Question: Refer to Google’s recent balance sheet
Refer to Google’s recent balance sheet in Appendix A. What property, plant and equipment assets does Google list on its balance sheet? What is the book value of its total net property, plant and equipment assets at December 31, 2013?
Google’s balance sheet from Appendix A:
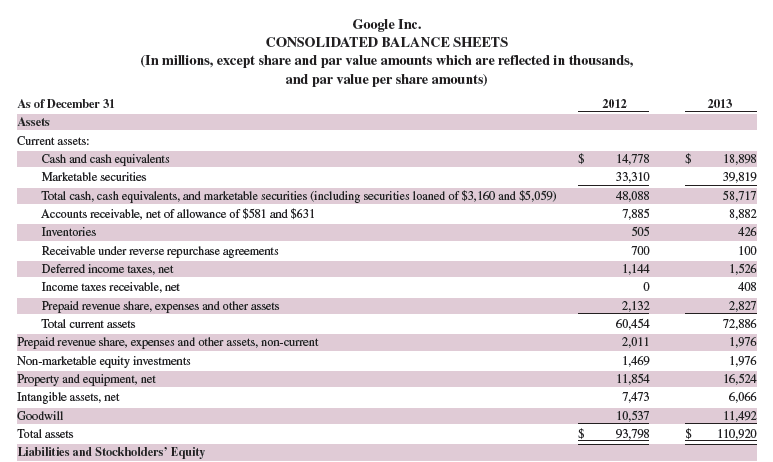
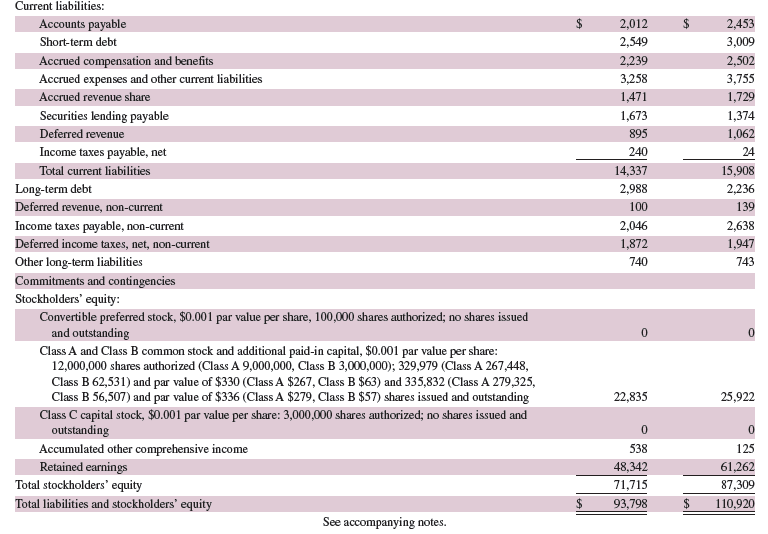
Transcribed Image Text:
Google Inc. CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (In millions, except share and par value amounts which are reflected in thousands, and par value per share amounts) As of December 31 2012 2013 Assets Current assets: Cash and cash equivalents 14,778 2$ 18,898 Marketable securities 33,310 39,819 Total cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities (including securities loaned of $3, 160 and $5,059) Accounts receivable, net of allowance of $581 and $631 48,088 58,717 7,885 8,882 Inventories 505 420 Receivable under reverse repurchase agreements 700 100 Deferred income taxes, net 1,144 1,526 Income taxes receivable, net 408 Prepaid revenue share, expenses and other assets 2,132 2,827 Total current assets 60,454 72,886 Prepaid revenue share, expenses and other assets, non-current 2,011 1,976 1,976 Non-marketable equity investments Property and equipment, net Intangible assets, net 1,469 11,854 16,524 7,473 6,066 Goodwill 10,537 11,492 Total assets $ 93,798 $ 110,920 Liabilities and Stockholders’ equity Current liabilities: Accounts payable 2$ 2,012 2,453 Short-term debt 2,549 3,009 Accrued compensation and benefits 2,239 2,502 Accrued expenses and other current liabilities 3,258 3,755 Accrued revenue share 1,471 1,729 Securities lending payable 1,673 1,374 Deferred revenue 895 1,062 Income taxes payable, net 240 24 Total current liabilities 14,337 15,908 Long-term debt 2,988 2,236 Deferred revenue, non-current 100 139 Income taxes payable, non-current Deferred income taxes, net, non-current 2,046 2,638 1,872 1,947 Other long-term liabilities Commitments and contingencies Stockholders' equity: Convertible preferred stock, $0.001 par value per share, 100,000 shares authorized; no shares issued and outstanding Class A and Class B common stock and additional paid-in capital, $0.001 par value per share: 12,000,000 shares authorized (Class A 9,000,000, Class B 3,000,000); 329,979 (Class A 267,448, Class B 62,531) and par value of $330 (Class A $267, Class B $63) and 335,832 (Class A 279,325, Class B 56,507) and par value of $336 (Class A $279, Class B $57) shares issued and outstanding Class C capital stock, $0.001 par value per share: 3,000,000 shares authorized; no shares issued and outstanding 740 743 22,835 25,922 125 Accumulated other comprehensive income Retained earnings Total stockholders' equity 538 48,342 61,262 71,715 87,309 Total liabilities and stockholders' equity 93,798 110,920 See accompanying notes.
