Question: Find the maximum and minimum values of
Find the maximum and minimum values of f subject to the given constraints. Use a computer algebra system to solve the system of equations that arises in using Lagrange multipliers. (If your CAS finds only one solution, you may need to use additional commands.)
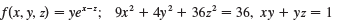
Transcribed Image Text:
f(x, у, 2) — yе**; 9х3 + 4y? + 362' %3 36, ху + уz —D 1
> Find the area of the surface. The part of the cylinder x2 + z2 = 4 that lies above the square with vertices (0, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1), and (1, 1)
> Evaluate the integral by reversing the order of integration. ∫_0^2 ∫_(y/2)^1y cos (x3 – 1) dx dy
> Evaluate the integral by reversing the order of integration. ∫_0^1 ∫_(√x)^1√(y^3+1) dy dx
> Evaluate the integral by reversing the order of integration. ∫_0^1 ∫_(x^2)^1√y sin y dy dx
> Sketch the region of integration and change the order of integration. ∫_0^1 ∫_arctanx^(π/4) f (x,y) dy dx
> Find the mass and center of mass of the lamina that occupies the region D and has the given density function ρ. D is the triangular region with vertices (0, 0), (2, 1), (0, 3); ρ (x, y) = x + y
> Sketch the region of integration and change the order of integration. ∫_1^2 ∫_0^lnxf (x,y) dy dx
> Sketch the region of integration and change the order of integration. ∫_(-2)^2 ∫_0^(√(4-y^2 ) f (x,y) dx dy
> Sketch the region of integration and change the order of integration. ∫_0^(π/2) ∫_0^cosxf (x,y) dy dx
> Sketch the region of integration and change the order of integration. ∫_0^2 ∫_(x^2)^4 f (x,y) dy dx
> Sketch the region of integration and change the order of integration. ∫_0^1 ∫_0^y f (x,y) dx dy
> Calculate the iterated integral ∫(-3)^3 ∫_0^(π/2) (y+y^2 cos x ) dx dy
> Use a computer algebra system to find the exact volume of the solid. Enclosed by z = 1 - x2 - y2 and z = 0
> Use a computer algebra system to find the exact volume of the solid. Between the paraboloids z = 2x2 + y2 and z = 8 - x2 - 2y2 and inside the cylinder x2 + y2 = 1
> Use the result of Exercise 40 part (c) to evaluate the following integrals. Exercise 40 part (c): Deduce that (a). ∫_0^∞ x^2 e^(-x^2 ) dx (b). ∫_0^∞ √x e-x dx
> (a). We define the improper integral (over the entire plane R2) where Da is the disk with radius a and center the origin. Show that (b). An equivalent definition of the improper integral in part (a) is where Sa is the square with vertices (Â&p
> Find the area of the surface. The part of the surface 2y + 4z - x2 = 5 that lies above the triangle with vertices (0, 0), (2, 0), and (2, 4)
> Use polar coordinates to combine the sum into one double integral. Then evaluate the double integral. Sa l ty dy dx + ftvdy dx + 4-x2 xy dy dx ху.
