Question: Suppose two assets have perfect negative
Suppose two assets have perfect negative correlation. Show that the standard deviation on a portfolio of the two assets is simply:
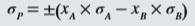
Transcribed Image Text:
op = ±(X, X o, ーX
> For Bill’s Bakery described in Problem 13, suppose instead that current earnings per share are $2.56. Calculate the share price for Bill’s Bakery.
> Bill’s Bakery expects earnings per share of $2.56 next year. Current book value is $4.70 per share. The appropriate discount rate for Bill’s Bakery is 11 percent. Calculate the share price for Bill’s Bakery if earnings grow at 3 percent forever.
> A certain stock has a beta of 1.3. If the risk-free rate of return is 3.2 percent and the market risk premium is 7.5 percent, what is the expected return of the stock? What is the expected return of a stock with a beta of 0.75?
> Joker stock has a sustainable growth rate of 8 percent, ROE of 14 percent, and dividends per share of $1.65. If the P/E ratio is 19, what is the value of a share of stock?
> Johnson Products earned $2.80 per share last year and paid a $1.25 per share dividend. If ROE was 14 percent, what is the sustainable growth rate?
> JJ Industries will pay a regular dividend of $2.40 per share for each of the next four years. At the end of the four years, the company will also pay out a $40 per share liquidating dividend, and the company will cease operations. If the discount rate is
> The value of beta for Country Point is: a. 1.09 b. 1.27 c. 1.00
> In Problem 5, assume the value-weighted index level was 408.16 at the beginning of the year. What is the index level at the end of the year? Data from Problem 5: Calculate the index return for the information in Problem 4 using a value-weighted index.
> In Problem 5, assume that you want to re index with the index value at the beginning of the year equal to 100. What is the index level at the end of the year? Data from Problem 5: Calculate the index return for the information in Problem 4 using a valu
> You are given the following information concerning two stocks that make up an index. What is the price-weighted return for the index? Price per Share Shares Beginning End of Outstanding of Year Year Kirk, Inc. 35,000 $37 $42 Picard Co. 26,000 84 9
> You find the following order book on a particular stock. The last trade on the stock was at $70.54. a. If you place a market buy order for 100 shares, at what price will it be filled? b. If you place a market sell order for 200 shares, at what price
> In Problem 1, assume that Baker undergoes a 4-for-1 stock split. What is the new divisor now? Data from Problem 1: Able, Baker, and Charlie are the only three stocks in an index. The stocks sell for $93, $312, and $78, respectively. If Baker undergoes
> Able, Baker, and Charlie are the only three stocks in an index. The stocks sell for $93, $312, and $78, respectively. If Baker undergoes a 2-for-1 stock split, what is the new divisor for the price-weighted index?
> A closed-end fund has total assets of $240 million and liabilities of $110,000. Currently, 11 million shares are outstanding. What is the NAV of the fund? If the shares currently sell for $19.25, what is the premium or discount on the fund?
> The largest expected loss for a portfolio is −20 percent with a probability of 95 percent. Relate this statement to the Value-at-Risk statistic.
> Explain the meaning of a Value-at-Risk statistic in terms of a smallest expected loss and the probability of such a loss.
> What is meant by a Sharpe-optimal portfolio?
> Given Ms. Nguyen’s estimate of Country Point’s terminal value in 2014, what is the growth assumption she must have used for free cash flow after 2014? a. 7 percent b. 9 percent c. 3 percent
> What are one advantage and one disadvantage of the Sharpe ratio?
> Explain the relationship between Jensen’s alpha and the security market line (SML) of the capital asset pricing model (CAPM).
> What is a common weakness of Jensen’s alpha and the Treynor ratio?
> Most sources report alphas and other metrics relative to a standard benchmark, such as the S&P 500. When might this method be an inappropriate comparison?
> A Treasury bond that settles on October 18, 2016, matures on March 30, 2035. The coupon rate is 5.30 percent and the bond has a 4.45 percent yield to maturity. What are the Macaulay duration and modified duration?
> A bond that settles on June 7, 2016, matures on July 1, 2036, and may be called at any time after July 1, 2026, at a price of 105. The coupon rate on the bond is 6 percent and the price is 115.00. What are the yield to maturity and yield to call on this
> A Treasury bond that settles on August 10, 2016, matures on April 15, 2021. The coupon rate is 4.5 percent and the quoted price is 106:17. What is the bond’s yield to maturity?
> Explain the difference between the Sharpe ratio and the Treynor ratio.
> You have a car loan with a nominal rate of 5.99 percent. With interest charged monthly, what is the effective annual rate (EAR) on this loan?
> A Treasury bill that settles on May 18, 2016, pays $100,000 on August 21, 2016. Assuming a discount rate of 0.44 percent, what are the price and bond equivalent yield?