> What is the difference between authorized shares and outstanding shares?
> Who is responsible for directing a corporation’s affairs?
> Suppose that a company has a facility located where disastrous weather conditions often occur. Should it report a probable loss from a future disaster as a liability on its balance sheet? Explain.
> Refer to the financial statements for Samsung in Appendix A. How much were its cash payments for treasury stock purchases for the year ended December 31, 2013? Samsung’s Financial Statements from Appendix A: Samsung Electronic
> Refer to the 2013 balance sheet for Google in Appendix A. What is the par value per share of its preferred stock? Suggest a rationale for the amount of par value it assigned. Google’s Balance Sheet from Appendix A: Google Inc. CON
> Refer to Apple’s fiscal 2013 balance sheet in Appendix A. How many shares of common stock are authorized? How many shares of voting common stock are issued? Apple’s Balance Sheet from Appendix A:
> How are organization expenses reported?
> What is a stock option?
> How are EPS results computed for a corporation with a simple capital structure?
> Why do laws place limits on treasury stock purchases?
> How does the purchase of treasury stock affect the purchaser’s assets and total equity?
> Courts have ruled that a stock dividend is not taxable income to stockholders. What justifies this decision?
> Why is the term liquidating dividend used to describe cash dividends debited against paid-in capital accounts?
> Why are warranty liabilities usually recognized on the balance sheet as liabilities even when they are uncertain?
> What are organization expenses? Provide examples.
> George, Burton, and Dillman have been partners for three years. The partnership is being dissolved. George is leaving the firm, but Burton and Dillman plan to carry on the business. In the final settlement, George places a $75,000 salary claim against th
> What does the term unlimited liability mean when it is applied to partnership members?
> Allocation of partnership income among the partners appears on what financial statement?
> Assume that the Barnes and Ardmore partnership agreement provides for a two-third/one-third sharing of income but says nothing about losses. The first year of partnership operation resulted in a loss, and Barnes argues that the loss should be shared equa
> Assume that Amey and Lacey are partners. Lacey dies, and her son claims the right to take his mother’s place in the partnership. Does he have this right? Why or why not?
> Can partners limit the right of a partner to commit their partnership to contracts? Would such an agreement be binding (a) on the partners and (b) on outsiders?
> How does a general partnership differ from a limited partnership?
> Apple began as a partnership. What does the term mutual agency mean when applied to a partnership?
