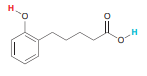
Question: In the following compound, two protons are
In the following compound, two protons are clearly identified. Determine which of the two is more acidic. After comparing the conjugate bases, you should get stuck on the following question: Is it more stabilizing for a negative charge to be spread out over one oxygen atom and three carbon atoms or to be spread out over two oxygen atoms? Draw all of the resonance structures of each conjugate base and then take a look at the pKa values listed in Table 3.1 to answer the question above.
Transcribed Image Text:
H.
> The following compound has been designed to allow for labeling of a specific site of a protein. Identify the four most acidic protons in this compound, and rank them in order of increasing acidity. CO,H H,N 'N' H
> In one step of a recent total synthesis of (−)-seimatopolide A, a potential antidiabetic drug, the following two structures reacted with each other in an acid-base reaction. a. Identify the acid and the base, draw the products of the r
> Most common amines (RNH2) exhibit pKa values between 35 and 45. R represents the rest of the compound (generally carbon and hydrogen atoms). However, when R is a cyano group, the pKa is found to be drastically lower: a. Explain why the presence of the c
> Below is the structure of rilpivirine, a promising new anti-HIV drug that combats resistant strains of HIV. Its ability to side-step resistance will be discussed in the upcoming chapter. a. Identify the two most acidic protons in rilpivirine. b. Identi
> Predict which of the following compounds is more acidic and explain your choice: -N- N- -NH2 -NH2
> There are only four constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C4H9NO2 that contain a nitro group (−NO2). Three of these isomers have similar pKa values, while the fourth isomer has a much higher pKa value. Draw all four isomers and identify which
> Consider the following compound with the molecular formula C4H8O2: a. Draw a constitutional isomer that you expect will be approximately one trillion (1012) times more acidic than the compound above. b. Draw a constitutional isomer that you expect will
> Consider the pKa values of the following constitutional isomers: Using the rules that we developed in this chapter (ARIO), we might have expected these two compounds to have the same pKa. Nevertheless, they are different. Salicylic acid is apparently mo
> As we will learn in Chapter 20, treating a lactone (a cyclic ester) with sodium hydroxide will initially produce an anion: This anion rapidly undergoes an intramolecular proton transfer (see Problem 3.2), in which the negatively charged oxygen atom abst
> a. Draw the products that are expected when tert-butyl bromide undergoes solvolysis in isopropanol, (CH3)2CHOH. b. The dielectric constant of isopropanol is 18. Would you expect the solvolysis of tert-butyl bromide in isopropanol to be faster or slower
> In Section 3.4, we learned four factors (ARIO) for comparing the relative acidity of compounds. When two of these factors are in competition, the order of priority is the order in which these factors were covered (“atomâ€
> Consider the structure of cyclopentadiene and then answer the following questions: a. How many sp3 -hybridized carbon atoms are present in the structure of cyclopentadiene? b. Identify the most acidic proton in cyclopentadiene. Justify your choice. c.
> Draw all constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C3H8O and rank them in terms of increasing acidity.
> Draw all constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C2H6S and rank them in terms of increasing acidity.
> In each case below, identify the acid and the base. Then draw the curved arrows showing a proton transfer reaction. Draw the products of that proton transfer and then predict the position of equilibrium: (a) O- LIOH (b) - Li H. (c) NaOH +
> For each compound below, identify the most acidic proton in the compound: -NH2 OH H-= (a) (b) SH (c) Он но (d) (е) NH2 () н CI OH HO (g) HO. (h) HS OH
> Rank the following anions in terms of increasing basicity: но
> For each reaction below, draw a mechanism (curved arrows) and then predict which side of the reaction is favored under equilibrium conditions: OH (a) H HO но H. (h) HS COH S S HS H2S (c) SH. 1. (d) +
> HA has a pKa of 15, while HB has a pKa of 5. Draw the equilibrium that would result upon mixing HB with NaA. Does the equilibrium favor formation of HA or formation of HB?
> For each pair of compounds below, identify the more acidic compound: OH SH OH он (a) (b) OH OH CI .CI NH2 CI CI (c) ČI (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) `NH2 HO,
> Later in this chapter (Section 7.12), we will see that a carbocation can be formed from an alcohol substrate in the presence of an acid, and an example of such a reaction is given below. This reaction was employed in the development of new synthetic meth
> In each case, identify the more stable anion. Explain why it is more stable: vs. (b) vs. (a) www vs. (c)
> Write an equation for the proton transfer reaction that occurs when each of the following bases reacts with water. In each case, draw curved arrows that show a mechanism for the proton transfer: (a) (b) (c) (d)
> Write an equation for the proton transfer reaction that occurs when each of the following acids reacts with water. In each case, draw curved arrows that show a mechanism for the proton transfer: H. H-0-S-0-H (a) HBr (Ы) (C)
> Would water be a suitable proton source to protonate the following compound? ONa
> Would ethanol (CH3CH2OH) be a suitable solvent in which to perform the following proton transfer? Explain your answer: NH, NH2 - H.
