they want life insurance benefits that could provide $40,000 per year for the nex
> Dave and Sharon Sampson are assessing the amount of health insurance and disability income insurance they have. The Sampsons’ health insurance is provided by a health maintenance organization (HMO). Recently, Dave and Sharon have heard about preferred pr
> As the next step in reviewing their finances, the Sampsons are assessing their insurance needs related to their vehicles and home. They indicated the amount of money they spend on insurance on their personal balance sheet. They currently have auto insura
> When the Sampsons purchased a home, they obtained a thirty-year mortgage with a fixed interest rate of 6%. Their monthly mortgage payment (excluding property taxes and insurance) is about $780 per month. The Sampsons still owe about $130,000 on their exi
> Recall from the previous chapter that the Sampsons had savings of $3,000 and credit card debt of $2,000. Assume that they have now paid off their credit card debt and have also accumulated total savings of $5,000 that they will use as a down payment on a
> This month, the Sampsons increased their savings by $3,000 because they paid most of their expenses with a credit card. However, now their credit card has a balance of about $2,000. They will likely earn about 2% on the savings. Meanwhile, their credit c
> The Sampsons’ credit card has a credit limit of $10,000. They have just received a letter from the credit card company offering to increase their credit limit to $20,000. The Sampsons have also read several articles on identity theft and are concerned wi
> The Sampsons have just started saving $800 per month. This money will be placed in CDs every month, which they chose in Chapter 5. These funds, earmarked for a down payment on a car and their children’s college education, are not available to the Sampson
> Recall that the Sampsons would like to save a total of $1,000 per month. They notice that their local bank offers the certificate of deposit (CD) rates listed in the following table; they now need to determine if they should invest in CDs, and if so, whi
> IRA Contributions. Hareem is single and earned $104,300 in taxable income. He contributed $4,200 to an IRA during the year. How much did Hareem’s IRA contribution lower his tax liability?
> Savings Rate. If Angela is saving $380 per month, what is her savings rate (i.e., savings as a percentage of disposable income)?
> How can your post-high school education decisions affect your wealth?
> How can an application of personal finance skills increase your wealth?
> Financial Goals and Life Insurance. How are your financial goals related to the decision about whether to purchase life insurance?
> Retirement Planning. What is the retirement account trade-off?
> Protecting Your Assets and Income. How can you protect your assets and income? What is the insurance trade-off?
> Effective Financial Planning. What is the most common problem that prevents effective financial planning? Why do some people spend too much money? How can you use a budget to help you with spending issues?
> Financial Goals. What are some common financial goals?
> Estate Taxes. Jill just inherited $12 million from her grandfather in 2018. How much of the inheritance is subject to estate tax?
> Types of Estate Plan Documents. List several important documents that are important for estate planning.
> Defined-Contribution Plan. What is a defined contribution plan? Why have many employers switched to this type of plan? List some of the benefits a defined-contribution plan offers to employees.
> Tax Liability. Compute Lana’s tax liability if she is single and earned $74,400 in wages. She will take the standard deduction.
> Annuity Fees. What is a surrender charge? How much are common annuity commissions or insurance fees?
> Health Care and Retirement. Discuss health care concerns in retirement
> Roth 401(k). How does a Roth 401(k) differ from a traditional 401(k)?
> Correlation. What is correlation? How can you use this concept to reduce risk?
> Discount or Premium. What does it mean for a closed-end fund to trade at a discount? What does it mean for a closed-end fund to trade at a premium?
> Hedge Funds. What is a hedge fund? What type of individual invests in a hedge fund?
> Junk Bond Fund. What is a junk bond fund? What type of investor might be attracted to junk bond funds?
> Hybrid Fund. What is a hybrid fund? What are some of the advantages of hybrid funds?
> Socially Responsible Stock Funds. What are socially responsible stock funds? What types of stocks would this type of fund typically avoid owning?
> Choosing a Mutual Fund. What are some factors to consider prior to choosing a mutual fund?
> FICA Taxes and High Incomes. Jauna made $178,400 in salary during 2018. How much were her FICA withholdings for that year?
> ETF Advantages and Disadvantages. List the advantages and disadvantages of ETFs.
> Types of ETFs. List and briefly describe the different types of ETFs.
> ETFs. What is an ETF? How do ETFs differ from open-end stock funds?
> Corporate Bonds. What are corporate bonds? Are corporate bonds subject to default risk?
> Convertible Bond. What is a convertible bond? How does a bond’s convertibility feature affect its return? How does a convertible feature affect investor interest in purchasing the bond?
> Bonds and Your Financial Plan. What is the danger of having too much exposure to bonds in your investment portfolio?
> Bonds and Your Financial Plan. What benefits do bonds provide in an investment portfolio?