> You have been given the following return information for two mutual funds (Papa and Mama), the market index, and the risk-free rate. Calculate the Sharpe ratio, Treynor ratio, Jensen’s alpha, information ratio, and R-squared for both
> You are given the following information concerning a stock and the market: Calculate the average return and standard deviation for the market and the stock. Next, calculate the correlation between the stock and the market, as well as the stockâ
> You are constructing a portfolio of two assets. Asset A has an expected return of 12 percent and a standard deviation of 24 percent. Asset B has an expected return of 18 percent and a standard deviation of 54 percent. The correlation between the two asse
> Suppose the CAC-40 Index (a widely followed index of French stock prices) is currently at 4,920, the expected dividend yield on the index is 2 percent per year, and the risk-free rate in France is 6 percent annually. If CAC-40 futures contracts that expi
> You shorted 15 March 2016 British pound futures contracts at the high price for the day. Looking back at Figure 14.1, if you closed your position at the settle price on this day, what was your profit? Figure 14.1: Futures Contracts|WSJ.com/commodit
> You went long 20 June 2016 crude oil futures contracts at a price of $42.18. Looking back at Figure 14.1, if you closed your position at the settle price on this day, what was your profit? Figure 14.1: Futures Contracts|WSJ.com/commoditles Metal &
> What are the Sharpe and Treynor ratios for the fund? Data for Problem 19: You have been given the following return information for a mutual fund, the market index, and the risk-free rate. You also know that the return correlation between th
> Your portfolio allocates equal amounts to three stocks. All three stocks have the same mean annual return of 14 percent. Annual return standard deviations for these three stocks are 30 percent, 40 percent, and 50 percent. The return correlations among al
> Mr. Spice asks Mr. Myers how a fixed-income manager would position his portfolio to capitalize on his expectations of increasing interest rates. Which of the following would be the most appropriate strategy? a. Lengthen the portfolio duration. b. Buy fix
> Using the same return means and standard deviations as in Problem 15 for Tyler Trucks and Michael Moped Manufacturing stocks, but assuming a return correlation of −.5, what is the smallest expected loss for your portfolio in the coming month with a proba
> Tyler Trucks stock has an annual return mean and standard deviation of 10 percent and 26 percent, respectively. Michael Moped Manufacturing stock has an annual return mean and standard deviation of 18 percent and 62 percent, respectively. Your portfolio
> A stock has an annual return of 11 percent and a standard deviation of 54 percent. What is the smallest expected loss over the next year with a probability of 1 percent? Does this number make sense?
> What is the formula for the Sharpe ratio for a portfolio of stocks and bonds with equal expected returns, i.e., E(RS) = E(RB), and a zero return correlation?
> What is the formula for the Sharpe ratio for an equally weighted portfolio of stocks and bonds?
> Look back at Problem 1. Assume that Able undergoes a 1-for-2 reverse stock split. What is the new divisor? Data from Problem 1: Able, Baker, and Charlie are the only three stocks in an index. The stocks sell for $93, $312, and $78, respectively. If Bak
> The beta for a certain stock is 1.15, the risk-free rate is 5 percent, and the expected return on the market is 13 percent. Complete the following table to decompose the stock’s return into the systematic return and the unsystematic ret
> Show that another way to calculate beta is to take the covariance between the security and the market and divide by the variance of the market’s return.
> Stock Y has a beta of 1.05 and an expected return of 13 percent. Stock Z has a beta of 0.70 and an expected return of 9 percent. If the risk-free rate is 5 percent and the market risk premium is 7 percent, are these stocks correctly priced?
> Derive our expression in the chapter for the portfolio weight in the minimum variance portfolio. (Danger! Calculus required!)
