Question: The SN2 reaction between a Grignard reagent
The SN2 reaction between a Grignard reagent and an epoxide works reasonably well when the epoxide is ethylene oxide. However, when the epoxide is substituted with groups that provide steric hindrance, a competing reaction can dominate, in which an allylic alcohol is produced. Propose a mechanism for this transformation and use the principles discussed in Section 7.11 to justify why the allylic alcohol would be the major product in this case below.
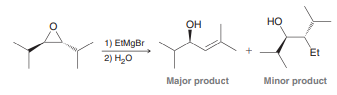
Transcribed Image Text:
OH но 1) EtMgBr Et 2) H,0 Major product Minor product
> Determine the hybridization state of each carbon atom in the following compounds. H H H нн ! ! H-C-CEC-C-C-H H H-C-C H-C-C-c. C-H H H H (a) (Ь) H H H (с) H H C=c=c=C (d) н H (е) н"
> When 2-iodobutane is treated with a variety of bases in DMSO at 50°C, the percentage of 1-butene formed among total butenes is found to be dependent on the choice of base, as seen in the chart below. a. Identify the trend observed by comparin
> Steroids and their derivatives are among the most widely used therapeutic agents. They are used in birth control, hormone replacement therapy, and in the treatment of inflammatory conditions and cancer. New steroid derivatives are discovered regularly by
> Biotin (compound 4) is an essential vitamin that plays a vital role in several important physiological processes. A total synthesis of biotin, developed by scientists at Hoffmann-La Roche, involved the preparation of compound 1. Conversion of 1 to 4 requ
> Halogenated derivatives of toluene will undergo hydrolysis via an SN1 process: The rate of hydrolysis is dependent on two main factors: 1. the stability of the leaving group, and 2. the stability of the intermediate carbocation. The following are rat
> The following reaction exhibits a second-order rate equation: a. What happens to the rate if the concentration of chlorocyclopentane is tripled and the concentration of sodium hydroxide remains the same? b. What happens to the rate if the concentration
> Compound 1 was prepared during a recent synthesis of 1-deoxynojirimycin, a compound with application to HIV chemotherapy. Upon formation, compound 1 rapidly undergoes ring contraction in the presence of chloride ion to form compound 2. Propose a plausibl
> Identify the electron configuration for each of the following atoms: a. Carbon b. Oxygen c. Boron d. Fluorine e. Sodium f. Aluminum
> Plastics and synthetic fibers are examples of the many materials made from repeating subunits of carbon-containing molecules called polymers. Although most synthetic polymers are prepared from fossil fuel sources, many researchers are exploring ways to m
> The regions of δ+ in a compound are the regions most likely to be attacked by an anion, such as hydroxide (HO−). In the compound shown, identify the two carbon atoms that are most likely to be attacked by a hydroxide ion.
> 99. For the following substitution reaction, which statement is FALSE? a. The process is bimolecular. b. Increasing the concentration of hydroxide will cause an increase in the rate of reaction. c. The use of a polar aprotic solvent will enhance the r
> The following sequence of reactions was performed during a synthesis of (+)-coronafacic acid, a key component in the plant toxin coronatine. Predict the product of this reaction sequence, and justify the regiochemical outcome of the second reaction.