> Assume a partner withdraws from a partnership and receives assets of greater value than the book value of his equity. Should the remaining partners share the resulting reduction in their equities in the ratio of their relative capital balances or accordi
> Identify the main difference between (a) plant assets and current assets, (b) plant assets and inventory, and (c) plant assets and long-term investments.
> Kay, Kat, and Kim are partners. In a liquidation, Kay’s share of partnership losses exceeds her capital account balance. Moreover, she is unable to meet the deficit from her personal assets, and her partners shared the excess losses. Does this relieve Ka
> What determines the amount deducted from an employee’s wages for federal income taxes?
> Which payroll taxes are the employee’s responsibility and which are the employer’s responsibility?
> What is the current Medicare tax rate? This rate is applied to what maximum level of salary and wages?
> What is the combined amount (in percent) of the employee and employer Social Security tax rate? (Assume wages do not exceed $200,000 per year.)
> If $988 is the total of a sale that includes its sales tax of 4%, what is the selling price of the item only?
> What are the three important questions concerning the uncertainty of liabilities?
> What is an estimated liability?
> Refer to Samsung’s balance sheet in Appendix A. List Samsung’s current liabilities as of December 31, 2013. Samsung’s Balance Sheet from Appendix A: / /
> Refer to Google’s balance sheet in Appendix A. What accrued expenses (liabilities) does Google report at December 31, 2013? Google’s Balance Sheet from Appendix A: Google Inc. CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS (In mill
> What is the difference between ordinary repairs and extraordinary repairs? How should each be recorded?
> Why does the direct write-off method of accounting for bad debts usually fail to match revenues and expenses?
> Refer to Apple’s balance sheet in Appendix A. What is the amount of Apple’s accounts payable as of September 28, 2013? Apple’s Balance Sheet from Appendix A: Apple Inc. CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEE
> What amount of income tax is withheld from the salary of an employee who is single with two withholding allowances and earning $725 per week? What if the employee earned $625 and has no withholding allowances? (Use Exhibit 11A.6.) Exhibit 11A.6: SI
> What is a wage bracket withholding table?
> What is the difference between a current and a long-term liability?
> What accounting concept justifies charging low-cost plant asset purchases immediately to an expense account?
> Why is the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System not generally accepted for financial accounting purposes?
> Why is the cost of a lump-sum purchase allocated to the individual assets acquired?
> What is different between land and land improvements?
> Refer to the December 31, 2013, balance sheet of Samsung in Appendix A. What long-term assets discussed in this chapter are reported by the company? Samsung’s Balance Sheet from Appendix A: / Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. and i
> What is the general rule for cost inclusion for plant assets?
> Assume that a company buys another business and pays for its goodwill. If the company plans to incur costs each year to maintain the value of the goodwill, must it also amortize this goodwill?
> Refer to Samsung’s balance sheet in Appendix A. What does it title its plant assets? What is the book value of its plant assets at December 31, 2013? Samsung’s Balance Sheet from Appendix A: / /
> On its recent balance sheet in Appendix A, Apple lists its plant assets as “Property, plant and equipment, net.” What does “net” mean in this title? Apple Balance Sheet from Appendi
> How is total asset turnover computed? Why would a financial statement user be interested in total asset turnover?
> What are the characteristics of an intangible asset?
> Is the declining-balance method an acceptable way to compute depletion of natural resources? Explain.
> What is the process of allocating the cost of natural resources to expense as they are used?
> What characteristics of a plant asset make it different from other assets?
> Explain the accounting constraint of materiality.
> Why should cash receipts be deposited on the day of receipt?
> When do we know that a company has goodwill? When can goodwill appear in a company’s balance sheet?
> What is a petty cash receipt? Who should sign it?
> Which of the following assets—inventory, building, accounts receivable, or cash—is most liquid? Which is least liquid?
> What are the limitations of internal controls?
> When a store purchases merchandise, why are individual departments not allowed to directly deal with suppliers?
> Why should the person who keeps the records of an asset not be the person responsible for its custody?
> Why should responsibility for related transactions be divided among different departments or individuals?