> The return calculation method most appropriate for evaluating the performance of a portfolio manager is a. Holding period b. Geometric c. Money-weighted (or dollar-weighted)
> Using the result in Problem 23, show that whenever two assets have perfect negative correlation, it is possible to find a portfolio with a zero standard deviation. What are the portfolio weights? (Hint: Let x be the percentage in the first asset and (1 &
> Suppose two assets have perfect positive correlation. Show that the standard deviation on a portfolio of the two assets is simply: Op = X, X 0, + Xg × OB
> You have a three-stock portfolio. Stock A has an expected return of 12 percent and a standard deviation of 41 percent, stock B has an expected return of 16 percent and a standard deviation of 58 percent, and stock C has an expected return of 13 percent a
> The stock of Bruin, Inc., has an expected return of 14 percent and a standard deviation of 42 percent. The stock of Wildcat Co. has an expected return of 12 percent and a standard deviation of 57 percent. The correlation between the two stocks is .25. Is
> Asset K has an expected return of 10 percent and a standard deviation of 28 percent. Asset L has an expected return of 7 percent and a standard deviation of 18 percent. The correlation between the assets is .40. What are the expected return and standard
> What are the expected return and standard deviation of the minimum variance portfolio in Problem 16? Data from Problem 16: Consider two stocks, stock D, with an expected return of 13 percent and a standard deviation of 31 percent, and stock I, an inter
> Consider two stocks, stock D, with an expected return of 13 percent and a standard deviation of 31 percent, and stock I, an international company, with an expected return of 16 percent and a standard deviation of 42 percent. The correlation between the t
> Fill in the missing information assuming a correlation of .30. Portfollo Welghts Stocks Bonds Expected Return Standard Devlatlon 1.00 12% 21% .80 .60 .40 .20 .00 7% 12%
> In Problem 12, what are the expected return and standard deviation on the minimum variance portfolio? Data from Problem 12: Use the following information to calculate the expected return and standard deviation of a portfolio that is 50 percent invested
> Ms. Yamisaka has determined that the average monthly return of another Mega client was 1.63 percent during the past year. What is the annualized rate of return? a. 5.13 percent b. 19.56 percent c. 21.41 percent
> Use the following information to calculate the expected return and standard deviation of a portfolio that is 50 percent invested in 3 Doors, Inc., and 50 percent invested in Down Co.: 3 Doors, Inc. Down Co. Expected return, E(R) 14% 10% Standard d
> Given the following information, calculate the expected return and standard deviation for a portfolio that has 35 percent invested in stock A, 45 percent in stock B, and the balance in stock C. Returns Probablity of State of Economy State of Econom
> You find that the one-, two-, three-, and four-year interest rates are 4.2 percent, 4.5 percent, 4.9 percent, and 5.1 percent. What is the yield to maturity of a four year bond with an annual coupon rate of 6.5 percent? Hint: Use the bootstrapping techni
> One method used to obtain an estimate of the term structure of interest rates is called bootstrapping. Suppose you have a one-year zero coupon bond with a rate of r1 and a two-year bond with an annual coupon payment of C. To bootstrap the two-year rate,
> You find a bond with 19 years until maturity that has a coupon rate of 8 percent and a yield to maturity of 7 percent. What is the Macaulay duration? The modified duration?
> Assume the bond in Problem 27 has a yield to maturity of 7 percent. What is the Macaulay duration now? What does this tell you about the relationship between duration and yield to maturity? Data from Problem 27: A bond with a coupon rate of 8 percent s
> A bond with a coupon rate of 8 percent sells at a yield to maturity of 9 percent. If the bond matures in 10 years, what is the Macaulay duration of the bond? What is the modified duration?
> What is the dollar value of an 01 for the bond in Problem 23? Data from Problem 23: What is the Macaulay duration of a 7 percent coupon bond with five years to maturity and a current price of $1,025.30? What is the modified duration?
> In Problem 23, suppose the yield on the bond suddenly increases by 2 percent. Use duration to estimate the new price of the bond. Compare your answer to the new bond price calculated from the usual bond pricing formula. What do your results tell you abou
> What is the Macaulay duration of a 7 percent coupon bond with five years to maturity and a current price of $1,025.30? What is the modified duration?
> Mr. Spice asks Mr. Myers to quantify the value changes from changes in interest rates. To illustrate, Mr. Myers computes the value change for the fixed-rate note. He assumes an increase in interest rates of 100 basis points. Which of the following is the
> You’ve just found a 10 percent coupon bond on the market that sells for par value. What is the maturity on this bond?
> LKD Co. has 8 percent coupon bonds with a YTM of 6.8 percent. The current yield on these bonds is 7.4 percent. How many years do these bonds have left until they mature?
> For the bond referred to in Problem 14, what would be the realized yield if it were held to maturity? Data from Problem 14: A zero coupon bond with a 6 percent YTM has 20 years to maturity. Two years later, the price of the bond remains the same. What’
> Soprano’s Spaghetti Factory issued 25-year bonds two years ago at a coupon rate of 7.5 percent. If these bonds currently sell for 108 percent of par value, what is the YTM?
> Great Wall Pizzeria issued 10-year bonds one year ago at a coupon rate of 6.20 percent. If the YTM on these bonds is 7.4 percent, what is the current bond price?
> Ghost Rider Corporation has bonds on the market with 10 years to maturity, a YTM of 7.5 percent, and a current price of $938. What must the coupon rate be on the company’s bonds?
> Based on the spot rates in Problem 21, and assuming a constant real interest rate of 2 percent, what are the expected inflation rates for the next four years?