> What reaction will take place if H2O is added to a mixture of NaNH2/NH3?
> In each reaction, identify the Lewis acid and the Lewis base: H OH (a) F (b) 'F CI ÇI CI CI-Al-CI (c) I- (e
> Compound A has a pKa of 7 and compound B has a pKa of 10. Compound A is how many times more acidic than compound B? a. 3 b. 3000 c. 1000
> Draw the conjugate acid for each of the following bases: (a) (b) (c) NANH2 (d) H,0 (e) HO. (f) NH2 (g) (h) NaOH
> Draw the conjugate base for each of the following acids: (a) OH (b) (c) NH3 (d) H3o* (e) (f) (9) NH4
> Draw the carbocation intermediate that is expected when each of the following alkyl chlorides undergoes ionization. In each case, if the carbocation is resonance-stabilized, make sure to draw the resonance structures. Br (b) (c) (d) Br (a) Br Br (е)
> The Nazarov cyclization is a versatile method for making five-membered rings, a common feature in many natural products. This process has been used successfully in the preparation of many complex structures with a wide variety of biological activities, i
> In each case below, identify the Lewis acid and the Lewis base: H. (d) H. F. F F F (е) + CI AI Al CI CI (a) H (b) H. Br el Br-A- Br-Br: Br Al Br Br (c) Br
> Predict which of the following compounds is more acidic: After making your prediction, use the pKa values from Table 3.1 to determine whether your prediction was correct. OH H. Ethanol Water
> We will learn the following reactions in upcoming chapters. For each of these reactions, notice that the product is an anion (ignore the positively charged ion in each case). In order to obtain a neutral product, this anion must be treated with a proton
> In each of the following cases, identify whether the reagent shown is suitable to accomplish the task described. Explain why or why not: (a) To protonate using H20 (d) To protonate using (b) To protonate using (e) To protonate using H H (c) To deprot
> The development of chemical sensors that can detect harmful contaminants, like the toxic cyanide anion, is a prevalent line of research. Compound 1 was explored as a chemical sensor for cyanide in water. When 1 comes into the presence of cyanide, it reve
> Predict the position of equilibrium for each of the following reactions: 人 H H H H ! ! ! ! н-с-с-с-с: H H H H I I I I н-с-с-с-с-н y- H. (а) H H H H H H HH он + H0 (Ь)
> Amphotericin B is a powerful antifungal agent used for intravenous treatment of severe fungal infections. Identify the most acidic proton in this compound: он он OH но. ÕH ÕH ÕH OH O он он Amphotericin B NH2
> The following compound is one of the strongest known acids: a. Explain why it is such a strong acid. b. Suggest a modification to the structure that would render the compound even more acidic. H F3C-S-N N=Ş=N N-S-CF3 ČF3 F3C CF3
> For each pair of compounds below, predict which will be more acidic: (а) нсI HBr (b) H,0 (c) NH3 CH4 (d) H-=H H,C=CH,
> Compound 2 was prepared as part of an effort to determine the absolute stereochemistry of compound 3, which was isolated from the liverwort plant. The synthesis of compound 2 involved the formation of four C=C double bonds. The first double bond was form
> In each compound below, two protons are color-coded (red and blue). Determine which of the two protons is more acidic: OH NH2 но (a) (b) H H (с) H. 'N' SH H HO (d) H (е) TH (f) H но N- OH H H (9) н (h) (i)
> Methods used in organic synthesis — the process of making new organic molecules — are continuously being developed.7 The following proton transfer reaction was used to study an improved method for synthesiz
> Identify the most acidic proton in each of the following compounds:
> Water disinfection has greatly reduced the incidence of waterborne infectious diseases; however, disinfectants also lead to the unintended formation of drinking water disinfection by-products (DBPs) from the reaction of disinfectants with any organic mat
> For each pair of compounds below, identify which compound is more acidic and explain your choice: Br OH OH OH (а) (b) Br
> Identify the most acidic proton in each of the following compounds and explain your choice: CI, CI Он HO (a) F3C 0-H (Ь)
> Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) does not contain a traditional carboxylic acid group, but it is, nevertheless, still fairly acidic (pKa = 4.2). Identify the acidic proton and explain your choice using resonance structures, if necessary: он но HO он Ascorbi
> In each compound below, two protons are color-coded (red and blue). Determine which of the two protons is more acidic: H -N -N- H -H (а) H (Ь) H (с) H. (d) H (e) H (f) H