> Compound 1 is observed to undergo debromination upon treatment with DMF to afford an alkene. The E-isomer (compound 2) is obtained exclusively (none of the Z-isomer is observed). A concerted mechanism (shown below) has been refuted by the observation tha
> Cyclopropyl chloride (1) cannot generally be converted into cyclopropanol (4) through a direct substitution reaction, because undesired, ring-opening reactions occur. The following represents an alternative method for preparing cyclopropanol. a. Compoun
> The optically pure octyl sulfonate shown below was treated with varying mixtures of water and dioxane, and the optical purity of the resulting product (2-octanol) was found to vary with the ratio of water to dioxane, as shown in the following table. As i
> Thienamycin is a potent antibacterial agent isolated from the fermentation broth of the soil microorganism, Streptomyces cattleya. The following SN2 process was utilized in a synthesis of thienamycin. Draw the product of this process (compound 3). Li
> Choline is a compound involved in neurotransmission. The biosynthesis of choline involves the transfer of a methyl group from SAM. Draw a mechanism for this transformation: CH3 H,C N- OH -он SAM H,C-N- CH3
> Assign a systematic name for each of the following compounds: Br, Br (b) (c) (d) Br CI (e) (f) (h)
> Assign a name for each of the following compounds. Be sure to assign the configuration of each chiral center and indicate the configuration(s) at the beginning of the name. Me (a) (b) (c)
> Assign a name for each of the following compounds: (a) (b)
> Predict the products for each of the following reactions: Excess HBr Excess HBr ? Excess HỊ ? ? Heat Нeat (a) (b) Heat yI? „O^E ? .O Excess HI Excess HBr Excess ? Heat Heat Heat (d) (e) (f)
> Show how you would use an alkoxymercuration-demercuration to prepare isopropyl propyl ether using propene as your only source of carbon and any other reagents of your choosing.
> How would you use an alkoxymercuration-demercuration to prepare dicyclopentyl ether using cyclopentene as your only source of carbon?
> Identify reagents that you could use to prepare each of the following ethers via an alkoxymercuration-demercuration: OEt (a) (b)
> Compound 2 was made as a potential anti-HIV agent, based on its structural similarity to other reported anti-HIV compounds. One of the early steps in the synthesis involved the creation of an ether group (highlighted) in compound 1. Identify reagents tha
> Show reagents that you could use to prepare each of the following ethers via a Williamson ether synthesis and explain your reasoning: -OMe (a) (b) (c) (d)
> Identify the missing reagent needed to achieve each of the following transformations: Br F Br KF NaF benzene benzene ? (a) (b) Br OH OH LIF KMNO, benzene benzene ? ? (c) (d)
> Identify the structure of a compound with the molecular formula C9H20 that exhibits four CH2 groups, all of which are chemically equivalent. How many total signals would you expect in the 1H NMR spectrum of this compound?
> Propose a plausible mechanism for each of the following transformations: OH 1) MeMgBr 2) H,0 (a) 1) Excess MeMgBr 2) H20 но он (Б)
> Diethyl ether was commonly used as an anesthetic before its negative effects on the human nervous system were recognized. As part of a study to develop a method for predicting toxicity based on structure, the observed toxicity of a variety of dialkyl eth
> Draw a structure for each of the following compounds: a. (R)-2-Ethoxy-1,1-dimethylcyclobutane b. Cyclopropyl isopropyl ether
> Provide an IUPAC name for each of the following compounds: .CI (а) (b) (с) он OE! (d) (е)
> Suggest an efficient synthesis for the following transformation: CI H H.
> A variety of phenyl-substituted acetylenes (1a–d) were treated with HCl to give a mixture of E and Z isomers, as shown below a. As we saw in Problem 9.72, vinyl carbocations can form if they are stabilized by resonance. Draw the vinyl
> The two lowest energy conformations of pentane are the anti-anti and the anti-gauche forms, in terms of arrangements around the two central C−C bonds. A recent study analyzed the conformations of 3-heptyne as an “elongated” analogue of pentane, where a c
> Brevetoxin B (compound 2) is produced by Ptychodiscus brevis Davis, a marine organism responsible for red tides. Brevetoxin B is a potent neurotoxin, as a result of its ability to bind to sodium channels and force them to remain open. Its biological acti
> The compound 5,9,12,16-tetramethyleicosane was synthesized as part of a study of the male sex pheromone of a Brazilian bug that feeds on the leaves and fruit of tomato plants. The synthesis of this alkane was reported using compounds Aâ
> Laureatin is a natural product isolated from the marine algae Laurencia nipponica that exhibits potent insecticidal activity against mosquitos. During an investigation toward the synthesis of laureatin, an interesting skeletal rearrangement was observed.