> Calculate the iterated integral ∫_0^1 ∫_1^2(x+e^(-y) dx dy
> (a). Newton’s method for approximating a root of an equation f (x) = 0 (see Section 4.8) can be adapted to approximating a solution of a system of equations f (x, y) = 0 and g (x, y) = 0. The surfaces z = f (x, y) and z = t (x, y) inter
> Each of these extreme value problems has a solution with both a maximum value and a minimum value. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the extreme values of the function subject to the given constraint. f(x, y) %3 ху; 4х? + y? %3D 8 = 8
> Express the double integral in terms of a single integral with respect to r. Then use your calculator to evaluate the integral correct to four decimal places. ∬D e^(x^2+y^2 )^2 dA, where D is the disk with center the origin and radius 1
> Evaluate the iterated integral by converting to polar coordinates. ∫_0^2 ∫_0^(√(2x-x^2 ) √(x^2+y^2 ) dy dx
> Evaluate the iterated integral by converting to polar coordinates. ∫_0^(1/2) ∫_(√3 y)^(√(1-y^2 ) xy^2 dx dy
> Evaluate the iterated integral by converting to polar coordinates. ∫_0^a ∫_(-√(a^2-y^2 ))^(√(a^2-y^2 ) (2x + y) dx dy
> Find the mass and center of mass of the lamina that occupies the region D and has the given density function ρ. D = {(x, y) | 1 < x < 3, 1 < y < 4}; ρ (x, y) = ky2
> Evaluate the iterated integral by converting to polar coordinates. ∫_0^2 ∫_0^(√(4-x^2 ) e^(-x^2-y^2 ) dy dx
> Find the volume of the given solid. Bounded by the planes z = x, y = x, x + y = 2, and z = 0
> Use polar coordinates to find the volume of the given solid. Inside both the cylinder x2 + y2 = 4 and the ellipsoid 4x2 + 4y2 + z2 = 64
> Use a computer algebra system to find the mass, center of mass, and moments of inertia of the lamina that occupies the region D and has the given density function. D is enclosed by the right loop of the four-leaved rose r = cos 2θ; θ (x, y) = x2 + y2
> (a). Find the maximum value of f (x1, x2, . . . , xn) = √(n&x_1 x_2…x_n ) given that x1, x2, . . ., xn are positive numbers and x1 + x2 + ∙ ∙ ∙ + xn = c, wher
> If you attempt to use Formula 2 to find the area of the top half of the sphere x2 + y2 + z2 = a2, you have a slight problem because the double integral is improper. In fact, the integrand has an infinite discontinuity at every point of the boundary circl
> Show that the area of the part of the plane z = ax + by + c that projects onto a region D in the xy-plane with area A (D) is √(a^2 + b^2 + 1) A (D).
> Find the area of the surface. The part of the plane 6x + 4y + 2z = 1 that lies inside the cylinder x2 + y2 = 25
> Find the exact area of the surface z = 1 + x + y + x2 -2 < x < 1 -1 < y < 1 Illustrate by graphing the surface.
> Find the exact area of the surface z = 1 + 2x + 3y + 4y2, 1 < x < 4, 0 < y < 1.
> (a). Use the Midpoint Rule for double integrals (see Section 15.1) with four squares to estimate the surface area of the portion of the paraboloid z = x2 + y2 that lies above the square [0, 1] × [0, 1]. (b). Use a computer algebra system to approximate t
> Find the area of the surface correct to four decimal places by expressing the area in terms of a single integral and using your calculator to estimate the integral. The part of the surface z = cos (x2 + y2) that lies inside the cylinder x2 + y2 = 1
> Find the area of the surface correct to four decimal places by expressing the area in terms of a single integral and using your calculator to estimate the integral. The part of the surface z = 1/ (1 + x2 + y2) that lies above the disk x2 + y2 < 1
> Find the maximum and minimum values of f subject to the given constraints. Use a computer algebra system to solve the system of equations that arises in using Lagrange multipliers. (If your CAS finds only one solution, you may need to use additional comm
> Find the center of mass of the lamina in Exercise 11 if the density at any point is proportional to the square of its distance from the origin. Exercise 11: A lamina occupies the part of the disk x2 + y2 < 1 in the first quadrant. Find its center of ma
> Find the area of the surface. The part of the sphere x2 + y2 + z2 = a2 that lies within the cylinder x2 + y2 = ax and above the xy-plane
> Find the area of the surface. The part of the sphere x2 + y2 + z2 = 4 that lies above the plane z = 1
> Find the area of the surface. The part of the plane 5x + 3y = z + 6 = 0 that lies above the rectangle [1, 4] × [2, 6]
> Find the mass and center of mass of the lamina that occupies the region D and has the given density function ρ. D is bounded by the curves y = e-x, y = 0, x = 0, x = 1; ρ (x, y) = xy
> Find the mass and center of mass of the lamina that occupies the region D and has the given density function ρ. D is bounded by y = x + 2 and y = x2; ρ (x, y) = kx2
> Find the mass and center of mass of the lamina that occupies the region D and has the given density function ρ. D is bounded by y = 1 - x2 and y − 0; ρ (x, y) = ky
> Find the mass and center of mass of the lamina that occupies the region D and has the given density function ρ. D is the triangular region enclosed by the lines y = 0, y = 2x, and x + 2y = 1; ρ (x, y) = x
> Find the mass and center of mass of the lamina that occupies the region D and has the given density function ρ. D = {(x, y) | 0 < x < a, 0 < y < b}; ρ (x, y) = 1 + x2 + y2
> Use polar coordinates to find the volume of the given solid. Below the cone z = √(x^2 + y^2 ) and above the ring 1 < x2 + y2 < 4
> Electric charge is distributed over the disk x2 + y2 < 1 so that the charge density at (x, y) is (x, y) = √(x^2 + y^2 ) (measured in coulombs per square meter). Find the total charge on the disk.