> Internal control procedures are important in every business, but at what stage in the development of a business do they become especially critical?
> Apple’s statement of cash flows in Appendix A describes changes in cash and cash equivalents for the year ended September 28, 2013. What total amount is provided (used) by investing activities? What amount is provided (used) by financin
> List the seven broad principles of internal control.
> When a general journal entry is used to record sales returns, the credit of the entry must be posted twice. Does this cause the trial balance to be out of balance? Explain.
> What general procedures are applied in accounting for the acquisition and potential cost allocation of intangible assets?
> When special journals are used, they are usually used to record each of four different types of transactions. What are these four types of transactions?
> What purpose is served by the output devices of an accounting system?
> What is the difference between data that are stored off-line and data that are stored online?
> What is the purpose of an input device? Give examples of input devices for computer systems.
> What are source documents? Give two examples.
> Locate “Note 15” that reports Google’s geographical segments from its 2013 annual report on its website (Google.com). Identify its geographical segments and list the revenues for each.
> Why should sales to and receipts of cash from credit customers be recorded and posted immediately?
> Describe the procedures involving the use of copies of a company’s sales invoices as a sales journal.
> What are five basic components of an accounting system?
> When preparing interim financial statements, what two methods can companies utilize to estimate cost of goods sold and ending inventory?
> Samsung’s balance sheet in Appendix A reports the change in cash and equivalents for the year ended December 31, 2013. Identify the cash generated (or used) by operating activities, by investing activities, and by financing (funding) ac
> What factors contribute to (or cause) inventory shrinkage?
> Buyers negotiate purchase contracts with suppliers. What type of shipping terms should a buyer attempt to negotiate to minimize freight-in costs?
> Refer to the income statement of Samsung in Appendix A. Does its income statement report a gross profit figure? If yes, what is the amount? Income Statement of Samsung from Appendix A: Samsung Electronics Co, Ltd. and its subsidiaries CONSOLIDATED
> Refer to the income statement for Samsung in Appendix A. What does Samsung title its cost of goods sold account? Income Statement of Samsung from Appendix A: Samsung Electronics Co, Ltd. and its subsidiaries CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME (In mi
> Refer to Google’s income statement in Appendix A. What title does it use for cost of goods sold? Google’s Income Statement from Appendix A: CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME (In millions, except per share amounts
> What guidance does the accounting constraint of conservatism offer?
> What is the meaning of market as it is used in determining the lower of cost or market for inventory?
> Explain the following statement: “Inventory errors correct themselves.”
> What notations are entered into the Posting Reference column of a ledger account?
> Does the accounting concept of consistency preclude any changes from one accounting method to another?
> Locate “Note 11” that reports Apple’s segments from its September 28, 2013, annual report on its website (Apple.com). Compute the ratio “Operating income/Net sales” for each segment. Comment on the results.
> Can a company change its inventory method each accounting period? Explain.
> What does the full-disclosure principle prescribe if a company changes from one acceptable accounting method to another?
> If costs are declining, will the LIFO or FIFO method of inventory valuation yield the lower cost of goods sold? Why?
> What are the five fundamental principles of accounting information systems?
> Where is the amount of merchandise inventory disclosed in the financial statements?
> Describe how costs flow from inventory to cost of goods sold for the following methods: (a) FIFO and (b) LIFO.
> Management uses a voucher system to help control and monitor cash disbursements. Which of the four documents listed below are prepared as part of a voucher system of control? ______ a. Purchase order ______ b. Outstanding check ______ c. Invoice _____
> A good system of internal control for cash provides adequate procedures for protecting both cash receipts and cash disbursements. Identify each of the following statements as either true or false regarding this protection. ______ a. A basic guideline for
> Choose from the following list of terms/phrases to best complete the following statements. a. Cash b. Cash equivalents c. Outstanding check d. Liquidity e. Bank reconciliation f. Current assets 1. The ______ category includes currency and coins along