> The following procedure is part of a synthetic strategy for the enantioselective preparation of carbohydrates (Chapter 24): a. Under these strongly basic conditions (NaOH), the alcohol group is deprotonated to give an alkoxide ion, which can then funct
> Predict the products for each of the following: 1) Og 2) DMS 3) Excess LIAIH, 4) H0 ? 1) Os 2) DMS 3) Excess LIAIH, 4) H20 (a) (b) 1) EIMgBr 2) H,0 3) Na, Cr,0, H,SO4, H,0 4) EIMgBr ? (c) 1) LIAIH, 2) H,0 3) TsCI, pyridine ? (d) H 1) Hgo 2) Na, Cr,0,
> How many signals do you expect in the 1H NMR spectrum of each of the following compounds: OH Geraniol Isoprene (b) A precursor for natural rubber Isolated from roses (a) and used in perfumes
> Halogenation of alkynes with Cl2 or Br2 can generally be achieved with high yields, while halogenation of alkynes with 2 typically gives low yields. However, the following reaction is successfully completed with 2 in high yields (94%) to afford a potenti
> Salvinorin A, isolated from the Mexican plant Salvia divinorum, is known to bind with opioid receptors, thereby generating a powerful hallucinogenic effect. It has been suggested that salvinorin A may be useful in the treatment of drug addiction. Termina
> Treatment of one mole of dimethyl sulfate (CH3OSO3CH3) with two moles of sodium acetylide results in the formation of two moles of propyne as the major product: a. Draw the inorganic, ionic species that is generated as a by-product of this reaction and
> Reboxetine mesylate is used in the treatment of depression and is currently marketed as the racemate. The (S,S)-enantiomer of reboxetine is being evaluated for the treatment of neuropathic pain. The following synthetic scheme was part of the synthesis of
> During a total synthesis of 2-methyl-d-erythritol (a sugar of importance to isoprenoid biosynthesis), epoxide 2 was required. a. Identify the reagents you would use to achieve a stereoselective synthesis of epoxide 2 from allylic alcohol 1. b. Propose
> Guggul is an herbal extract from the resin of the mukul myrrh tree, and it shows potential for treating high cholesterol. In a recent synthesis of (+)-myrrhanol A (a compound present in guggul), compound 1 was treated with MCPBA, followed by
> Sphingolipids are a class of compounds that play an important role in signal transmission and cell recognition. Fumonisin B1 is a potent sphingolipid biosynthesis inhibitor. A recent synthesis of fumonisin B1 employed the following transformation, invol
> The following sequence of reactions was employed during synthetic studies on reidispongiolide A, a cytotoxic marine natural product.8 Draw the structures of compounds A, B, C, and D cat. OsO. B Ph 1) CH2=CHMgBr 1) NaH A 2) CHI C + D Ph Ph 2) Н,о NMO
> Identify the reagents you would use to accomplish each of the following transformations: он он (а) (b) Он но. HO. (c) (d) он он H (е) (f)
> Using bromobenzene and ethylene oxide as your only sources of carbon, show how you could prepare trans-2,3-diphenyloxirane (a racemic mixture of enantiomers). + Enantiomer
> A compound with the molecular formula C9H18 exhibits a 1H NMR spectrum with only one signal and a 13C NMR spectrum with two signals. Deduce the structure of this compound.