> Arsenic is an element that can cause a variety of cancers. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the World Health Organization (WHO) have thus set limits on acceptable levels of arsenic in drinking water. Monitoring these limits in developing cou
> Predict the major and minor products for each of the following E2 reactions: Br ? ? NaOEt NaOEt CI (a) (b) Br ? ? NaOE! NaOE! (c) (d) Br Br ? ? -BUOK -BUOK (e) (f)
> In each compound below, two protons are color-coded (red and blue). Determine which of the two protons is more acidic: H H-Ç-N, N-H HS, H (а) H (Ь) H (с) он (d) н
> Amino acids, such as glycine, are the key building blocks of proteins and will be discussed in greater detail in Chapter 25. At the pH of the stomach, glycine exists predominantly in a protonated form in which there are two acidic protons of interest. Th
> Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a biocompatible polymer material that is used to make medical implants. The conjugate base of hydroquinone is used in the synthesis of PEEK. Is hydroxide a strong enough base for deprotonating hydroquinone? to Polyet
> Determine the position of equilibrium for each acid-base reaction below: OH = (a) OH (b) 1 CD I-O H (c) H H. HA H (d) H-cEc-H NH2 H-CEc: NH, 1
> Nicotine is an addictive natural product found in tobacco. It has been proposed that the amount of nicotine taken in by the body may depend on the relative proportions of the free base 1, as compared to its mono- and di-protonated forms, 2 and 3. Using t
> Compound 1 was isolated from a species of Streptomyces bacteria and has been shown to have antibacterial and anticonvulsant properties. Compound 1 has also been made in the laboratory; however, it was prepared as its conjugate acid rather than in its neu
> Identify the stronger base in each of the following cases: (a) H-CEc TH (b) (с) H H H-C-C-H H-CEC e (d) OH (е) н (f) a OH
> L-dopa is used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Using Table 3.1, identify the four most acidic protons in the compound and then arrange them in order of increasing acidity (two of the protons will be very similar in acidity and
> Propranolol is an antihypertensive agent (used to treat high blood pressure). Using Table 3.1, identify the most acidic proton in the compound and indicate the approximate expected pKa. From Table 3.1: OH H Propranolol TABLE 3.1 pK VALUES OF COMMON
> For each pair of compounds below, identify the more acidic compound: H TH (а) (b) O-4 H TH H-CECH (с) н (d) н" C-H H H-C-C-H H-CEC-H H-0-S-o-H (е) н H (f)
> Predict which of the following two compounds will undergo an E2 reaction more rapidly: CI CI
> Dextromethorphan is a commonly used cough suppressant (antitussive) that is under investigation for other therapeutic uses, including treatment of bipolar disorder.1 To increase its shelf-life, the drug is prepared as its hydrobromide salt by treating it
> In an intramolecular proton transfer reaction, the acidic site and the basic site are tethered together in the same structure, and a proton is passed from the acidic region of the structure to the basic region of the structure. An example is shown. Draw
> All of the following acid-base reactions are reactions that we will study in greater detail in the chapters to follow. For each one, draw a mechanism and then clearly label the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base: он (а) (Ь) H (с) N. O-4 о
> Draw all constitutional isomers with the following molecular formula. a. C3H7Cl b. C4H10 c. C5H12 d. C4H10O e. C3H6Cl2
> Coumarin and its derivatives exhibit a broad array of industrial applications, including, but not limited to, cosmetics, food preservatives, and fluorescent laser dyes. Some derivatives of coumarin, such as warfarin, exhibit antithrombic activity and are
> Polymers are very large compounds, assembled from smaller units, called monomers. For example, polymer 2, called poly(vinyl acetate), is made from vinyl acetate (1). Polymer 2 can be converted to polymer 4, called poly(vinyl alcohol), or PVA, via a proce
> Many compounds with desirable medicinal properties are isolated from natural sources and are thus referred to as natural products. However, a compound’s medicinal properties are often known before the structure of the compound has been
> Progesterone is a female hormone that plays a critical role in the menstrual cycle by preparing the lining of the uterus for implantation of an egg. During W. S. Johnson’s biomimetic synthesis of progesterone (a synthesis that draws ins
> CL-20 and HMX are both powerful explosives. CL-20 produces a more powerful blast but is generally considered too shock-sensitive for practical use. HMX is significantly less sensitive and is used as a standard military explosive. When a 2:1 mixture of th