> Use polar coordinates to find the volume of the given solid. Under the paraboloid z = x2 + y2 and above the disk x2 + y2 < 25
> Find the moments of inertia Ix, Iy, I0 for the lamina of Exercise 6. Exercise 6: Find the mass and center of mass of the lamina that occupies the region D and has the given density function ρ. D is the triangular region enclosed by the lines y = 0, y =
> Find the moments of inertia Ix, Iy, I0 for the lamina of Exercise 3. Exercise 3: Find the mass and center of mass of the lamina that occupies the region D and has the given density function ρ. D = {(x, y) | 1 < x < 3, 1 < y < 4}; ρ (x, y) = ky2
> A lamina occupies the region inside the circle x2 + y2 = 2y but outside the circle x2 + y2 = 1. Find the center of mass if the density at any point is inversely proportional to its distance from the origin.
> Find the center of mass of a lamina in the shape of an isosceles right triangle with equal sides of length a if the density at any point is proportional to the square of the distance from the vertex opposite the hypotenuse.
> Find the center of mass of the lamina in Exercise 13 if the density at any point is inversely proportional to its distance from the origin. Exercise 13: The boundary of a lamina consists of the semicircles y = √(1 - x^2 ) and y = √(4 - x^2 ) together w
> The boundary of a lamina consists of the semicircles y = √(1 - x^2 ) and y = √(4 - x^2 ) together with the portions of the x-axis that join them. Find the center of mass of the lamina if the density at any point is proportional to its distance from the o
> The plane 4x - 3y + 8z = 5 intersects the cone z2 = x2 + y2 in an ellipse. (a). Graph the cone and the plane, and observe the elliptical intersection. (b). Use Lagrange multipliers to find the highest and lowest points on the ellipse.
> A lamina occupies the part of the disk x2 + y2 < 1 in the first quadrant. Find its center of mass if the density at any point is proportional to its distance from the x-axis.
> Find the mass and center of mass of the lamina that occupies the region D and has the given density function ρ. D is enclosed by the curves y = 0 and y = cos x, -π/2 < x < π/2; ρ (x, y) = y
> Evaluate the given integral by changing to polar coordinates. ∬R sin (x2 + y2) dA, where R is the region in the first quadrant between the circles with center the origin and radii 1 and 3.
> Evaluate the given integral by changing to polar coordinates. ∬R (2x – y) dA, where R is the region in the first quadrant enclosed by the circle x2 + y2 = 4 and the lines x = 0 and y = x
> Evaluate the given integral by changing to polar coordinates. ∬D x2y dA, where D is the top half of the disk with center the origin and radius 5.
> Evaluate the iterated integral. ∫_0^1 ∫_0^(e^y) √(1+e^y) dw dv
> A region R is shown. Decide whether to use polar coordinates or rectangular coordinates and write∬R f (x, y) dA as an iterated integral, where f is an arbitrary continuous function on R. y. 3 х -3+
> A region R is shown. Decide whether to use polar coordinates or rectangular coordinates and write ∬R f (x, y) dA as an iterated integral, where f is an arbitrary continuous function on R. yA -1 1 R -1
> The plane x + y + 2z = 2 intersects the paraboloid z = x2 + y2 in an ellipse. Find the points on this ellipse that are nearest to and farthest from the origin.