> Based on the spot interest rates in the previous question, what are the following forward rates, where fk,1 refers to a forward rate beginning in k years and extending for 1 year? f21 = ; fa =
> Consider the following spot interest rates for maturities of one, two, three, and four years. What are the following forward rates, where f1, k refers to a forward rate for the period beginning in one year and extending for k years? , = 4.3% r2 =
> According to the pure expectations theory of interest rates, how much do you expect to pay for a five-year STRIPS on November 15, 2016? How much do you expect to pay for a two-year STRIPS on November 15, 2018? Data for Problem 17: U.S. Treasury STRIPS,
> What is Vega’s geometric average return over the five-year period? a. 7.85 percent b. 9.00 percent c. 15.14 percent
> What is the cost of capital that Ms. Nguyen used for her valuation of Country Point? a. 18 percent b. 17 percent c. 15 percent
> What is the yield of the November ’17 STRIPS expressed as an EAR? Data for Problem 15: U.S. Treasury STRIPS, close of business November 15, 2015: Maturity Price Maturity Price November '16 99.471 November '19 95.035 November '1
> The treasurer of a large corporation wants to invest $20 million in excess short-term cash in a particular money market investment. The prospectus quotes the instrument at a true yield of 3.15 percent; that is, the EAR for this investment is 3.15 percent
> A Treasury bill purchased in December 2016 has 55 days until maturity and a bank discount yield of 2.48 percent. What is the price of the bill as a percentage of face value? What is the bond equivalent yield?
> A Treasury bill with 64 days to maturity is quoted at 99.012. What are the bank discount yield, the bond equivalent yield, and the effective annual return?
> Given your answers in Problems 27–30, do you feel Beagle Beauties is overvalued or undervalued at its current price of around $82? At what price do you feel the stock should sell? Data for Problem 31: Beagle Beauties engages in the de
> Use the information from Problem 29 and calculate the stock price with the clean surplus dividend. Do you get the same stock price as in Problem 29? Why or why not? Data from Problem 29: Assume the sustainable growth rate and required return you calcul
> Assume the sustainable growth rate and required return you calculated in Problem 27 are valid. Use the clean surplus relationship to calculate the share price for Beagle Beauties with the residual income model. Data for Problem 29: Beagle Beauties enga
> Using the P/E, P/CF, and P/S ratios, estimate the 2016 share price for Beagle Beauties. Data for Problem 28: Beagle Beauties engages in the development, manufacture, and sale of a line of cosmetics designed to make your dog look glamorous.
> What are the sustainable growth rate and required return for Beagle Beauties? Using these values, estimate the current share price of Beagle Beauties stock according to the constant dividend growth model. Data for Problem 27: Beagle Beauties engages in
> The current price of Parador Industries stock is $67 per share. Current sales per share are $18.75, the sales growth rate is 8 percent, and Parador does not pay a dividend. The expected return on Parador stock is 13 percent. What one-year-ahead P/S ratio
> In regard to the table that Dr. Miles constructed, which of the following is true? a. The receiving foreign currency position is correct; the action is incorrect. b. The receiving foreign currency position is incorrect; the action is also incorrect. c. T
> The current price of Parador Industries stock is $67 per share. Current earnings per share are $3.40, the earnings growth rate is 6 percent, and Parador does not pay a dividend. The expected return on Parador stock is 13 percent. What one year-ahead P/E
> In Problem 21, suppose the dividends per share over the same period were $1.00, $1.08, $1.17, $1.25, $1.35, and $1.40, respectively. Compute the expected share price at the end of 2017 using the perpetual growth method. Assume the market risk premium is
> Sea Side, Inc., just paid a dividend of $1.68 per share on its stock. The growth rate in dividends is expected to be a constant 5.5 percent per year indefinitely. Investors require an 18 percent return on the stock for the first three years, then a 13 pe
> Leisure Lodge Corporation is expected to pay the following dividends over the next four years: $15.00, $10.00, $5.00, and $2.20. Afterwards, the company pledges to maintain a constant 4 percent growth rate in dividends forever. If the required return on
> Jonah’s Fishery has EBITDA of $65 million. Jonah’s has market value of equity and debt of $420 million and $38 million, respectively. Jonah’s has cash on the balance sheet of $12 million. What is Jonah’s EV ratio?
> Netscrape Communications does not currently pay a dividend. You expect the company to begin paying a $4 per share dividend in 15 years, and you expect dividends to grow perpetually at 5.5 percent per year thereafter. If the discount rate is 15 percent, h
> Could I Industries just paid a dividend of $1.10 per share. The dividends are expected to grow at a 20 percent rate for the next six years and then level off to a 4 percent growth rate indefinitely. If the required return is 12 percent, what is the value
> In Problem 16, will your answers change if the Douglas McDonnell stock splits? Why or why not? Data from Problem 16: Repeat Problem 14 if a value-weighted index is used. Assume the index is scaled by a factor of 10 million; that is, if the average firm