> Propose an efficient synthesis for the following transformation: он + Enantiomer ÖH
> Consider the following two compounds. When treated with NaOH, one of these compounds forms an epoxide quite rapidly, while the other forms an epoxide very slowly. Identify which compound reacts more rapidly and explain the difference in rate between the
> When methyloxirane is treated with HBr, the bromide ion attacks the less substituted position. However, when phenyloxirane is treated with HBr, the bromide ion attacks the more substituted position Explain the difference in regiochemistry in terms of a
> Epoxides can be formed by treating α-haloketones with sodium borohydride. Propose a mechanism for formation of the following epoxide: NABH,
> Predict the product of the following reaction: Me 1) LIAID. ? Me 2) H,0
> Propose a structure for a compound with the molecular formula C4H10O that exhibits the following 1H NMR spectrum: Proton NMR 3 3.5 3.0 Chemical shift (ppm) 4.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0
> Propose a structure for a compound with the molecular formula C4H8O that exhibits the following 13C NMR and FTIR spectra: Carbon NMR 07.7 25.4- 80 70 10 60 Chemical shift (ppm) 100 90 50 40 30 20 100 80 60 40 20 0- 4000 2500 3500 3000 2000 1500 1000
> Propose a structure for a compound with the molecular formula C8H18O that exhibits the following 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra: Proton NMR 3 2.0 Chemical shift (ppm) 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 1.5 1.0 0.5 Carbon NMR -70.5 31.6- 19.3- -13.7 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 Che
> Draw a mechanism for each of the following reactions: он PEr он Br SOCI2 (a) Py (b) 1) Excess LiAIHe 2) H,0 CH,OH (c) он
> Propose a structure for an ether with the molecular formula C7H8O that exhibits the following 13C NMR spectrum: Carbon NMR 129.5- 120.7 55.1- 159.7- 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 Chemical shift (ppm)
> Propose an efficient synthesis for each transformation. (a) OH (b) (c) CI (d) CI Xor (e) HO. OH OH (f) (h) + En (k) (0) OH (m) OH (n) LOH (о) HO. (p) 'CI он (9) CI H. он (r) OH HO, (s) + En (t) OH + En (u) OMe
> Consider the following compound: a. How many signals do you expect in the 1H NMR spectrum of this compound? b. Rank the protons in terms of increasing chemical shift. c. How many signals do you expect in the 13C NMR spectrum? d. Rank the carbon atoms
> Using compounds that possess no more than two carbon atoms, propose an efficient synthesis for the following compound:
> Dimethoxyethane (DME) is a polar aprotic solvent often used for SN2 reactions. Propose an efficient synthesis for DME using acetylene and methyl iodide as your only sources of carbon atoms. Dimethoxyethane
> Propose an efficient synthesis for 1,4-dioxane using acetylene as your only source of carbon atoms. 1,4-Dioxane
> When meso-2,3-epoxybutane is treated with aqueous sodium hydroxide, two products are obtained. Draw both products and describe their relationship.
> When the following chiral epoxide is treated with aqueous sodium hydroxide, only one product is obtained, and that product is achiral. Draw the product and explain why only one product is formed. NaOH H,0 ? Me 'Me
> Fill in the missing products below 1) Hg(OAc)2, EIOH Excess HỊ ? 2) NABH, Нeat ? RCO,H H-CEC: Na ? ? 1) NaSEt 2) H,0 ? HBr
> Fill in the missing reagents below. OH Me OH ? HO OEt ? |? ? Br OH HO, SMe Me OEt ? ? OMe DEt OH OH CN
> Predict the product and draw a mechanism for each of the following reactions: 1) LIAIH. 2) H,0 ? 1) NABH, 2) MEOH ? (a) (b)
> Using acetylene and ethylene oxide as your only sources of carbon atoms, propose a synthesis for each of the following compounds: HO он (а) (b)
> Predict the product for each of the following reaction sequences: 1) Hg(OAc), MeOH 2) NABH, ? (a) он 1) Hg(OAc)2. :? 2) NABH, (b)
> Propose a stepwise mechanism for the following transformation: Et Me Me 1) Excess EtMgBr Он 2) H,0 Et
> Draw the expected 1H NMR spectrum of the following compound:
> Compound B has the molecular formula C6H10O and does not possess any π bonds. When treated with concentrated HBr, cis-1, 4-dibromocyclohexane is produced. Identify the structure of compound B.
> What product do you expect when tetrahydrofuran is heated in the presence of excess HBr?