> Compound 2 is produced by the fungus Exserohilum rostratum and has been shown to fight inflammation and block/prevent tissue scarring. Compound 2 was made in the laboratory from compound 1, as shown. One of the early steps in this process involves the fo
> When menthyl chloride is treated with a strong base, only one elimination product is observed. Yet, when neomenthyl chloride is treated with a strong base, two elimination products are observed. Draw the products and explain. "ci 'CI Neomenthyl chlor
> Ramelteon is a hypnotic agent used in the treatment of insomnia: a. What is the molecular formula of this compound? b. How many sp3 -hybridized carbon atoms are present in this structure? c. How many sp2 -hybridized carbon atoms are presen
> Cycloserineis anantibiotic isolated from the microbe Streptomyces orchidaceous. It is used in conjunction with other drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis. a. What is the molecular formula of this compound? b. How many sp3 -hybridized carbon atoms ar
> Enamines, compounds with an amino group attached to a double bond, are electron-rich alkenes that have important synthetic applications. Draw the major resonance contributors for the enamine shown and determine which site(s) on the structure are most ele
> Draw and rank all significant resonance forms for the following compound. Briefly explain your rankings. HC
> Use resonance structures to help you identify all sites of high electron density (δ−) in the following compound: но OH
> Use resonance structures to help you identify all sites of low electron density (δ+) in the following compound:
> Draw all significant resonance structures for each of the following compounds: OH OH H. HO Estradiol Testosterone (Female sex hormone) (Male sex hormone)
> Melatonin is an animal hormone believed to have a role in regulating the sleep cycle: The structure of melatonin incorporates two nitrogen atoms. What is the hybridization state and geometry of each nitrogen atom? Explain your answer. OCH, H Melaton
> Consider the structure of ozone: Ozone is formed in the upper atmosphere, where it absorbs short wavelength UV radiation emitted by the sun, thereby protecting us from harmful radiation. Draw all significant resonance structures for ozone. (Hint: Begin
> A mixture of sulfuric acid and nitric acid will produce small quantities of the nitronium ion (NO2+): Does the nitronium ion have any significant resonance structures? Why or why not? 0=N=0:
> Retinol, one of the forms of vitamin A, is found in animal food sources and is essential for good vision. Below are two organohalides that were used to make synthetic forms of vitamin A. Upon treatment with a strong base, each of these compounds undergoe
> Draw a bond-line structure for each of the following compounds: a. CH2=CHCH2C(CH3)3 b. (CH3CH2)2CHCH2CH2OH c. CH≡COCH2CH(CH3)2 d. CH3CH2OCH2CH2OCH2CH3 e. (CH3CH2)3CBr f. (CH3)2C=CHCH3
> Consider each pair of compounds below and determine whether the pair represents the same compound, constitutional isomers, or different compounds that are not isomeric at all: (b) (c) (d)
> Determine the relationship between the two structures below. Are they resonance structures or are they constitutional isomers?
> Draw resonance structures for each of the following: (a) (b) (c) 'N NH2 (e) (f) (g) (h) HO. (j)
> Draw bond-line structures for all constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C4H9Cl.
> Identify the number of carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms in the compound below:
> What is the molecular formula for each compound in the previous problem?
> Write a condensed structural formula for each of the following compounds: OH (a) (b) (с)
> Draw all significant resonance structures for each of the following: OH (а) (b) (с)
> Each structure below exhibits one lone pair. In each case, identify the type of atomic orbital that the lone pair occupies. (a) (b) (c)
> Identify the major and minor products for the E2 reaction that occurs when each of the following substrates is treated with a strong base: Br Br Br (а) (Ь) (c) (d) (e) (f) ** (g) (h)
> Amino acids are biological compounds with the following structure, where the R group can vary. The structure and biological function of amino acids will be discussed in Chapter 25. Identify the total number of lone pairs present in an amino acid, assumin
> Identify the number of sp3 -hybridized carbon atoms in the following compound: (CH3)2C=CHC(CH3)3
> Identify which two compounds below are constitutional isomers: (CHa),CÖCH, (CH3)»CHÖCH, (CH,),CHÖCH,CH,