> Use polar coordinates to find the volume of the given solid. Bounded by the paraboloids z = 6 - x2 - y2 and z = 2x2 + 2y2
> Use polar coordinates to find the volume of the given solid. Above the cone z = √(x^2 + y^2 ) and below the sphere x2 + y2 + z2 = 1
> Use polar coordinates to find the volume of the given solid. Bounded by the paraboloid z = 1 + 2x2 + 2y2 and the plane z = 7 in the first octant
> Use polar coordinates to find the volume of the given solid. A sphere of radius a
> Use polar coordinates to find the volume of the given solid. Inside the sphere x2 + y2 + z2 = 16 and outside the cylinder x2 + y2 = 4
> Use polar coordinates to find the volume of the given solid. Below the plane 2x + y + z = 4 and above the disk x2 + y2 < 1
> A region R is shown. Decide whether to use polar coordinates or rectangular coordinates and write ∬R f (x, y) dA as an iterated integral, where f is an arbitrary continuous function on R. y. 1 R -1 1 x
> Evaluate the double integral. ∬D (x2 + 2y) dA, D is bounded by y = x, y = x3, x > 0
> Evaluate the double integral. ∬D x cos y dA, D is bounded by y = 0, y = x2, x = 1
> Calculate the iterated integral ∫_0^1 ∫_0^1 (x+y)^2 dx dy
> Find the maximum and minimum volumes of a rectangular box whose surface area is 1500 cm2 and whose total edge length is 200 cm.
> Calculate the iterated integral ∫_1^4 ∫_0^2 (6x^2 y - 2x) dy dx
> Evaluate the given integral by changing to polar coordinates. ∬D x dA, where D is the region in the first quadrant that lies between the circles x2 + y2 = 4 and x2 + y2 = 2x
> Find ∫_0^2 f (x,y) dx and ∫_0^3 f(x,y) dy f (x, y) = x + 3x2y2
> Evaluate the given integral by changing to polar coordinates. ∬R cos √(x^2 + y^2 ) dA, where D is the disk with center the origin and radius 2
> Evaluate the given integral by changing to polar coordinates. ∬D e^(-x^2-y^2 ) dA, where D is the region bounded by the semicircle x = √(4 - y^2 ) and the y-axis.
> Evaluate the given integral by changing to polar coordinates. ∬R y^2/(x^2 + y^2 ) dA, where R is the region that lies between the circles x2 + y2 = a2 and x2 + y2 = b2 with 0 < a < b
> A region R is shown. Decide whether to use polar coordinates or rectangular coordinates and write ∬R f (x, y) dA as an iterated integral, where f is an arbitrary continuous function on R. T5 R 2 5 2.
> Evaluate the double integral. ∬D e^(-y^2 ) dA, D = {(x, y) | 0 < y < 3, 0 < x < y}
> Evaluate the double integral. ∬D (2x + y) dA, D = {(x, y) | 1 < y < 2, y - 1 < x < 1}
> Use Lagrange multipliers to give an alternate solution to the indicated exercise in Section 14.7. Exercise 55 14.7 Exercise 55: If the length of the diagonal of a rectangular box must be L, what is the largest possible volume?
> Evaluate the iterated integral. ∫_0^1 ∫_0^(x^2)cos (s^3) dt ds
> Use a computer algebra system to find the exact volume of the solid. Under the surface z = x3y4 + xy2 and above the region bounded by the curves y = x3 - x and y = x2 + x for x > 0
> Sketch the solid whose volume is given by the iterated integral. ∫_0^1 ∫_0^(1-x^2) (1 - x) dy dx
> Evaluate the iterated integral. ∫_0^(π/2) ∫_0^x〖(x siny)〗dy dx
> Find the volume of the solid lying under the elliptic paraboloid x2/4 + y2/9 + z = 1 and above the rectangle R = [-1, 1] × [-2, 2].
> Find the volume of the solid by subtracting two volumes. The solid in the first octant under the plane z = x + y, above the surface z = xy, and enclosed by the surfaces x = 0, y = 0, and x2 + y2 = 4
> Calculate the double integral. ∬R 1/(1+ x+ y) dA, R = [1, 3] × [1, 2]
> Use a graphing calculator or computer to estimate the x-coordinates of the points of intersection of the curves y = x4 and y = 3x - x2. If D is the region bounded by these curves, estimate ∬D x dA.
> Find the volume of the given solid. Bounded by the cylinders x2 + y2 = r2 and y2 + z2 = r2
> Find the volume of the given solid. Bounded by the cylinder x2 + y2 = 1 and the planes y = z, x = 0, z = 0 in the first octant
> Use Lagrange multipliers to give an alternate solution to the indicated exercise in Section 14.7. Exercise 52 14.7 Exercise 52: The base of an aquarium with given volume V is made of slate and the sides are made of glass. If slate costs five times as m