> Propose a plausible mechanism for each of the following transformations: OH 1) EtMgBr 2) I1,0 (a) 1) NaH OEt OH 2) EI (b) но 1) H-CEC: Na - 2) H,0 (c) OH MESH Mes (d) NaH (e) NAOH (ехcess) (f)
> Predict the products for each of the following: 1) RCO,H 2 MeMgBr 3) H,0 ? ia) 1) Hg(OAc), Meон 2) NABH, ? (b) ? 1) RCO,H ? OH 1) Na 2) NaSMe 3) Н,о 2) EICI (c) (d) 1) Na ? -HO- 2) (e) 3) H,0 ? CI 1) Mg, diethyl ether 2) A 3) H,0 (f)
> Problem 13.34 outlines a general method for the preparation of cis- or trans-disubstituted epoxides. Using that method, identify reagents that you could use to prepare a racemic mixture of each of the following epoxides from acetylene: Hur 'Et Me (a)
> When 5-bromo-2,2-dimethyl-1-pentanol is treated with sodium hydride, a compound with the molecular formula C7H14O is obtained. Identify the structure of this compound. Br NaH, C,H,o
> Using 2-propanol as your only source of carbon, show how you would prepare 2-methyl-2-pentanol.
> The following two isomeric ketones were among the 68 compounds isolated from the steam-distilled volatile oil of fresh and air-dried marijuana buds. Propose a separate synthesis for each of these two compounds using only disubstituted alkenes containing
> Propose a structure for a compound with the molecular formula C8H10O that exhibits the following 1H NMR spectrum: Proton NMR Chemical shift (ppm)
> Propose two possible structures for a compound with the molecular formula C5H12O that exhibits the following 13C NMR and IR spectra: Carbon 13 NMR 29.1- 9.5- 73.8 100 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 Chemical shift (ppm) 100 80 60 40 20 0- 4000 2000 3500 3
> Propose a structure for a compound with the molecular formula C3H8O that exhibits the following 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectra: Proton NMR 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.4 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 Chemical shift (ppm) Carbon 13 NIMR 64.2- 25.7 10.0 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 Ch
> For each of the following compounds, compare the two indicated protons and determine whether they are enantiotopic, homotopic, or diastereotopic: Me (a) Me (b) H TH (c) H. H- -H- (d) H- (е) H (f) нн F он Me H H нн (h) (1) H HO H но, H (k) "OH OH Cl.
> Propose a structure for a compound with the molecular formula C10H14O that exhibits the following 1 H NMR spectrum: Proton NMR 4 2 Chemical shift ippm)
> Estragole is an insect repellant that has been isolated from the leaves of the Clausena anisata tree. Propose a synthesis of estragole starting from 4-methylphenol. Estragole
> The compound duryne was one of several structurally related compounds isolated from a marine sponge. Propose an efficient synthesis of duryne starting with any compounds containing eleven or fewer carbon atoms. OH OH (CH (CH Duryne
> Briarellin E (compound 3) is produced by coral in the Caribbean and Mediterranean seas and belongs to a larger family of marine natural products that are currently being investigated as potential anticancer agents. During a recent synthesis of 3, compoun
> (S)-Gizzerosine is an amino acid that is believed to be responsible for a serious disease called “black vomit” in chickens. However, the same compound is a potential drug for the treatment of osteoporosis and acid buil
> Consider the following sequence of reactions and identify the structures of compounds A, B, and C: Mg Compound A (C,H,„Br) Compound B 2) H,0 Conc. H,SO, Heat Compound C
> Determine whether the pinacol rearrangement, shown in the previous problem, is a reduction, an oxidation, or neither.
> A carbocation is resonance stabilized when it is adjacent to an oxygen atom: Such a carbocation is even more stable than a tertiary carbocation. Using this information, propose a mechanism for the following transformation exhibited by a diol. This react
> Propose a mechanism for the following transformation: 1) Excess LIAIH4 CH,OH 2) H0
> Show reagents that can be used to achieve the following transformation:
> Consider the following acid-catalyzed hydration reaction: Which of the following ions are intermediates in the accepted mechanism for this process? a. I, II, and III b. I and II c. None of the above. The process is concerted. d. Only IV Dilute H
> Which of the following represents an efficient method for preparing the alcohol shown? (a) OH 1) ВНз THF 2) H-Ог. NaOH (b) OH H3O+ (с) OH 1) ВНз THF 2) НаОг, NaOH (d) OH

